Android Camera 四 Camera HAL 分析
Android Camera 一 源码路径
Android Camera 二 JNI JAVA和C/CPP图像数据传输流程分析
Android Camera 三 CameraService 和 Client 链接到 HAL
Android Camera 四 Camera HAL 分析
Android Camera 五 Camera HAL v1
Linux v4l2 一 应用层
Linux v4l2 二 驱动和 usb 摄像头
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraModule.cpp
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/device3/Camera3Device.cpp
frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraModule.cpp
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/camera_common.h
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/QCamera2Hal.cpp
hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/QCamera2Factory.cpp
hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/HAL/QCameraMuxer.cpp
hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/HAL/QCamera2HWI.cpp
hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera_interface.c
hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera.h
hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera.c
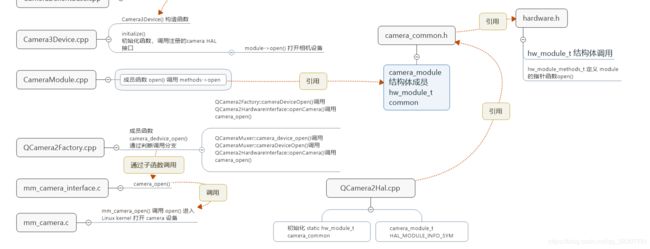
在上一节讲到Camera3Device::initialize( CameraModule *module) 进入 HAL 层。
接下来从分析 CameraModule 的open() 成员函数开始分析。
关于 Android 中的 HAL 模块的注册机制,不做展开。
// frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/device3/Camera3Device.cpp
// 该函数中 module->open() ,调用HAL层注册的相机模块 open 函数
status_t Camera3Device::initialize(CameraModule *module)
{
......
/** Open HAL device */
status_t res;
String8 deviceName = String8::format("%d", mId);
camera3_device_t *device;
ATRACE_BEGIN("camera3->open");
res = module->open(deviceName.string(),
reinterpret_cast(&device)); // 打开相机设备
ATRACE_END();
......
} 各厂商遵从 Android HAL 规则,编写驱动代码,适配 Android系统。
CameraModule::open() 成员函数根据 HAL 规则,调用各厂商适配的相机驱动打开对应的相机设备。
// frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraModule.cpp
// camera_module_t *mModule
int CameraModule::open(const char* id, struct hw_device_t** device) {
int res;
ATRACE_BEGIN("camera_module->open");
res = filterOpenErrorCode(mModule->common.methods->open(&mModule->common, id, device));
ATRACE_END();
return res;
}
来看看 camera_module_t 结构体,该结构体定义的指针函数成员,类似 CPP 的抽象类封装。
这种方式把各厂商的相机驱动和 HAL 层衔接起来,让 Android 适配更多的相机设备。
// hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/camera_common.h
typedef struct camera_module {
/**
* 相机模块的常用方法。该结构体必须是 camera_module 模块的第一个成员,
* 因为该结构的用户将在已知 hw_module_t 模块引用 camera_module 模块的上下文中,
*
* The return values for common.methods->open for camera_module are:
*
* 0: On a successful open of the camera device.
*
* -ENODEV: The camera device cannot be opened due to an internal
* error.
*
* -EINVAL: The input arguments are invalid, i.e. the id is invalid,
* and/or the module is invalid.
*
* -EBUSY: The camera device was already opened for this camera id
* (by using this method or open_legacy),
* regardless of the device HAL version it was opened as.
*
* -EUSERS: The maximal number of camera devices that can be
* opened concurrently were opened already, either by
* this method or the open_legacy method.
*
* All other return values from common.methods->open will be treated as
* -ENODEV.
*/
hw_module_t common;
/**
* get_number_of_cameras:
*
* 返回可通过相机模块访问的相机设备数量。摄像机设备编号为0到 N-1,其中 N 是此调用返回的值。
* The name of the camera device for open() is
* simply the number converted to a string. That is, "0" for camera ID 0,
* "1" for camera ID 1.
*/
int (*get_number_of_cameras)(void);
int (*get_camera_info)(int camera_id, struct camera_info *info);
int (*set_callbacks)(const camera_module_callbacks_t *callbacks);
void (*get_vendor_tag_ops)(vendor_tag_ops_t* ops);
int (*open_legacy)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
uint32_t halVersion, struct hw_device_t** device);
int (*set_torch_mode)(const char* camera_id, bool enabled);
int (*init)();
/* reserved for future use */
void* reserved[5];
} camera_module_t;hw_module_t common 结构体是保存设备驱动在 HAL 注册的信息。
// hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
typedef struct hw_module_t
{
/** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG */
uint32_t tag;
uint16_t module_api_version;
#define version_major module_api_version
uint16_t hal_api_version;
#define version_minor hal_api_version
/** Identifier of module */
const char *id;
/** Name of this module */
const char *name;
/** Author/owner/implementor of the module */
const char *author;
/** Modules methods */
/** 结构体中定义模块指针函数 open() */
struct hw_module_methods_t* methods;
/** module's dso */
void* dso;
#ifdef __LP64__
uint64_t reserved[32-7];
#else
/** padding to 128 bytes, reserved for future use */
uint32_t reserved[32-7];
#endif
} hw_module_t;
// struct hw_module_methods_t* methods
// mModule->common.methods->open(&mModule->common, id, device) 的 open() 函数
typedef struct hw_module_methods_t {
/** Open a specific device */
int (*open)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
struct hw_device_t** device);
} hw_module_methods_t;通过上述代码知道 CameraModule::open() 方法是调用 hw_module_methods_t 结构体中的成员指针函数 method->open() ,
搜索关键字 hw_module_methods_t 查找哪里定义并注册 hw_module_methods_t 指针函数 method->open() 。
grep -R "hw_module_t" hardware/qcom/camera/打开文件 QCamera2Hal.cpp
QCamera2Hal.cpp 声明并初始化了 hw_module_t 和 camera_module_t 结构体变量。
静态变量 camera_common 中注册了 指针函数 method->open() ,
methods = &qcamera::QCamera2Factory::mModuleMethods; 开始顺藤摸瓜,找到真正打开 camera 设备的函数。
// hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/QCamera2Hal.cpp
#include "QCamera2Factory.h"
#include "HAL3/QCamera3VendorTags.h"
static hw_module_t camera_common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.module_api_version = CAMERA_MODULE_API_VERSION_2_4,
.hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION,
.id = CAMERA_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "QCamera Module",
.author = "Qualcomm Innovation Center Inc",
.methods = &qcamera::QCamera2Factory::mModuleMethods, // 打开相机的方法
.dso = NULL,
.reserved = {0}
};
camera_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = camera_common,
.get_number_of_cameras = qcamera::QCamera2Factory::get_number_of_cameras,
.get_camera_info = qcamera::QCamera2Factory::get_camera_info,
.set_callbacks = qcamera::QCamera2Factory::set_callbacks,
.get_vendor_tag_ops = qcamera::QCamera3VendorTags::get_vendor_tag_ops,
.open_legacy = qcamera::QCamera2Factory::open_legacy,
.set_torch_mode = qcamera::QCamera2Factory::set_torch_mode,
.init = NULL,
.reserved = {0}
};
从 QCamera2Factory::mModuleMethods 定位到 QCamera2Factory 类
// hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/QCamera2Factory.cpp
struct hw_module_methods_t QCamera2Factory::mModuleMethods =
{
.open = QCamera2Factory::camera_device_open,
};
int QCamera2Factory::camera_device_open(
const struct hw_module_t *module, const char *id,
struct hw_device_t **hw_device)
{
int rc = NO_ERROR;
if(module != &HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM.common)
{
LOGE("Invalid module. Trying to open %p, expect %p",
module, &HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM.common);
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
if(!id)
{
LOGE("Invalid camera id");
return BAD_VALUE;
}
#ifdef QCAMERA_HAL1_SUPPORT
if(gQCameraMuxer)
rc = gQCameraMuxer->camera_device_open(module, id, hw_device);
else
#endif
rc = gQCamera2Factory->cameraDeviceOpen(atoi(id), hw_device);
return rc;
}两个分支的调用流程:
- QCamera2Factory::cameraDeviceOpen() → QCamera2HardwareInterface::openCamera() → camera_open()
- QCameraMuxer::camera_device_open() → QCameraMuxer::cameraDeviceOpen() → QCamera2HardwareInterface::openCamera() → camera_open()
两个分支经过不同的路径调用函数 camera_open() 。
mm_camera_interface.c 的函数 camera_open() 调用
- mm_camera_open() → open(dev_name, O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
打开相机设备
// hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera_interface.c
int32_t camera_open(uint8_t camera_idx, mm_camera_vtbl_t **camera_vtbl)
{
......
rc = mm_camera_open(cam_obj);
......
}
mm_camera.c 中函数 mm_camera_open() → open() 真正的打开了 camera 设备。
在执行 open() 后,从 HAL 层进入 Linux kernel 。即将离开 Android ,进入 Linux 的世界。
Linux的思想:一切皆文件,对文件的操作分为三个步骤:
- 打开设备 open();
- 读写设备 read()/write();
- 关闭设备 close()。
如下代码所示, 调用 open() 打开了 camera 设备。 read()/write()/close() 不做叙述。
// hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera.c
int32_t mm_camera_open(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj)
{
......
do
{
n_try--;
errno = 0;
my_obj->ctrl_fd = open(dev_name, O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
l_errno = errno;
LOGD("ctrl_fd = %d, errno == %d", my_obj->ctrl_fd, l_errno);
if((my_obj->ctrl_fd >= 0) || (errno != EIO && errno != ETIMEDOUT) || (n_try <= 0))
{
break;
}
LOGE("Failed with %s error, retrying after %d milli-seconds",
strerror(errno), sleep_msec);
usleep(sleep_msec * 1000U);
}
while(n_try > 0);
......
}打开设备之后,如何获取图像呢? v4l2 是 Linux的视频框架,Android 也是使用类似的方式获取视频图像。
这里给出 mm_camera.h 和 Linux V4L2 类似的接口函数声明,简化对 camera 底层框架理解。
// hardware/qcom/camera/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera.h
extern int32_t mm_camera_open(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj);
extern int32_t mm_camera_close(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj);
extern int32_t mm_camera_register_event_notify(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj,
mm_camera_event_notify_t evt_cb,
void * user_data);
extern int32_t mm_camera_qbuf(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj,
uint32_t ch_id,
mm_camera_buf_def_t *buf);
extern int32_t mm_camera_get_queued_buf_count(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj,
uint32_t ch_id, uint32_t stream_id);
extern int32_t mm_camera_query_capability(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj);
extern int32_t mm_camera_set_parms(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj,
parm_buffer_t *parms);
extern int32_t mm_camera_get_parms(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj,
parm_buffer_t *parms);
extern int32_t mm_camera_map_buf(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj,
uint8_t buf_type,
int fd,
size_t size,
void *buffer);
extern int32_t mm_camera_map_bufs(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj,
const cam_buf_map_type_list *buf_map_list);
extern int32_t mm_camera_unmap_buf(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj,
uint8_t buf_type);通过跟踪 Android 7.1 源码 “open camera ”的流程分析完成:
- framework层的JNI → hardware → Linux
感兴趣的朋友继续分析 Camera 的 read()/write()/close()的流程,加深理解 Camera 框架。