Spring源码分析(一)IOC容器的创建-XMLBeanFactory篇
在spring4.0中加载配置文件的类发生了变化,spring不在支持使用XmlBeanFactory 创建factory加载配置文件。而是采用了ClassPathXmlApplicationContext创建factory
具体查看下面代码
spring4.0之前可以采用下面这种方式
privatestatic XmlBeanFactory beanFactory;
privatefinal static Object lock=new Object();
publicstatic void init(){
XmlBeanFactory factory1 = newXmlBeanFactory(new InputStreamResource(
BeansFactory.class.getResourceAsStream("application.factory.xml")));
beanFactory=factory1;
}
spring4.0之后的采用这种新版的加载方式:
privatestatic BeanFactory beanFactory ;
privatefinal static Object lock=new Object();
publicstatic void init(){
beanFactory= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.factory.xml");
设计理念:Spring将所有的东西都当成是Resource。外界只传递Resource对象就可了
Spring通过beanFactory来加载配置、管理对象
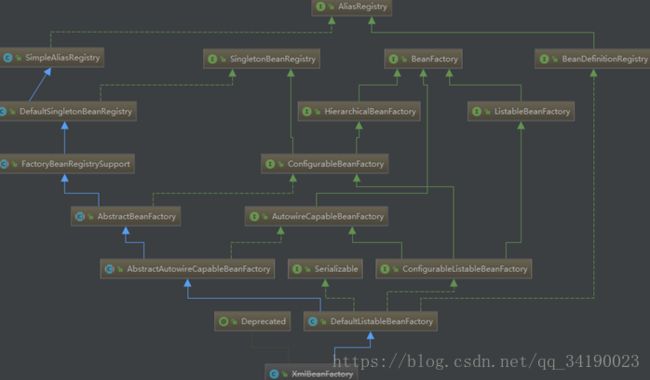
XmlBeanFactory[Spring3.1之前使用,后面被标记为Deprecated](用xml来定义IOC容器中的bean): 通过使用模板模式来得到对IOC 容器的抽象- AbstractBeanFactory,DefaultListableBeanFactory 这些抽象类为其提供模板服务。
通过resource 接口来抽象bean定义数据,对Xml定义文件的解析通过委托给XmlBeanDefinitionReader来完成。
使用方法:
XMLBeanFactory factoty= new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource(“beans.xml”));
factory.getBean(“person”);
读取xml文件,解析文件,将元素中的东西封装为对象。被spring管理
演示IOC容器的创建过程(不使用XMLBeanFactory的时候):
ClassPathResourceres = new ClassPathResource("beans.xml"); // 创建IOC配置文件的抽象资源
DefaultListableBeanFactoryfactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); // 创建一个BeanFactory
XmlBeanDefinitionReaderreader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory); //把读取配置信息的BeanDefinitionReader,这里是XmlBeanDefinitionReader配置给BeanFactory
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res); //从定义好的资源位置读入配置信息,具体的解析过程由XmlBeanDefinitionReader来完成
Spring加载资源并装配对象的过程:
1. 定义好spring的配置文件
2. 通过Resource对象将spring的配置文件进行抽象,抽象成一个Resource对象
3. 定义好bean工厂
4. 定义好XMLBeanDefinitionReader对象,并将工厂作为参数传递进去供后续回调使用
5. 通过XMLBeanDefinitionReader对象读取之前抽象出的Resource对象(包含了xml文件解析过程)
6. 本质上,xml文件的解析是由XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象交由BeanDefinitionParserDelegate委托来完成,实际上这里使用了委托模式。
7. IOC、容器创建完毕,可以通过容器获得所有对象的信息。
1定义好spring的配置文件beans.xml
2通过Resource对象将spring的配置文件进行抽象,抽象成一个Resource对象【new ClassPathResource(“beans.xml”】
3定义好bean工厂XmlBeanFactory
4XmlBeanFactory内部维护了一个XMLBeanDefinitionReader对象,在XmlBeanFactory构造的时候,将XmlBeanFactory对象注入保存为BeanDefinitionRegistry(XmlBeanDefinitionReader中)。
5通过XMLBeanDefinitionReader对象调用loadBeanDefinitions读取之前抽象出的Resource对象(包含了xml文件解析过程)
6xml文件的解析是由XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象交由BeanDefinitionParserDelegate委托来完成,使用了委托模式。
XmlBeanDefinitionReader内部维护了一个DocumentLoader还有ThreadLocal等。
loadBeanDefinitions方法将先从ThreadLocal中获取资源容器set。如果没有则创建一个四空间大小的。然后set进去。如果有了,就把当前的资源文件add到这个set容器中。将这个资源文件转为字节流(如果编码了会进行转码),然后调用doLoadBeanDefinitions方法进行加载配置。
doLoadBeanDefinitions方法将先调用doLoadDocument对传入的资源字节流进行转换为Document。最后调用registerBeanDefinitions进行注册,返回注册的bean的数量。
doLoadDocument方法是使用DefaultDocumentLoader的loadDocument方法,最终返回一个Document
registerBeanDefinitions则是使用DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver进行解析Document,调用其registerBeanDefinitions进行注入。
DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver 的registerBeanDefinitions方法中先是获取了xml的根元素,然后根据根元素调用doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法去逐个获取元素。
doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法委托了BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类进行解析。调用了parseBeanDefinitions方法来解析元素。【委托模式可以实现业务的解耦】
parseBeanDefinitions方法中,循环进行遍历,调用parseDefaultElement进行比对,如果是对应的配置,如bean,则调用相应的方法,比方说bean的就调用了processBeanDefinition方法
processBeanDefinition方法中最终调用了BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition。这里会最终调用到BeanDefinitionRegistry,也就是当前的XmlBeanFactory的registerBeanDefinition方法,这个方法主要就是put元素进到内部维护的map中(在XmlBeanFactory的父类中实现,也就是DefaultListableBeanFactory中实现。同理,这里实现了其他的注册,都是以map的方式进行维护的)
7委托得到的结果(bean等),通过调用XmlBeanFactory的父类DefaultListableBeanFactory的registerBeanDefinition方法,put到map中进行维护。IOC、容器创建完毕,可以通过容器获得所有对象的信息
@Deprecated
@SuppressWarnings({"serial", "all"})
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
//定义了一个默认使用的bean定义读取器 ,完成对xml的读取
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
//在初始化函数中使用读取器来对资源进行读取,得到bean定义信息
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); // 调用了xmlBeanDefinitionReafer进行加载配置资源
}
}
读取器读取资源和注册bean定义信息的整个过程,基本上是和上下文的处理是一样的,
从这里可看到上下文和XmlBeanFactory这两种IOC容器的区别:
BeanFactory往往不具备对资源定义的能力,
而上下文可自己完成资源定义,从这个角度上看上下文更好用一些。
DefaultListableBeanFactory:
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
// 这里将把bean注入到map中。【不管如何,最后都是要put进去的】
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Va ";
}
}
BeanDefinition oldBeanDefinition;
oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannd.");
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (oldBeanDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionReader implements EnvironmentCapable, BeanDefinitionReader {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry; // 这里保存了XmlBeanFactory
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
private Environment environment;
private BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = new DefaultBeanNameGenerator();
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this.registry = registry;
if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry;
}
else {
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
}
// Inherit Environment if possible
if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable) this.registry).getEnvironment();
}
else {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
。。。
private static final Constants constants = new Constants(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.class);
private int validationMode = VALIDATION_AUTO;
private boolean namespaceAware = false;
private Class documentReaderClass = DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class;
private ProblemReporter problemReporter = new FailFastProblemReporter();
private ReaderEventListener eventListener = new EmptyReaderEventListener();
private SourceExtractor sourceExtractor = new NullSourceExtractor();
private NamespaceHandlerResolver namespaceHandlerResolver;
private DocumentLoader documentLoader = new DefaultDocumentLoader();
private EntityResolver entityResolver;
private ErrorHandler errorHandler = new SimpleSaxErrorHandler(logger);
private final XmlValidationModeDetector validationModeDetector = new XmlValidationModeDetector();
private final ThreadLocal> resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded =new NamedThreadLocal>("XML bean definition resources currently being loaded");
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry); // 将XmlBeanFactory进行保存
}
…….
protected EntityResolver getEntityResolver() {
if (this.entityResolver == null) {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader != null) {
this.entityResolver = new ResourceEntityResolver(resourceLoader);
} else {
this.entityResolver = new DelegatingEntityResolver(getBeanClassLoader());
}
}
return this.entityResolver;
}
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); // 包装了一下
}
// 返回发现bean的个数
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Set currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); //尝试获取
if (currentResources == null) { // 如果没有,是刚初始化,就进行初始化
currentResources = new HashSet(4); // 默认空间大小为4
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { // 添加当前的资源文件到Set容器中
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try { // 获得配置文件的输入流(将配置资源文件转换为流)
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); // 包装了这个流,为Source
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { // 是否编码。编码了就进行解码
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); // 这里加载这个配置
} finally {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {。。。。
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource); //
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { // 如果为空,则从ThreadLocal中移除
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, "resource loaded through SAX InputSource");
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, String resourceDescription) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, new DescriptiveResource(resourceDescription));
}
//实际完成对xml进行载入的方法
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try { // Document代表xml文档对象
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); // 总之这里会返回一个Document
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); // 将返回的Document注册
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex; ….
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),"Unexpected om ");
}
}
// 加载xml文件,返回Document。使用DefaultDocumentLoader的loadDocument方法,返回一个Document
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
}
//使用DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver 进行解析Document
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
// 用代理对象
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); // 获取父类的BeanDefinitionRegistry(这里也就是IOC容器XmlBeanFactory),然后调用getBeanDefinitionCount方法。获得注册之前的数量
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));// 这里进行了解析和注入,DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader中实现
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; // 这里返回了数量
}
protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader() {
return BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class.cast(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass));
}
public XmlReaderContext createReaderContext(Resource resource) {
return new XmlReaderContext(resource, this.problemReporter, this.eventListener, this.sourceExtractor, this, getNamespaceHandlerResolver());
}
public NamespaceHandlerResolver getNamespaceHandlerResolver() { // 单例模式获取
if (this.namespaceHandlerResolver == null) {
this.namespaceHandlerResolver = createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver();
}
return this.namespaceHandlerResolver;
}
protected NamespaceHandlerResolver createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver() {
return new DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(getResourceLoader().getClassLoader());
}
}
DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver:
public class DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader implements BeanDefinitionDocumentReader {
public static final String BEAN_ELEMENT = BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.BEAN_ELEMENT;
public static final String NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT = "beans";
public static final String ALIAS_ELEMENT = "alias";
public static final String NAME_ATTRIBUTE = "name";
public static final String ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE = "alias";
public static final String IMPORT_ELEMENT = "import";
public static final String RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE = "resource";
public static final String PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE = "profile";
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private XmlReaderContext readerContext;
private BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate;
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();// 获得xml文档的根元素
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
protected final XmlReaderContext getReaderContext() {
return this.readerContext;
}
protected Object extractSource(Element ele) {
return getReaderContext().extractSource(ele);
}
// 获取元素
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
// 创建了代理类(本质,xml文件解析是由代理进行)
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
}
// 模板装饰模式
preProcessXml(root); // 本类中为空实现,供子类复写实现
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); // 解析元素
postProcessXml(root); // 本类中为空实现
this.delegate = parent;
}
protected BeanDefinitionParserDelegate createDelegate(XmlReaderContext readerContext, Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parentDelegate) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(readerContext);
delegate.initDefaults(root, parentDelegate);
return delegate;
}
// 这里解析了元素
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { // 根据元素的数量一个一个解析出元素
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); // 这里对元素进行解析,同名就解析出来
} else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
} else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {//import
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
} else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {//alias
processAliasRegistration(ele);
} else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {//bean
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
} else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) { //nested
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
protected void importBeanDefinitionResource(Element ele) {
String location = ele.getAttribute(RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(location)) {
getReaderContext().error("Resource location must not be empty", ele);
return;
}
location = getReaderContext().getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location);
Set actualResources = new LinkedHashSet(4);
boolean absoluteLocation = false;
try {
absoluteLocation = ResourcePatternUtils.isUrl(location) || ResourceUtils.toURI(location).isAbsolute();
} catch (URISyntaxException ex) {
}
if (absoluteLocation) {
try {
int importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(location, actualResources);
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to import bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]", ele, ex);
}
}
else {
try {
int importCount;
Resource relativeResource = getReaderContext().getResource().createRelative(location);
if (relativeResource.exists()) {
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(relativeResource);
actualResources.add(relativeResource);
} else {
String baseLocation = getReaderContext().getResource().getURL().toString();
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(
StringUtils.applyRelativePath(baseLocation, location), actualResources);
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to resolve current resource location", ele, ex);
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to import bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]",ele, ex);
}
}
Resource[] actResArray = actualResources.toArray(new Resource[actualResources.size()]);
getReaderContext().fireImportProcessed(location, actResArray, extractSource(ele));
}
protected void processAliasRegistration(Element ele) {
String name = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
String alias = ele.getAttribute(ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean valid = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
getReaderContext().error("Name must not be empty", ele);
valid = false;
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(alias)) {
getReaderContext().error("Alias must not be empty", ele);
valid = false;
}
if (valid) {
try {
getReaderContext().getRegistry().registerAlias(name, alias);
} catch (Exception ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register alias '" + alias +"' for bean with name '" + name + "'", ele, ex);
}
getReaderContext().fireAliasRegistered(name, alias, extractSource(ele));
}
}
// 这里是解析bean的
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry()); // 这里会最终调用到BeanDefinitionRegistry,也就是当前的XmlBeanFactory的registerBeanDefinition方法,这个方法主要就是put元素进到内部维护的map中(在XmlBeanFactory的父类中实现,也就是DefaultListableBeanFactory中实现。同理,这里实现了其他的注册,都是以map的方式进行维护的)
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
protected void preProcessXml(Element root) { }
protected void postProcessXml(Element root) {}
}
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate:Spring真正的解析代理类:
public class BeanDefinitionParserDelegate {
public static final String BEANS_NAMESPACE_URI = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans";
public static final String MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS = ",; ";
public static final String TRUE_VALUE = "true";
public static final String FALSE_VALUE = "false";
public static final String DEFAULT_VALUE = "default";
public static final String DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT = "description";
public static final String AUTOWIRE_NO_VALUE = "no";
public static final String AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME_VALUE = "byName";
public static final String AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE_VALUE = "byType";
public static final String AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR_VALUE = "constructor";
public static final String AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT_VALUE = "autodetect";
public static final String DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ALL_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE = "all";
public static final String DEPENDENCY_CHECK_SIMPLE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE = "simple";
public static final String DEPENDENCY_CHECK_OBJECTS_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE = "objects";
public static final String NAME_ATTRIBUTE = "name";
public static final String BEAN_ELEMENT = "bean";
public static final String META_ELEMENT = "meta";
public static final String ID_ATTRIBUTE = "id";
public static final String PARENT_ATTRIBUTE = "parent";
public static final String CLASS_ATTRIBUTE = "class";
public static final String ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE = "abstract";
public static final String SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE = "scope";
private static final String SINGLETON_ATTRIBUTE = "singleton";
public static final String LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE = "lazy-init";
public static final String AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE = "autowire";
public static final String AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATE_ATTRIBUTE = "autowire-candidate";
public static final String PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE = "primary";
public static final String DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE = "dependency-check";
public static final String DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE = "depends-on";
public static final String INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "init-method";
public static final String DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "destroy-method";
public static final String FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "factory-method";
public static final String FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE = "factory-bean";
public static final String CONSTRUCTOR_ARG_ELEMENT = "constructor-arg";
public static final String INDEX_ATTRIBUTE = "index";
public static final String TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = "type";
public static final String VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = "value-type";
public static final String KEY_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = "key-type";
public static final String PROPERTY_ELEMENT = "property";
public static final String REF_ATTRIBUTE = "ref";
public static final String VALUE_ATTRIBUTE = "value";
public static final String LOOKUP_METHOD_ELEMENT = "lookup-method";
public static final String REPLACED_METHOD_ELEMENT = "replaced-method";
public static final String REPLACER_ATTRIBUTE = "replacer";
public static final String ARG_TYPE_ELEMENT = "arg-type";
public static final String ARG_TYPE_MATCH_ATTRIBUTE = "match";
public static final String REF_ELEMENT = "ref";
public static final String IDREF_ELEMENT = "idref";
public static final String BEAN_REF_ATTRIBUTE = "bean";
public static final String LOCAL_REF_ATTRIBUTE = "local";
public static final String PARENT_REF_ATTRIBUTE = "parent";
public static final String VALUE_ELEMENT = "value";
public static final String NULL_ELEMENT = "null";
public static final String ARRAY_ELEMENT = "array";
public static final String LIST_ELEMENT = "list";
public static final String SET_ELEMENT = "set";
public static final String MAP_ELEMENT = "map";
public static final String ENTRY_ELEMENT = "entry";
public static final String KEY_ELEMENT = "key";
public static final String KEY_ATTRIBUTE = "key";
public static final String KEY_REF_ATTRIBUTE = "key-ref";
public static final String VALUE_REF_ATTRIBUTE = "value-ref";
public static final String PROPS_ELEMENT = "props";
public static final String PROP_ELEMENT = "prop";
public static final String MERGE_ATTRIBUTE = "merge";
public static final String QUALIFIER_ELEMENT = "qualifier";
public static final String QUALIFIER_ATTRIBUTE_ELEMENT = "attribute";
public static final String DEFAULT_LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE = "default-lazy-init";
public static final String DEFAULT_MERGE_ATTRIBUTE = "default-merge";
public static final String DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE = "default-autowire";
public static final String DEFAULT_DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE = "default-dependency-check";
public static final String DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATES_ATTRIBUTE = "default-autowire-candidates";
public static final String DEFAULT_INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "default-init-method";
public static final String DEFAULT_DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "default-destroy-method";
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private final XmlReaderContext readerContext;
private final DocumentDefaultsDefinition defaults = new DocumentDefaultsDefinition();
private final ParseState parseState = new ParseState();
private final Set usedNames = new HashSet();
、。。。。。。以下是详细解析的方法
public void initDefaults(Element root) {
initDefaults(root, null);
}
public void initDefaults(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent) {
populateDefaults(this.defaults, (parent != null ? parent.defaults : null), root);
this.readerContext.fireDefaultsRegistered(this.defaults);
}
protected void populateDefaults(DocumentDefaultsDefinition defaults, DocumentDefaultsDefinition parentDefaults, Element root) {
String lazyInit = root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE);
if (DEFAULT_VALUE.equals(lazyInit)) {
lazyInit = (parentDefaults != null ? parentDefaults.getLazyInit() : FALSE_VALUE);
}
defaults.setLazyInit(lazyInit);
String merge = root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_MERGE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (DEFAULT_VALUE.equals(merge)) {
merge = (parentDefaults != null ? parentDefaults.getMerge() : FALSE_VALUE);
}
defaults.setMerge(merge);
String autowire = root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (DEFAULT_VALUE.equals(autowire)) {
autowire = (parentDefaults != null ? parentDefaults.getAutowire() : AUTOWIRE_NO_VALUE);
}
defaults.setAutowire(autowire); defaults.setDependencyCheck(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE));
if (root.hasAttribute(DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATES_ATTRIBUTE)) {
defaults.setAutowireCandidates(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATES_ATTRIBUTE));
}
else if (parentDefaults != null) {
defaults.setAutowireCandidates(parentDefaults.getAutowireCandidates());
}
if (root.hasAttribute(DEFAULT_INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
defaults.setInitMethod(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE));
}
else if (parentDefaults != null) {
defaults.setInitMethod(parentDefaults.getInitMethod());
}
if (root.hasAttribute(DEFAULT_DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
defaults.setDestroyMethod(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE));
}
else if (parentDefaults != null) {
defaults.setDestroyMethod(parentDefaults.getDestroyMethod());
}
defaults.setSource(this.readerContext.extractSource(root));
}
。。。。。
XMLBeanFactory的getBean是父类的方法。调用的是父类的:
大致过程:
1. Spring的bean实际上是缓存在CurrentHashMap对象中
2. 在创建bean之前,首先需要将该bean的创建标识设定好,表示该bean已经或是即将被创建,为的是增加缓存的效率
3. 根据bean的scope属性来确定是singleton还是prototype等范围,然后创建相应的bean对象
4. 通过java反射来创建bean的实例,在创建之前首先检查访问修饰符,如果不是public,则调用setAccessible(true)来突破java的语法限制,使得可以通知如私有的构造方法来创建对象实例
5. 接下来,寻找bean的属性值,完成属性的注入
6. 将所创建出的singleton对象添加到缓存当中,供下次调用使用