简介
JanusGraph的优势
JanusGraph在设计上针对图操作进行了优化,以便进行大规模的图运算,它的计算和存储能力远超单机图数据库所能提供的。实时图遍历和图分析是JanusGraph最基本的能力。本章将会探讨JanusGraph的各种具体优势以及它潜在的,可支持的持久化方案。
基本优势
- 支持超大图。 JanusGraph图规模依赖于集群中机器的数量。
- 支持超大规模并发事务和可操作图运算。JanusGraph事务处理能力依赖于集群中的机器数量,同时JanusGraph可以支撑在巨型图上的复杂遍历查询毫秒级响应。
- 通过Hadoop架构,支持全图分析或者批量图处理。
- 支持对超大图的定点和边的基于地理范围查询,数字范围查询,支持全文检索。
- 支持常见属性图数据模型(property graph data model) 基于开源图计算框架 Apache TinkerPop.
- 支持图查询语言 Gremlin.
- 大量图级配置提供了效果微调能力
- 以顶点为中心的索引提供顶点级查询以缓解臭名昭著的超级节点问题 super node problem.
- 优化磁盘表示以提供高效存储和快速访问。
- 开源符合规范 Apache 2 license.
JanusGraph 联合 Apache Cassandra
Continuously available 没有单点故障问题,保障持续可用性。
因为不是主从结构,不存在图的读写瓶颈问题。
Elastic scalability 弹性可扩展允许随时添加或者删减机器。
缓存层确保经常被访问的数据存储在内存中。
随着集群中机器的增加,缓存层的大小也会增加。
整合 Apache Hadoop.
开源符合规范 Apache 2 license.
JanusGraph 联合 HBase
- 高度整合 Apache Hadoop 生态系统.
- 符合强一致性原则 strong consistency.
- 添加机器符合线性扩展原则。
- Strictly consistent 绝对一致性读取和写入。
- 有便捷的基础类库支持使用Hbase表的Hadoop MapReduce jobs
- 支持指标(是指的监控吗?)导出通过 JMX.
- 开源符合规范 Apache 2 license.
JanusGraph 与 the CAP 原理
不管你做的多完美,你的系统仍然会面临众多的错误情况。因此你必须在降低产量(减少响应请求)和减少收成(基于部分数据给出结果)之间做出选择。当然选择应该取决于业务需求。
— Coda Hale
在使用数据库的时候, 需要考虑CAP原理 CAP theorem (C=一致性(Consistency), A=可用性(Availability), P=可靠性(Partitionability)). JanusGraph支持三种数据库后端系统: Apache Cassandra, Apache HBase, and Oracle Berkeley DB Java Edition. 需要注意的是 BerkeleyDB JE 是一种非分布式数据库,所以一般是用于测试和探索。
HBase gives preference to consistency at the expense of yield, i.e. the probability of completing a request. Cassandra gives preference to availability at the expense of harvest, i.e. the completeness of the answer to the query (data available/complete data).
开动
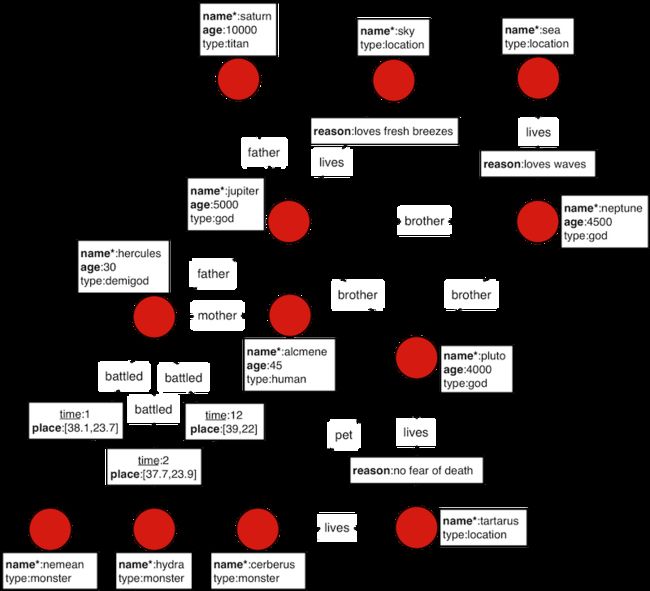
The examples in this section make extensive use of a toy graph distributed with JanusGraph called The Graph of the Gods. This graph is diagrammed below. The abstract data model is known as a Property Graph Model and this particular instance describes the relationships between the beings and places of the Roman pantheon. Moreover, special text and symbol modifiers in the diagram (e.g. bold, underline, etc.) denote different schematics/typings in the graph.
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 粗体字 | 图索引标记 |
| 带星号的粗体字 | 有唯一值的图索引标记 |
| 带下划线的字 | 以顶点为中心的索引标记 |
| 带空箭头的边 | 功能性的?/唯一的边 (不重复) |
| 带尾缘的边 | 单向边 (只能向一个方向移动) |
下载 JanusGraph 并运行 Gremlin 控制台
JanusGraph 可以在下面的地址下载到: Releases . 下载完成后解压缩,就可以打开 Gremlin 控制台了. Gremlin 控制台是一个 REPL (i.e. 互动shell) 它与JanusGraph一起发行,与标准Gremlin Console的区别仅在于,JanusGraph是一个预安装和预加载的软件包。 或者,用户可以从项目仓库中下载JanusGraph软件包,并在现有的Gremlin Console中安装并激活JanusGraph。 在下面的示例中,使用了“janusgraph.zip”,但是请确保解压缩下载的zip文件。
重要提示
JanusGraph 需要 Java 8 (Standard Edition). 推荐使用Oracle Java 8. JanusGraph的 shell 脚本需要配置环境变量,你需要把 $JAVA_HOME 环境变量指向 JRE or JDK 的安装路径.
$ unzip janusgraph-0.4.0-hadoop2.zip
Archive: janusgraph-0.4.0-hadoop2.zip
creating: janusgraph-0.4.0-hadoop2/
...
$ cd janusgraph-0.4.0-hadoop2
$ bin/gremlin.sh
\,,,/
(o o)
-----oOOo-(3)-oOOo-----
09:12:24 INFO org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.HadoopGraph - HADOOP_GREMLIN_LIBS is set to: /usr/local/janusgraph/lib
plugin activated: tinkerpop.hadoop
plugin activated: janusgraph.imports
gremlin>
The Gremlin 控制台使用 Apache Groovy 来解析命令. Groovy是Java的超集,具有各种速记符号,使交互式编程更容易。 同理 Gremlin-Groovy 是 Groovy 的超集,具有各种速记符号,使图遍历更加容易。下面的基本示例演示了如何处理 numbers, strings 和 maps. 本章的剩余部分讲讨论关于图处理的特定操作。
gremlin> 100-10
==>90
gremlin> "JanusGraph:" + " The Rise of Big Graph Data"
==>JanusGraph: The Rise of Big Graph Data
gremlin> [name:'aurelius', vocation:['philosopher', 'emperor']]
==>name=aurelius
==>vocation=[philosopher, emperor]
Tip
参考 Apache TinkerPop, SQL2Gremlin, and Gremlin Recipes 获取更多使用 Gremlin的信息.
加载众神图导入 JanusGraph
本示例将会加载一个众神之图的数据集进入 JanusGraph 并生成一个图实例。 JanusGraphFactory 提供了一系列静态的 open 方法, 每个‘open’方法都以配置作为参数并返回一个图实例。本教程使用一种配置调用其中一个‘open’方法,该示例使用BerkeleyDB 做存储,使用 Elasticsearch做索引,使用助手类来加载众神之图. 本节忽略了配置细节,关于更多关于存储,索引和配置的详细信息可以参见其他章节 Storage Backends, Index Backends, and Configuration Reference.
gremlin> graph = JanusGraphFactory.open('conf/janusgraph-berkeleyje-es.properties')
==>standardjanusgraph[berkeleyje:../db/berkeley]
gremlin> GraphOfTheGodsFactory.load(graph)
==>null
gremlin> g = graph.traversal()
==>graphtraversalsource[standardjanusgraph[berkeleyje:../db/berkeley], standard]
The JanusGraphFactory.open() 和 GraphOfTheGodsFactory.load() 方法在返回新图之前做了如下步骤:
- 在图上创建全局和顶点中心索引的集合。
- 将所有顶点及其属性添加到图中。
- 将所有边及其属性添加到图中。
请查看 GraphOfTheGodsFactory source code 了解更多细节.
对于使用 JanusGraph/Cassandra (or JanusGraph/HBase), 确保使用配置文件conf/janusgraph-cql-es.properties (or conf/janusgraph-hbase-es.properties) 和 GraphOfTheGodsFactory.load().
gremlin> graph = JanusGraphFactory.open('conf/janusgraph-cql-es.properties')
==>standardjanusgraph[cql:[127.0.0.1]]
gremlin> GraphOfTheGodsFactory.load(graph)
==>null
gremlin> g = graph.traversal()
==>graphtraversalsource[standardjanusgraph[cql:[127.0.0.1]], standard]
你也可能会用到 conf/janusgraph-cql.properties, conf/janusgraph-berkeleyje.properties, or conf/janusgraph-hbase.properties 配置文件来打开一个不带有索引后端配置(without an indexing backend configured)的图。 在这样的情况下,你需要使用 GraphOfTheGodsFactory.loadWithoutMixedIndex() 方法来加载众神的图,这样它就不会尝试利用索引后端。
==>standardjanusgraph[cql:[127.0.0.1]]
gremlin> GraphOfTheGodsFactory.loadWithoutMixedIndex(graph, true)
==>null
gremlin> g = graph.traversal()
==>graphtraversalsource[standardjanusgraph[cql:[127.0.0.1]], standard]
全局图指数
The typical pattern for accessing data in a graph database is to first locate the entry point into the graph using a graph index.在图数据库中访问数据的典型模式是首先使用图索引定位入口在图中的位置。该入口点是一个元素(或一组元素),即顶点或边。 Gremlin路径描述描述了从入口元素开始,如何通过显式图结构遍历图中的其他元素。
假定name字段为唯一索引,Saturn可以被访问。 然后可以查看Saturn节点的属性图(即Saturn的键/值对)。 如图所示,Saturn顶点的name字段为“Saturn”,年龄为10000,类型为“Titan”。通过遍历我们可以找到Saturn的孙子节点,该查询可以表示为:“谁是Saturn的孙子?”(“father”的反向是“儿子”)。我们查询的结果就是Hercules。
gremlin> saturn = g.V().has('name', 'saturn').next()
==>v[256]
gremlin> g.V(saturn).valueMap()
==>[name:[saturn], age:[10000]]
gremlin> g.V(saturn).in('father').in('father').values('name')
==>hercules
图索引中也包含place属性. place 是一种边属性。因此,JanusGraph也可以在图索引中为边建立索引。因此要在 The Graph of the Gods 查询所有发生在 Athens (经度:37.97 and 纬度:23.72)周围五十公里以内的事件也是可以的。 然后把涉及这些事件的顶点的信息都给出来。
gremlin> g.E().has('place', geoWithin(Geoshape.circle(37.97, 23.72, 50)))
==>e[a9x-co8-9hx-39s][16424-battled->4240]
==>e[9vp-co8-9hx-9ns][16424-battled->12520]
gremlin> g.E().has('place', geoWithin(Geoshape.circle(37.97, 23.72, 50))).as('source').inV().as('god2').select('source').outV().as('god1').select('god1', 'god2').by('name')
==>[god1:hercules, god2:hydra]
==>[god1:hercules, god2:nemean]
图索引是JanusGraph中索引结构的一种类型。 JanusGraph自动选择图形索引来按照要求给出所有满足一个或多个约束(例如,具有或间隔)的所有顶点(g.V)或所有边(g.E)的索引。 JanusGraph中索引的第二个优势是以顶点为中心的索引。 以顶点为中心的索引可加快图形内部的遍历速度。 顶点中心索引将在稍后介绍。
Graph Traversal Examples
Hercules, 是 Jupiter 出轨和 Alcmene生的儿子, 他生来就是大力神. Hercules 是一个半神 Demigod 因为他爸是神但他妈是人. Juno, Jupiter的老婆, 对于Jupiter的出轨极为愤怒. 为了报复,她使用神力让Hercules精神错乱,杀死了自己的孩子和妻子,并且还弄瞎了自己。为了赎罪,Oracle of Delphi 下令让 Hercules 服侍 Eurystheus. Eurystheus 命令Hercules做 12 项工作.
在前面的章节,我们已经知道 Saturn’s 孙子是 Hercules. 可以说这里运用了 loop. 在本质上, Hercules是距离Saturn两步远的定点,沿着 in('father') 这条线.
gremlin> hercules = g.V(saturn).repeat(__.in('father')).times(2).next()
==>v[1536]
Hercules是一个半神. 为了证明Hercules 是一般人一半神,那么他父母的血统都应该被验证。因此,从Hercules节点出发访问他的母亲和父亲节点都应该是可以的。最终,我们可以判定他们的类型“神”和“人”。
gremlin> g.V(hercules).out('father', 'mother')
==>v[1024]
==>v[1792]
gremlin> g.V(hercules).out('father', 'mother').values('name')
==>jupiter
==>alcmene
gremlin> g.V(hercules).out('father', 'mother').label()
==>god
==>human
gremlin> hercules.label()
==>demigod
迄今为止,例子都是围绕罗马万神殿中各个角色的遗传体系的。这个众神的属性图模型 Property Graph Model 足够充分的表达多种事物的类型和关系。同样的,The Graph of the Gods 这个图也能标记Hercules的各种英勇事迹——他最著名的十二项工作。在前面的章节,我们可以知道Hercules参与了Athens附近的两场战斗。同样的,通过遍历从Hercules顶点出发的battled边属性也能找到这些事件。
gremlin> g.V(hercules).out('battled')
==>v[2304]
==>v[2560]
==>v[2816]
gremlin> g.V(hercules).out('battled').valueMap()
==>[name:[nemean]]
==>[name:[hydra]]
==>[name:[cerberus]]
gremlin> g.V(hercules).outE('battled').has('time', gt(1)).inV().values('name')
==>cerberus
==>hydra
以顶点为中心的索引会为一个顶点存在战争的边的时间属性建立索引。通过限制/过滤时间来检索Hercules的战争边事件要比对所有边进行线性扫描和过滤的速度快(通常时间复杂度是O(log n),其中n是事件边的数目)。JanusGraph可以使用以顶点为中心的索引,这很有效而且很高端。 下面我们用一个 Gremlin 的 toString() 表达式来显示了拆解的步骤 。
gremlin> g.V(hercules).outE('battled').has('time', gt(1)).inV().values('name').toString()
==>[GraphStep([v[24744]],vertex), VertexStep(OUT,[battled],edge), HasStep([time.gt(1)]), EdgeVertexStep(IN), PropertiesStep([name],value)]
一个更复杂的图遍历的栗子
Pluto住在塔尔塔洛斯(地狱)的深处。由于Hercules抽了他的宠物Cerberus,他和Hercules的关系变得紧张。但是Hercules是他的侄子,所以,他应该如何让Hercules为傲慢无礼付出代价呢?
下面的Gremlin语句为遍历“众神之图”提供了更多示例。在每句重要的命令前面,都用 // 作为注释进行了解释。
COHABITERS OF TARTARUS 塔尔塔洛斯的居民
gremlin> pluto = g.V().has('name', 'pluto').next()
==>v[2048]
gremlin> // who are pluto's cohabitants? 谁和pluto住在一起?
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('lives').in('lives').values('name')
==>pluto
==>cerberus
gremlin> // pluto can't be his own cohabitant pluto不能是他自己的同居人
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('lives').in('lives').where(is(neq(pluto))).values('name')
==>cerberus
gremlin> g.V(pluto).as('x').out('lives').in('lives').where(neq('x')).values('name')
==>cerberus
PLUTO’S BROTHERS ploto的兄弟
gremlin> // where do pluto's brothers live? pluto的兄弟住在哪
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('brother').out('lives').values('name')
==>sky
==>sea
gremlin> // which brother lives in which place? 哪个兄弟住在哪个地方
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('brother').as('god').out('lives').as('place').select('god', 'place')
==>[god:v[1024], place:v[512]]
==>[god:v[1280], place:v[768]]
gremlin> // what is the name of the brother and the name of the place? 兄弟的名称和住所的名称
gremlin> g.V(pluto).out('brother').as('god').out('lives').as('place').select('god', 'place').by('name')
==>[god:jupiter, place:sky]
==>[god:neptune, place:sea]
最后,Pluto因为不关心死亡所以住在塔尔塔洛斯。他的兄弟们,也处于自己的热爱而选择了自己所居住的地方。
gremlin> g.V(pluto).outE('lives').values('reason')
==>no fear of death
gremlin> g.E().has('reason', textContains('loves'))
==>e[6xs-sg-m51-e8][1024-lives->512]
==>e[70g-zk-m51-lc][1280-lives->768]
gremlin> g.E().has('reason', textContains('loves')).as('source').values('reason').as('reason').select('source').outV().values('name').as('god').select('source').inV().values('name').as('thing').select('god', 'reason', 'thing')
==>[god:neptune, reason:loves waves, thing:sea]
==>[god:jupiter, reason:loves fresh breezes, thing:sky]
Architectural Overview 架构概述
JanusGraph是一个图形数据库引擎。 JanusGraph本身专注于紧凑的图形序列化,丰富的图形数据建模和有效的查询执行。 此外,JanusGraph利用Hadoop进行图分析和批量图处理。 JanusGraph为数据持久性,数据索引和客户端访问实现了强大的模块化接口。 JanusGraph的模块化的体系结构使其可以与多种存储,索引和客户端技术进行交互。 另外,扩展的JanusGraph支持新的也很方便。
在JanusGraph和磁盘之间放置一个或多个存储和索引适配器。 JanusGraph是以下适配器的标准配置,但JanusGraph的模块化体系结构支持第三方适配器。
- 数据存储:
- Apache Cassandra
- Apache HBase
- Oracle Berkeley DB Java Edition
- 索引, 加速和支撑复杂查询:
- Elasticsearch
- Apache Solr
- Apache Lucene
广义上讲,应用程序可以通过两种方式与JanusGraph交互:
将JanusGraph嵌入应用程序中执行 Gremlin 查询直接针对graph,使用相同的JVM。 查询执行,JanusGraph的缓存和事务处理都在与应用程序相同的JVM中进行,而从存储后端检索的数据可能是本地的或远程的。
-
通过将Gremlin查询提交到服务器,与本地或远程JanusGraph实例进行交互。JanusGraph支持 Apache TinkerPop 堆栈的Gremlin服务器组件。