tensorflow实现空洞卷积(dilated connvolution也叫扩张卷积)
https://www.zhihu.com/question/54149221/answer/192025860
关于在tensorflow中实现一般的卷积,可以参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/u010866505/article/details/80917180
https://blog.csdn.net/mao_xiao_feng/article/details/78004522
由于一般cnn在昨晚卷积之后会对feature map进行downSampling,这样会造成一定的信息丢失.那么空洞卷积就是没有pooling层,同时可以扩大感受野(如上知乎的讲解)
接下来,我用tensorflow的api来介绍一下空洞卷积的发生过程。
tf.nn.atrous_conv2d(value,filters,rate,padding,name=None)
这是tensorflow的空洞卷积的api,value和filter是输入和卷积核.详细可参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/u010866505/article/details/80917180
rate:在一般的cnn的api中,会有stride这个参数,但是在空洞卷积里面是没有的.这个参数是扩大采样间隔,即在卷积核中插入rate-1个'0'得到新的卷积核,当rate=1时,新的卷积核和旧的相同,卷积过程等同于安普通的卷积过程.
padding:这个和是之前的一样.
接下来用一个例子来说明空洞卷积的过程:
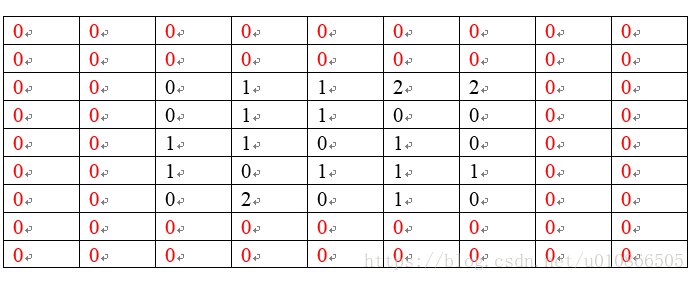
如下三张通道图(5*5):
即input:
0 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
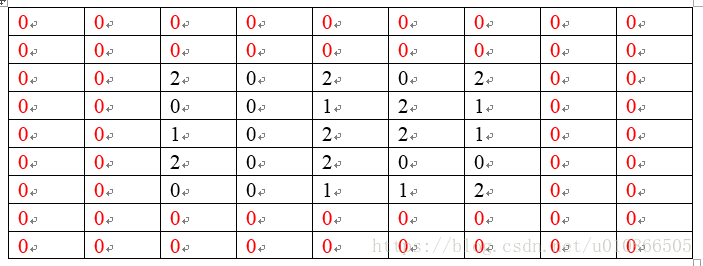
三个滤波器(3*3):
-1 |
-1 |
0 |
-1 |
1 |
0 |
-1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
-1 |
0 |
-1 |
0 |
-1 |
-1 |
0 |
0 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
-1 |
0 |
接下来,我们看取rate=1和rate=2两种情况来说明,这里padding选取'SAME',取'VALID'原理一样。
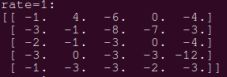
当rate=1,此时的卷积过程和普通卷积过程是一样的.
最终输出的结果是:
接下来着重讲rate=2:
当rate=2时,之前的卷积核,需要在每个点中间插入1个'0',于是乎,之前的卷积核就是如下图所示:
以上就是新的卷积核。根据公式计算出新的输入需要pad的像素点:
padding='SAME':
new_width = 5:
需要pad的像素点是(new_width-1)*S + F - W
S=1(在后面的卷积过程中,滤波器每次只移动一步)
F = 5(新卷积核的size=5*5)
W = 5(输入的size=5*5)
因此需要pad的像素点是4,上下各一半都为2,因此输入的矩阵就变成了如下所示的:
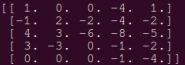
然后用新的卷积核和新的输入,进行卷积,求和,最后得到的结果是:
上述结果经过笔验算成功.
如下是上述的简易代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
input_data=[
[[0,1,1,2,2],
[0,1,1,0,0],
[1,1,0,1,0],
[1,0,1,1,1],
[0,2,0,1,0]],
[[1,1,1,2,0],
[0,2,1,1,2],
[1,2,0,0,2],
[0,2,1,2,1],
[2,0,1,2,0]],
[[2,0,2,0,2],
[0,0,1,2,1],
[1,0,2,2,1],
[2,0,2,0,0],
[0,0,1,1,2]]
]
weights_data=[
[[ -1, -1, 0],
[-1, 1, 0],
[ -1,1, 0]],
[[1, -1, 0],
[ -1, 0, -1],
[ -1, 0, 0]],
[[-1, 0, 1],
[ 1, 0, 1],
[ 0, -1, 0]]
]
def get_shape(tensor):
[s1,s2,s3]= tensor.get_shape()
s1=int(s1)
s2=int(s2)
s3=int(s3)
return s1,s2,s3
def chw2hwc(chw_tensor):
[c,h,w]=get_shape(chw_tensor)
cols=[]
for i in range(c):
#每个通道里面的二维数组转为[w*h,1]即1列
line = tf.reshape(chw_tensor[i],[h*w,1])
cols.append(line)
#横向连接,即将所有竖直数组横向排列连接
input = tf.concat(cols,1)#[w*h,c]
#[w*h,c]-->[h,w,c]
input = tf.reshape(input,[h,w,c])
return input
def hwc2chw(hwc_tensor):
[h,w,c]=get_shape(hwc_tensor)
cs=[]
for i in range(c):
#[h,w]-->[1,h,w]
channel=tf.expand_dims(hwc_tensor[:,:,i],0)
cs.append(channel)
#[1,h,w]...[1,h,w]---->[c,h,w]
input = tf.concat(cs,0)#[c,h,w]
return input
def tf_dilatedConv2d(input,weights,rate,pad):
conv = tf.nn.atrous_conv2d(input, weights, rate, pad)
return conv
def main():
const_input = tf.constant(input_data , tf.float32)
const_weights = tf.constant(weights_data , tf.float32 )
input = tf.Variable(const_input,name="input")
#[3,5,5]------>[5,5,3]
input=chw2hwc(input)
#[5,5,3]------>[1,5,5,32]
input=tf.expand_dims(input,0)
weights = tf.Variable(const_weights,name="weights")
#[3,3,3]-->[3,3,3]
weights=chw2hwc(weights)
#[3,3,3]-->[3,3,3,1]
weights=tf.expand_dims(weights,3)
#[b,h,w,c]
conv=tf_dilatedConv2d(input,weights,1,'SAME')
rs=hwc2chw(conv[0])
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess=tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
conv_val = sess.run(rs)
print('rate=1:')
print(conv_val[0])
conv=tf_dilatedConv2d(input,weights,2,'SAME')
rs=hwc2chw(conv[0])
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess=tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
conv_val = sess.run(rs)
print('rate=2:')
print(conv_val[0])
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
如果OK,点个赞呗.哈哈!