Android使用ViewGroup实现流式标签布局(靠左,靠右,居中)
在此之前都所使用的的布局都是第三方的,看了一些资料,自己稍微修改了下,今天借此机会来实现一个简单的流式布局,左对齐,右对齐和 居中三种模式。作为一个little tinny note吧,哈哈哈!
大致的实现思路:
1.继承ViewGroup重写onMeasure()和onLayout()方法;
2.在onMeasure()方法中测量所有子View的宽和高,此处会使用一个List来存储每一行所能放置的最大子View数量,并且记录下每一行所需要的宽度;方便后续在onLayout()方 法中进行布局。
3.在onLayout()方法中,根据设定的模式(setDefaultDisplayMode()方法包含两种模式:
//靠左放置标签
public static final int START_FROM_LEFT = 1;
//居中放置标签
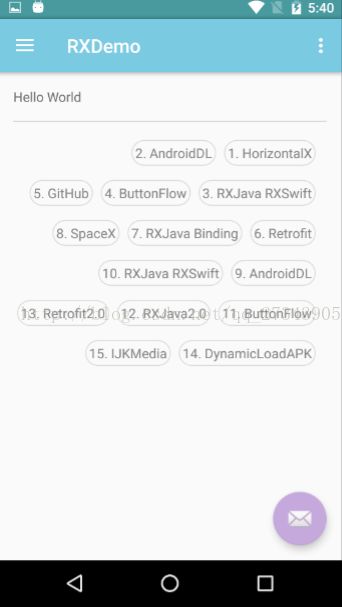
public static final int START_FROM_CENTER = 0;
//靠右放置标签
public static final int START_FROM_RIGHT = -1;
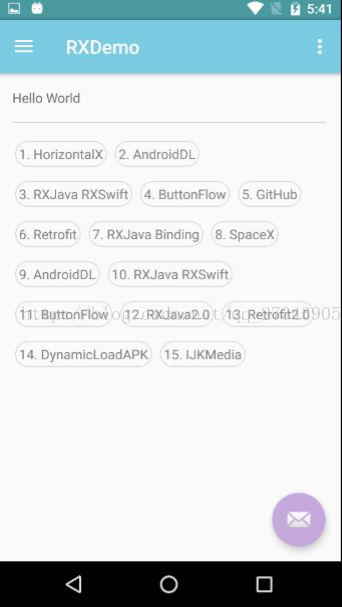
效果图:
1.
2.
3.
贴代码代码:
1.自定义标签布局SQLFlowLayout类(继承自ViewGroup)
public class SQLFlowLayout extends ViewGroup { //靠左放置标签 public static final int START_FROM_LEFT = 1; //居中放置标签 public static final int START_FROM_CENTER = 0; //靠右放置标签 public static final int START_FROM_RIGHT = -1; private int lineMode = START_FROM_LEFT; // 水平间距,单位为px private int horizontalSpacing = 25; // 竖直间距,单位为px private int verticalSpacing = 45; // 行集合 private List<Line> lines = new ArrayList<Line>(); // 当前的行 private Line line; // 当前行使用的空间 private int lineUsedSize = 0; public void setDefaultDisplayMode(int lineMode) { this.lineMode = lineMode; } public SQLFlowLayout(Context context) { super(context); } public SQLFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } public SQLFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); } /** * 计算出所有子控件的宽和高,从而确定当前父布局的宽和高 * * @param widthMeasureSpec * @param heightMeasureSpec */ @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); // 实际可以用的宽和高(去除 padding 内边距) int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight(); int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) - getPaddingBottom() - getPaddingTop(); int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); // Line初始化 restoreLine(); initLine(); for (int count = getChildCount(), i = 0; i < count; i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); // 测量所有的childView int childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width, widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? MeasureSpec.AT_MOST : widthMode); int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height, heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? MeasureSpec.AT_MOST : heightMode); //也可以 measureChild(child, childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); // 计算当前行已使用的宽度 int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); // 如果添加进去后宽度超过可用的宽度,需要换行,否则childView继续添加到当前的行上 if (lineUsedSize + measuredWidth > width) { // 先换行,先将上一行保存到 lines 集合中,再换行 saveAndNewLine(); } //存储当前行已使用的宽度 line.setUsedLineSize(lineUsedSize += measuredWidth + horizontalSpacing); //继续添加到当前行 line line.addChild(child); } // 如果有最后一行(未填满)把它记录到集合中 if (line != null && !lines.contains(line)) { saveAndNewLine(); } // 把所有行的高度加上 int totalHeight = 0; for (Line curLine: lines) { totalHeight += curLine.getHeight(); } // 加上行的竖直间距 totalHeight += verticalSpacing * (lines.size() - 1); // 加上上下padding totalHeight += getPaddingBottom(); totalHeight += getPaddingTop(); /** * 设置自身尺寸,设置布局的宽高,宽度直接采用父 View 传递过来的最大宽度,而不用考虑子view是否填满宽度 * 因为该布局的特性就是填满一行后,再换行。 * 高度根据设置的模式来决定采用所有子View的高度之和还是采用父view传递过来的高度 */ setMeasuredDimension(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec), resolveSize(totalHeight, heightMeasureSpec)); } /** * 指定所有childView的位置,调用Line对象中的layout方法。 * @param changed * @param l * @param t * @param r * @param b */ @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft(); int paddingTop = getPaddingTop(); int totalUsableWidth = getMeasuredWidth() - paddingLeft - paddingTop; for (Line curLine : lines) { curLine.layout(lineMode, paddingLeft, paddingTop, totalUsableWidth, horizontalSpacing); // 计算下一行 Y 轴起点坐标 paddingTop = paddingTop + curLine.getHeight() + verticalSpacing; } } /** * 与当前ViewGroup对应的LayoutParams */ @Override public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) { return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs); } private void initLine() { if (line == null) { // 创建新一行 line = new Line(); } } private void restoreLine() { lines.clear(); line = new Line(); lineUsedSize = 0; } /** * 换行,先将上一行保存到 lines 集合中,再换行 */ private void saveAndNewLine() { //过滤 当前行最后一个子控件末尾 horizontalSpacing if (lineUsedSize > 0) { line.setUsedLineSize(lineUsedSize - horizontalSpacing); } // 把之前的行记录下来加入到行集合中 if (line != null) { lines.add(line); } //重置已用宽度为0 lineUsedSize = 0; // 创建新的一行 line = new Line(); } //TODO................new class here.......... }
2.封装的存储每一行子View的类Line:
public class Line { // 子控件集合 private List<View> childList = new ArrayList<View>(); // 行高 private int height; // 当前行已经使用的宽度 private int lineUsedSize = 0; /** * 添加childView * * @param childView 子控件 */ public void addChild(View childView) { childList.add(childView); // 更新行高为当前最高的一个childView的高度 if (height < childView.getMeasuredHeight()) { height = childView.getMeasuredHeight(); } } /** * 设置childView的绘制区域 * * @param left 左上角x轴坐标 * @param top 左上角y轴坐标 */ public void layout(int lineMode, int left, int top, int totalUsableWidth, int horizontalSpacing) { // 当前childView的左上角x轴坐标 switch (lineMode) { case SQLFlowLayout.START_FROM_LEFT: for (View view : childList) { // 设置childView的绘制区域 view.layout(left, top, left + view.getMeasuredWidth(), top + view.getMeasuredHeight()); // 计算下一个childView的位置 left += view.getMeasuredWidth() + horizontalSpacing; } break; case SQLFlowLayout.START_FROM_CENTER: int square = (horizontalSpacing * (childList.size() - 1) + totalUsableWidth - lineUsedSize) / (childList.size() + 1); for (View view : childList) { // 设置childView的绘制区域 left += square; view.layout(left, top, left + view.getMeasuredWidth(), top + view.getMeasuredHeight()); // 计算下一个childView的位置 left += view.getMeasuredWidth(); } break; case SQLFlowLayout.START_FROM_RIGHT: left += totalUsableWidth - lineUsedSize; if (childList.size() > 0) { for (int index = childList.size() - 1; index >= 0; index --) { // 设置childView的绘制区域 childList.get(index).layout(left, top, left + childList.get(index).getMeasuredWidth(), top + childList.get(index).getMeasuredHeight()); // 计算下一个childView的位置 left += childList.get(index).getMeasuredWidth() + horizontalSpacing; } } break; } } public int getHeight() { return height; } public int getChildCount() { return childList.size(); } public void setUsedLineSize(int lineUsedSize) { this.lineUsedSize = lineUsedSize; } }
3.在MainActivity中测试效果:
private String[] mTags = new String[]{ "1. HorizontalX", "2. AndroidDL", "3. RXJava RXSwift", "4. ButtonFlow", "5. GitHub", "6. Retrofit", "7. RXJava Binding", "8. SpaceX", "9. AndroidDL", "10. RXJava RXSwift", "11. ButtonFlow", "12. RXJava2.0", "13. Retrofit2.0", "14. DynamicLoadAPK", "15. IJKMedia"}; private SQLFlowLayout mFlowLayout; private LayoutInflater mInflater; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(this); mFlowLayout = (SQLFlowLayout) findViewById(R.id.layout_flow);
//设置mFlowLayout布局显示模式
mFlowLayout
.setDefaultDisplayMode
(
SQLFlowLayout
.
START_FROM_RIGHT
)
;
//将子View添加到容器中...... for (String textName : mTags) { TextView tv = (TextView) mInflater.inflate(R.layout.view_tv, mFlowLayout, false); tv.setText(textName); mFlowLayout.addView(tv); }
TextView XML布局文件:
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:padding="4dp"
android:textSize="14sp"
android:text="Hello Wordld"
android:textColor="@color/colorGrayDark"
android:background="@drawable/shape_line_backround_gray"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
TextView>
TextView背景shape_line_backround_gray.xml文件:
”
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<corners android:radius="16dp" />
<stroke
android:width="1dp"
android:color="#d9d9d9" />
shape>
MainActivity布局文件:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/content_main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior" tools:context="com.example.admins.rxdemo.MainActivity" tools:showIn="@layout/app_bar_main"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_type" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Hello World" /> <View android:layout_below="@+id/tv_type" android:layout_marginTop="16dp" android:id="@+id/driver_h" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="1dp" android:background="@color/colorGrayLight">View> <com.example.admins.rxdemo.common.view.SQLFlowLayout android:layout_below="@+id/driver_h" android:padding="3dp" android:layout_marginTop="16dp" android:id="@+id/layout_flow" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> com.example.admins.rxdemo.common.view.SQLFlowLayout> RelativeLayout>