Android自定义View精品(LineBreakLayout-自动换行的标签容器)
版权声明:本文为openXu原创文章【openXu的博客】,未经博主允许不得以任何形式转载
最近一段时间比较忙,都没有时间更新博客,今天公司的事情忙完得空,继续为我的自定义控件系列博客添砖加瓦。本篇博客讲解的是标签自动换行的布局容器,正好前一阵子有个项目中需要,想了想没什么难度就自己弄了。而自定义控件系列文章中对于自定义ViewGroup上次只是讲解了一些基础和步骤 Android自定义ViewGroup(四、打造自己的布局容器),这次就着这个例子我们来完成一个能在项目中使用的自定义布局容器。
1. 初步分析
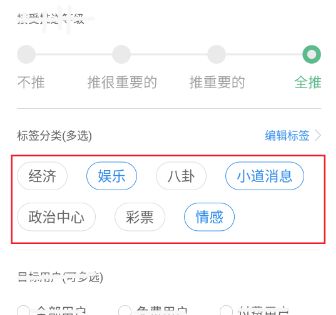
上面红色标示出的就是我们要实现的效果,Android自带的布局容器是没办法达到这样的效果的。每个标签长度不一定,当一行摆放满需要自动换行,标签之间左右上下有一定的距离,这就是这个容器的需求。其中每个标签可以用TextView,标签点击之后有选中的效果(边框和字体变为蓝色)。初步分析,我们自定义的容器需要两个自定义属性,维护两个标签集合(所有标签、选中标签)。接下来我们就动手一步步完成。
2. 定义属性
在values/attrs.xml中为我们的容器定义两个属性,一个是标签左右的间隔距离LEFT_RIGHT_SPACE ,另一个是标签的行距ROW_SPACE,然后在构造方法中获取属性值:
values/attrs.xml
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="LineBreakLayout">
<attr name="leftAndRightSpace" format="dimension" />
<attr name="rowSpace" format="dimension" />
declare-styleable>
resources>
布局中使用
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:openXu="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.openxu.lbl.LineBreakLayout
android:id="@+id/lineBreakLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="20dip"
openXu:leftAndRightSpace="20dip"
openXu:rowSpace="10dip"/>
LinearLayout>
LineBreakLayout.java
public class LineBreakLayout extends ViewGroup {
private final static String TAG = "LineBreakLayout";
/**
* 所有标签
*/
private List lables;
/**
* 选中标签
*/
private List lableSelected = new ArrayList<>();
//自定义属性
private int LEFT_RIGHT_SPACE; //dip
private int ROW_SPACE;
public LineBreakLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public LineBreakLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public LineBreakLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.LineBreakLayout);
LEFT_RIGHT_SPACE = ta.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.LineBreakLayout_leftAndRightSpace, 10);
ROW_SPACE = ta.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.LineBreakLayout_rowSpace, 10);
ta.recycle(); //回收
// ROW_SPACE=20 LEFT_RIGHT_SPACE=40
Log.v(TAG, "ROW_SPACE="+ROW_SPACE+" LEFT_RIGHT_SPACE="+LEFT_RIGHT_SPACE);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
}
}
3. 单个标签
values/color.xml
<color name="tv_gray">#666666color>
<color name="tv_blue">#308BE9color> //蓝色
<color name="divider_gray">#d9d9d9color>//细分割线颜色
标签背景drawable/shape_item_lable_bg.xml
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<item android:state_selected="true">
<shape >
<solid android:color="#ffffff" />
<stroke android:color="@color/tv_blue"
android:width="2px"/>
<corners android:radius="10000dip"/>
shape>
item>
<item>
<shape >
<solid android:color="#ffffff" />
<stroke android:color="@color/divider_gray"
android:width="2px"/>
<corners android:radius="10000dip"/>
shape>
item>
selector>
标签布局layout/item_lable.xml
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/shape_item_lable_bg"
android:paddingBottom="5dip"
android:paddingLeft="12dip"
android:paddingRight="12dip"
android:paddingTop="5dip"
android:text="lable"
android:textSize="15sp"
android:textColor="@color/tv_gray" />
4. 提供接口setlables(List lables)向容器中添加标签
/**
* 添加标签
* @param lables 标签集合
* @param add 是否追加
*/
public void setLables(List lables, boolean add){
if(this.lables == null){
this.lables = new ArrayList<>();
}
if(add){
this.lables.addAll(lables);
}else{
this.lables.clear();
this.lables = lables;
}
if(lables!=null && lables.size()>0){
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(getContext());
for (final String lable : lables) {
//获取标签布局
final TextView tv = (TextView) inflater.inflate(R.layout.item_lable, null);
tv.setText(lable);
//设置选中效果
if (lableSelected.contains(lable)) {
//选中
tv.setSelected(true);
tv.setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.tv_blue));
} else {
//未选中
tv.setSelected(false);
tv.setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.tv_gray));
}
//点击标签后,重置选中效果
tv.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
tv.setSelected(tv.isSelected() ? false : true);
if (tv.isSelected()) {
tv.setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.tv_blue));
//将选中的标签加入到lableSelected中
lableSelected.add(lable);
} else {
tv.setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.tv_gray));
lableSelected.remove(lable);
}
}
});
//将标签添加到容器中
addView(tv);
}
}
}
5. 重写onMeasure()计算容器高度
对于onMeasure()方法,之前已有一篇博客详细讲解,如果不明白可参考 Android自定义View(三、深入解析控件测量onMeasure)。这里针对本布局单独说明一下,本布局在宽度上是使用的建议的宽度(填充父窗体或者具体的size),如果需要wrap_content的效果,还需要重新计算,当然这种需求是非常少见的,所以直接用建议宽度即可;布局的高度就得看其中的标签需要占据多少行(row ),那么高度就为row * 单个标签的高度+(row -1) * 行距,具体实现代码如下:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//为所有的标签childView计算宽和高
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//获取高的模式
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//建议的高度
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//布局的宽度采用建议宽度(match_parent或者size),如果设置wrap_content也是match_parent的效果
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int height ;
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
//如果高度模式为EXACTLY(match_perent或者size),则使用建议高度
height = heightSize;
} else {
//其他情况下(AT_MOST、UNSPECIFIED)需要计算计算高度
int childCount = getChildCount();
if(childCount<=0){
height = 0; //没有标签时,高度为0
}else{
int row = 1; // 标签行数
int widthSpace = width;// 当前行右侧剩余的宽度
for(int i = 0;i= childW ){
//如果剩余的宽度大于此标签的宽度,那就将此标签放到本行
widthSpace -= childW;
}else{
row ++; //增加一行
//如果剩余的宽度不能摆放此标签,那就将此标签放入一行
widthSpace = width-childW;
}
//减去标签左右间距
widthSpace -= LEFT_RIGHT_SPACE;
}
//由于每个标签的高度是相同的,所以直接获取第一个标签的高度即可
int childH = getChildAt(0).getMeasuredHeight();
//最终布局的高度=标签高度*行数+行距*(行数-1)
height = (childH * row) + ROW_SPACE * (row-1);
Log.v(TAG , "总高度:"+height +" 行数:"+row+" 标签高度:"+childH);
}
}
//设置测量宽度和测量高度
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
6. 重写onLayout()摆放标签
onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b)方法是一个抽象方法,自定义ViewGroup时必须实现它,用于给布局中的子控件分配位置,其中的参数l,t,r,b分别代表本ViewGroup的可用空间(除去margin和padding后的剩余空间)的左、上、右、下的坐标(相对于自身),相当于一个约束,如果子控件摆放的位置超过这个范围,超出的部分将不可见。onLayout()的实现代码如下,注释已经很清楚,就不再赘述:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int row = 0;
int right = 0; // 标签相对于布局的右侧位置
int botom; // 标签相对于布局的底部位置
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
int childW = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int childH = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
//右侧位置=本行已经占有的位置+当前标签的宽度
right += childW;
//底部位置=已经摆放的行数*(标签高度+行距)+当前标签高度
botom = row * (childH + ROW_SPACE) + childH;
// 如果右侧位置已经超出布局右边缘,跳到下一行
// if it can't drawing on a same line , skip to next line
if (right > (r - LEFT_RIGHT_SPACE)){
row++;
right = childW;
botom = row * (childH + ROW_SPACE) + childH;
}
Log.d(TAG, "left = " + (right - childW) +" top = " + (botom - childH)+
" right = " + right + " botom = " + botom);
childView.layout(right - childW, botom - childH,right,botom);
right += LEFT_RIGHT_SPACE;
}
}
7. 使用
到此为止,这个自动换行的标签布局已经定义完成,现在就让我们使用看看运行效果怎么样,这里为布局设置了红色背景,用于直观的查看我们的计算有没有出错,可以看到,标签没有超出布局,布局的宽高也正好包裹所有标签:
List lable = new ArrayList<>();
lable.add("经济");
lable.add( "娱乐");
lable.add("八卦");
lable.add("小道消息");
lable.add("政治中心");
lable.add("彩票");
lable.add("情感");
//设置标签
lineBreakLayout.setLables(lable, true);
//获取选中的标签
List selectedLables = lineBreakLayout.getSelectedLables();
8.总结
这个布局的实现在技术上来说是比较简单的,但是它非常具有代表性,非常典型的自定义ViewGroup,相信如果能完全写下这个示例,下次需要自定义ViewGroup的时候也不会有太大难度了。当然这个布局不是完美的,就算Android自带的布局也不能说完美,只要它能满足我们项目中的开发需求就ok。对于自定义ViewGroup还有一些重要的知识点(事件处理等)在后面的博客中会陆续讲解。
欢迎关注,希望在这里有你想要的,博主会持续更新高(di)质(ji)量(shu)的文章和大家交流学习
喜欢请点赞,no爱请勿喷~O(∩_∩)O谢谢
##源码下载:
注:没有积分的童鞋 请留言索要代码喔
http://download.csdn.net/detail/u010163442/9698873
https://github.com/openXu/LineBreakLayout