ListView 源码详解 有这一篇就够了!!!
虽然现在大家使用ListView的机会相对RecyclerView的机会较少,但官方并没有标注 ListView 类过期,哈哈,就说明它一定还是有他的特殊之处,这篇文章就来分析下,ListView的内部机制以及几个重要的点。
将从下面几个方面开始着手分析ListView,将会分两篇文章进行解析
- 类的继承关系
- ListView 的构造方法
- RecycleBin主要方法讲解
- ListView 的绘制原理以及缓存回收过程 (onMeasure onLayout onDraw)
- Listview 的滑动过程
- setAdapter 原理
- notifyDataSetChanged 原理
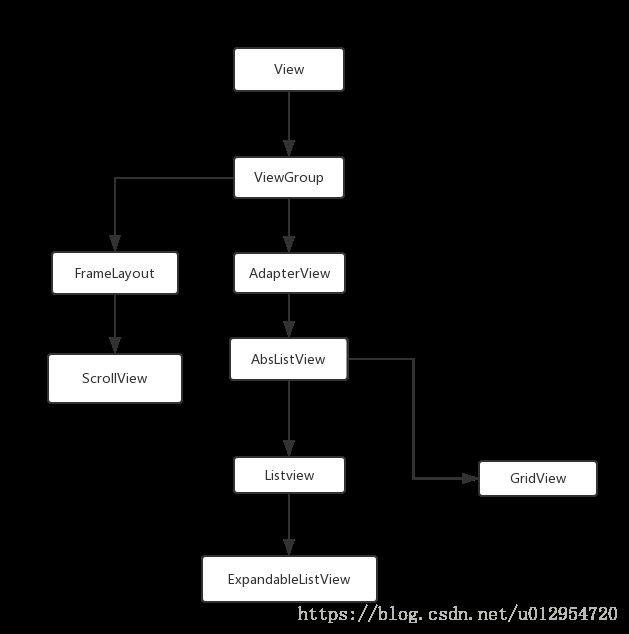
(1)ListView 的继承关系
(2)ListView 的构造函数
public ListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
// 这里是调用的父类AbsListView的构造方法
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(
attrs, R.styleable.ListView, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
final CharSequence[] entries = a.getTextArray(R.styleable.ListView_entries);
if (entries != null) {
// ListView 的默认Adapter
setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<>(context, R.layout.simple_list_item_1, entries));
}
// 设置分割线样式 用户可以重写ListView_divider样式
final Drawable d = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.ListView_divider);
if (d != null) {
// Use an implicit divider height which may be explicitly
// overridden by android:dividerHeight further down.
setDivider(d);
}
// 设置 ListView 的footer和header
final Drawable osHeader = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.ListView_overScrollHeader);
if (osHeader != null) {
setOverscrollHeader(osHeader);
}
final Drawable osFooter = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.ListView_overScrollFooter);
if (osFooter != null) {
setOverscrollFooter(osFooter);
}
// 分割线高度
// Use an explicit divider height, if specified.
if (a.hasValueOrEmpty(R.styleable.ListView_dividerHeight)) {
final int dividerHeight = a.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.ListView_dividerHeight, 0);
if (dividerHeight != 0) {
setDividerHeight(dividerHeight);
}
}
mHeaderDividersEnabled = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.ListView_headerDividersEnabled, true);
mFooterDividersEnabled = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.ListView_footerDividersEnabled, true);
a.recycle();
}AbsListView.java 的构造方法
public AbsListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
initAbsListView();
...
}
private void initAbsListView() {
// Setting focusable in touch mode will set the focusable property to true
// 设置可点击
setClickable(true);
// 设置 触摸可以获取焦点
setFocusableInTouchMode(true);
// 设置可以绘制
setWillNotDraw(false);
// 设置对于透明的地方,显示最底层的背景
setAlwaysDrawnWithCacheEnabled(false);
// 设置 是否缓存卷动项
setScrollingCacheEnabled(true);
// 设置相关事件变量初始化
final ViewConfiguration configuration = ViewConfiguration.get(mContext);
mTouchSlop = configuration.getScaledTouchSlop();
mVerticalScrollFactor = configuration.getScaledVerticalScrollFactor();
mMinimumVelocity = configuration.getScaledMinimumFlingVelocity();
mMaximumVelocity = configuration.getScaledMaximumFlingVelocity();
mOverscrollDistance = configuration.getScaledOverscrollDistance();
mOverflingDistance = configuration.getScaledOverflingDistance();
mDensityScale = getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
}
ListView 的构造方法中主要做一些资源的初始化工作。
(3) RecycleBin主要方法讲解
RecycleBin是 AbsListView的内部类,它的代码不多,这里主要介绍几个变量含义和方法功能
class RecycleBin {
private RecyclerListener mRecyclerListener;
/**
* The position of the first view stored in mActiveViews.
*/
private int mFirstActivePosition;
/**
* Views that were on screen at the start of layout. This array is populated at the start of
* layout, and at the end of layout all view in mActiveViews are moved to mScrapViews.
* Views in mActiveViews represent a contiguous range of Views, with position of the first
* view store in mFirstActivePosition.
*/
private View[] mActiveViews = new View[0];
/**
* Unsorted views that can be used by the adapter as a convert view.
*/
private ArrayList[] mScrapViews;
private int mViewTypeCount;
private ArrayList mCurrentScrap;
private ArrayList mSkippedScrap;
private SparseArray mTransientStateViews;
private LongSparseArray mTransientStateViewsById;
public void setViewTypeCount(int viewTypeCount) {
if (viewTypeCount < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can't have a viewTypeCount < 1");
}
//noinspection unchecked
ArrayList[] scrapViews = new ArrayList[viewTypeCount];
for (int i = 0; i < viewTypeCount; i++) {
scrapViews[i] = new ArrayList();
}
mViewTypeCount = viewTypeCount;
mCurrentScrap = scrapViews[0];
mScrapViews = scrapViews;
}
public void markChildrenDirty() {
if (mViewTypeCount == 1) {
final ArrayList scrap = mCurrentScrap;
final int scrapCount = scrap.size();
for (int i = 0; i < scrapCount; i++) {
scrap.get(i).forceLayout();
}
} else {
final int typeCount = mViewTypeCount;
for (int i = 0; i < typeCount; i++) {
final ArrayList scrap = mScrapViews[i];
final int scrapCount = scrap.size();
for (int j = 0; j < scrapCount; j++) {
scrap.get(j).forceLayout();
}
}
}
if (mTransientStateViews != null) {
final int count = mTransientStateViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
mTransientStateViews.valueAt(i).forceLayout();
}
}
if (mTransientStateViewsById != null) {
final int count = mTransientStateViewsById.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
mTransientStateViewsById.valueAt(i).forceLayout();
}
}
}
public boolean shouldRecycleViewType(int viewType) {
return viewType >= 0;
}
/**
* Clears the scrap heap.
*/
void clear() {
if (mViewTypeCount == 1) {
final ArrayList scrap = mCurrentScrap;
clearScrap(scrap);
} else {
final int typeCount = mViewTypeCount;
for (int i = 0; i < typeCount; i++) {
final ArrayList scrap = mScrapViews[i];
clearScrap(scrap);
}
}
clearTransientStateViews();
}
/**
* Fill ActiveViews with all of the children of the AbsListView.
*
* @param childCount The minimum number of views mActiveViews should hold
* @param firstActivePosition The position of the first view that will be stored in
* mActiveViews
*/
void fillActiveViews(int childCount, int firstActivePosition) {
if (mActiveViews.length < childCount) {
mActiveViews = new View[childCount];
}
mFirstActivePosition = firstActivePosition;
//noinspection MismatchedReadAndWriteOfArray
final View[] activeViews = mActiveViews;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
AbsListView.LayoutParams lp = (AbsListView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// Don't put header or footer views into the scrap heap
if (lp != null && lp.viewType != ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER) {
// Note: We do place AdapterView.ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_IGNORE in active views.
// However, we will NOT place them into scrap views.
activeViews[i] = child;
// Remember the position so that setupChild() doesn't reset state.
lp.scrappedFromPosition = firstActivePosition + i;
}
}
}
/**
* Get the view corresponding to the specified position. The view will be removed from
* mActiveViews if it is found.
*
* @param position The position to look up in mActiveViews
* @return The view if it is found, null otherwise
*/
View getActiveView(int position) {
int index = position - mFirstActivePosition;
final View[] activeViews = mActiveViews;
if (index >=0 && index < activeViews.length) {
final View match = activeViews[index];
activeViews[index] = null;
return match;
}
return null;
}
View getTransientStateView(int position) {
if (mAdapter != null && mAdapterHasStableIds && mTransientStateViewsById != null) {
long id = mAdapter.getItemId(position);
View result = mTransientStateViewsById.get(id);
mTransientStateViewsById.remove(id);
return result;
}
if (mTransientStateViews != null) {
final int index = mTransientStateViews.indexOfKey(position);
if (index >= 0) {
View result = mTransientStateViews.valueAt(index);
mTransientStateViews.removeAt(index);
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Dumps and fully detaches any currently saved views with transient
* state.
*/
void clearTransientStateViews() {
final SparseArray viewsByPos = mTransientStateViews;
if (viewsByPos != null) {
final int N = viewsByPos.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
removeDetachedView(viewsByPos.valueAt(i), false);
}
viewsByPos.clear();
}
final LongSparseArray viewsById = mTransientStateViewsById;
if (viewsById != null) {
final int N = viewsById.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
removeDetachedView(viewsById.valueAt(i), false);
}
viewsById.clear();
}
}
/**
* @return A view from the ScrapViews collection. These are unordered.
*/
View getScrapView(int position) {
final int whichScrap = mAdapter.getItemViewType(position);
if (whichScrap < 0) {
return null;
}
if (mViewTypeCount == 1) {
return retrieveFromScrap(mCurrentScrap, position);
} else if (whichScrap < mScrapViews.length) {
return retrieveFromScrap(mScrapViews[whichScrap], position);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Puts a view into the list of scrap views.
*
* If the list data hasn't changed or the adapter has stable IDs, views
* with transient state will be preserved for later retrieval.
*
* @param scrap The view to add
* @param position The view's position within its parent
*/
void addScrapView(View scrap, int position) {
final AbsListView.LayoutParams lp = (AbsListView.LayoutParams) scrap.getLayoutParams();
if (lp == null) {
// Can't recycle, but we don't know anything about the view.
// Ignore it completely.
return;
}
lp.scrappedFromPosition = position;
// Remove but don't scrap header or footer views, or views that
// should otherwise not be recycled.
final int viewType = lp.viewType;
if (!shouldRecycleViewType(viewType)) {
// Can't recycle. If it's not a header or footer, which have
// special handling and should be ignored, then skip the scrap
// heap and we'll fully detach the view later.
if (viewType != ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER) {
getSkippedScrap().add(scrap);
}
return;
}
scrap.dispatchStartTemporaryDetach();
// The the accessibility state of the view may change while temporary
// detached and we do not allow detached views to fire accessibility
// events. So we are announcing that the subtree changed giving a chance
// to clients holding on to a view in this subtree to refresh it.
notifyViewAccessibilityStateChangedIfNeeded(
AccessibilityEvent.CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_SUBTREE);
// Don't scrap views that have transient state.
final boolean scrapHasTransientState = scrap.hasTransientState();
if (scrapHasTransientState) {
if (mAdapter != null && mAdapterHasStableIds) {
// If the adapter has stable IDs, we can reuse the view for
// the same data.
if (mTransientStateViewsById == null) {
mTransientStateViewsById = new LongSparseArray<>();
}
mTransientStateViewsById.put(lp.itemId, scrap);
} else if (!mDataChanged) {
// If the data hasn't changed, we can reuse the views at
// their old positions.
if (mTransientStateViews == null) {
mTransientStateViews = new SparseArray<>();
}
mTransientStateViews.put(position, scrap);
} else {
// Otherwise, we'll have to remove the view and start over.
clearScrapForRebind(scrap);
getSkippedScrap().add(scrap);
}
} else {
clearScrapForRebind(scrap);
if (mViewTypeCount == 1) {
mCurrentScrap.add(scrap);
} else {
mScrapViews[viewType].add(scrap);
}
if (mRecyclerListener != null) {
mRecyclerListener.onMovedToScrapHeap(scrap);
}
}
}
private ArrayList getSkippedScrap() {
if (mSkippedScrap == null) {
mSkippedScrap = new ArrayList<>();
}
return mSkippedScrap;
}
/**
* Finish the removal of any views that skipped the scrap heap.
*/
void removeSkippedScrap() {
if (mSkippedScrap == null) {
return;
}
final int count = mSkippedScrap.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
removeDetachedView(mSkippedScrap.get(i), false);
}
mSkippedScrap.clear();
}
/**
* Move all views remaining in mActiveViews to mScrapViews.
*/
void scrapActiveViews() {
final View[] activeViews = mActiveViews;
final boolean hasListener = mRecyclerListener != null;
final boolean multipleScraps = mViewTypeCount > 1;
ArrayList scrapViews = mCurrentScrap;
final int count = activeViews.length;
for (int i = count - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final View victim = activeViews[i];
if (victim != null) {
final AbsListView.LayoutParams lp
= (AbsListView.LayoutParams) victim.getLayoutParams();
final int whichScrap = lp.viewType;
activeViews[i] = null;
if (victim.hasTransientState()) {
// Store views with transient state for later use.
victim.dispatchStartTemporaryDetach();
if (mAdapter != null && mAdapterHasStableIds) {
if (mTransientStateViewsById == null) {
mTransientStateViewsById = new LongSparseArray();
}
long id = mAdapter.getItemId(mFirstActivePosition + i);
mTransientStateViewsById.put(id, victim);
} else if (!mDataChanged) {
if (mTransientStateViews == null) {
mTransientStateViews = new SparseArray();
}
mTransientStateViews.put(mFirstActivePosition + i, victim);
} else if (whichScrap != ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER) {
// The data has changed, we can't keep this view.
removeDetachedView(victim, false);
}
} else if (!shouldRecycleViewType(whichScrap)) {
// Discard non-recyclable views except headers/footers.
if (whichScrap != ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER) {
removeDetachedView(victim, false);
}
} else {
// Store everything else on the appropriate scrap heap.
if (multipleScraps) {
scrapViews = mScrapViews[whichScrap];
}
lp.scrappedFromPosition = mFirstActivePosition + i;
removeDetachedView(victim, false);
scrapViews.add(victim);
if (hasListener) {
mRecyclerListener.onMovedToScrapHeap(victim);
}
}
}
}
pruneScrapViews();
}
/**
* At the end of a layout pass, all temp detached views should either be re-attached or
* completely detached. This method ensures that any remaining view in the scrap list is
* fully detached.
*/
void fullyDetachScrapViews() {
final int viewTypeCount = mViewTypeCount;
final ArrayList[] scrapViews = mScrapViews;
for (int i = 0; i < viewTypeCount; ++i) {
final ArrayList scrapPile = scrapViews[i];
for (int j = scrapPile.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
final View view = scrapPile.get(j);
if (view.isTemporarilyDetached()) {
removeDetachedView(view, false);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Makes sure that the size of mScrapViews does not exceed the size of
* mActiveViews, which can happen if an adapter does not recycle its
* views. Removes cached transient state views that no longer have
* transient state.
*/
private void pruneScrapViews() {
final int maxViews = mActiveViews.length;
final int viewTypeCount = mViewTypeCount;
final ArrayList[] scrapViews = mScrapViews;
for (int i = 0; i < viewTypeCount; ++i) {
final ArrayList scrapPile = scrapViews[i];
int size = scrapPile.size();
while (size > maxViews) {
scrapPile.remove(--size);
}
}
final SparseArray transViewsByPos = mTransientStateViews;
if (transViewsByPos != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < transViewsByPos.size(); i++) {
final View v = transViewsByPos.valueAt(i);
if (!v.hasTransientState()) {
removeDetachedView(v, false);
transViewsByPos.removeAt(i);
i--;
}
}
}
final LongSparseArray transViewsById = mTransientStateViewsById;
if (transViewsById != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < transViewsById.size(); i++) {
final View v = transViewsById.valueAt(i);
if (!v.hasTransientState()) {
removeDetachedView(v, false);
transViewsById.removeAt(i);
i--;
}
}
}
}
/**
* Puts all views in the scrap heap into the supplied list.
*/
void reclaimScrapViews(List views) {
if (mViewTypeCount == 1) {
views.addAll(mCurrentScrap);
} else {
final int viewTypeCount = mViewTypeCount;
final ArrayList[] scrapViews = mScrapViews;
for (int i = 0; i < viewTypeCount; ++i) {
final ArrayList scrapPile = scrapViews[i];
views.addAll(scrapPile);
}
}
}
/**
* Updates the cache color hint of all known views.
*
* @param color The new cache color hint.
*/
void setCacheColorHint(int color) {
if (mViewTypeCount == 1) {
final ArrayList scrap = mCurrentScrap;
final int scrapCount = scrap.size();
for (int i = 0; i < scrapCount; i++) {
scrap.get(i).setDrawingCacheBackgroundColor(color);
}
} else {
final int typeCount = mViewTypeCount;
for (int i = 0; i < typeCount; i++) {
final ArrayList scrap = mScrapViews[i];
final int scrapCount = scrap.size();
for (int j = 0; j < scrapCount; j++) {
scrap.get(j).setDrawingCacheBackgroundColor(color);
}
}
}
// Just in case this is called during a layout pass
final View[] activeViews = mActiveViews;
final int count = activeViews.length;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View victim = activeViews[i];
if (victim != null) {
victim.setDrawingCacheBackgroundColor(color);
}
}
}
private View retrieveFromScrap(ArrayList scrapViews, int position) {
final int size = scrapViews.size();
if (size > 0) {
// See if we still have a view for this position or ID.
// Traverse backwards to find the most recently used scrap view
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final View view = scrapViews.get(i);
final AbsListView.LayoutParams params =
(AbsListView.LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();
if (mAdapterHasStableIds) {
final long id = mAdapter.getItemId(position);
if (id == params.itemId) {
return scrapViews.remove(i);
}
} else if (params.scrappedFromPosition == position) {
final View scrap = scrapViews.remove(i);
clearScrapForRebind(scrap);
return scrap;
}
}
final View scrap = scrapViews.remove(size - 1);
clearScrapForRebind(scrap);
return scrap;
} else {
return null;
}
}
private void clearScrap(final ArrayList scrap) {
final int scrapCount = scrap.size();
for (int j = 0; j < scrapCount; j++) {
removeDetachedView(scrap.remove(scrapCount - 1 - j), false);
}
}
private void clearScrapForRebind(View view) {
view.clearAccessibilityFocus();
view.setAccessibilityDelegate(null);
}
private void removeDetachedView(View child, boolean animate) {
child.setAccessibilityDelegate(null);
AbsListView.this.removeDetachedView(child, animate);
}
} 变量:
RecycleBin中 mActiveViews:当前在屏幕上展示的view
mScrapViews :存储滑出屏幕的View; mViewTypeCount>1的时候,ScrapViews数组就会有多个值,分别缓存一个类型的item
mCurrentScrap :和mScrapViews 功能类似,mViewTypeCount=1,也就是listView中只有一种类型的item时(不包括header和footer),item是存入到mCurrentScrap中。
mViewTypeCount : 当前ListView 的item的种类
if (mViewTypeCount == 1) {
mCurrentScrap.add(scrap);
} else {
mScrapViews[viewType].add(scrap);
}方法:
fillActiveViews:根据传入的参数,要存储view的数量以及第一个可见元素的位置,往mActiveViews添加View
getActiveView: 和fillActiveViews相对,从mActiveViews获取View,从getActiveView方法可以看到,在读取match之后,就 activeViews[index] = null; 说明 activeViews 中的view只能复用一次。
getScrapView: 从mScrapViews 或者mCurrentScrap中获取尾部的View
addScrapView: 将滚出屏幕的View添加到mScrapViews 或者mCurrentScrap中
(4) ListView 的绘制原理以及缓存回收过程
在看过ListView的初始化操作之后,之后就是由ViemRootImpl的 performTraversals 方法主持View的整个绘制过程, 这里简单介绍下View的启动过程,用UML图表示他们的调用关系,具体的源码大家可以再细细研究。
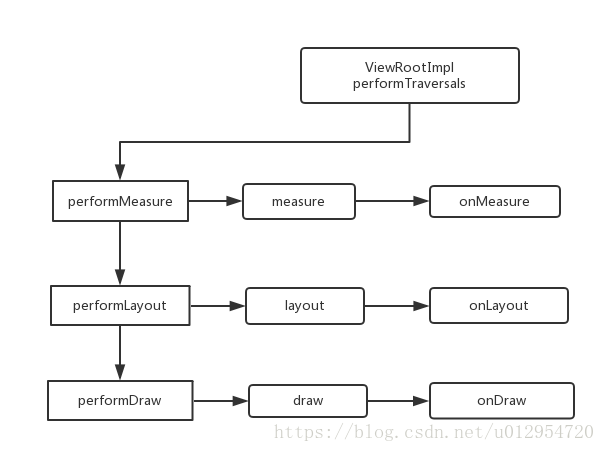
ViemRootImpl的 performTraversals 完成依次执行performMeasure performLayout performDraw三个方法,其中performMeasure 中调用measure方法,在measure方法中又会调用onMeasure方法,在onMeasure方法中会对所有的子元素进行measure过程,这个时候measure流程就从父容器传递到子元素中,这样就完成了一次measure过程。接着子元素会重复父容器的measure过程,如此反复完成整个View树的遍历。同理,performLayout和performDraw传递流程和perwformMeasure类似,唯一不同的是,performDraw过程实在draw方法中通过dispatchOnDraw来实现的,之后再进行onDraw,不过这并没有本质的差别。
接下来就来剖析ListView的绘制过程。
onMeasure 测量过程和其他View功能类似,测量好view的宽度和高度以及对应的SpecMode SpecSize
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// Sets up mListPadding
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 初始化 宽度和高度 的模式和大小
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int childWidth = 0;
int childHeight = 0;
int childState = 0;
...
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
mWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
}ListView 的绘制过程主要在onLayout,ListView 中没有onLayout在父类AbsListView 中
AbsListView 中的onLayout
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mInLayout = true;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
if (changed) {
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
getChildAt(i).forceLayout();
}
mRecycler.markChildrenDirty();
}
layoutChildren();
mOverscrollMax = (b - t) / OVERSCROLL_LIMIT_DIVISOR;
// TODO: Move somewhere sane. This doesn't belong in onLayout().
if (mFastScroll != null) {
mFastScroll.onItemCountChanged(getChildCount(), mItemCount);
}
mInLayout = false;
}
// AbsListView 中的layoutChildren的实现分别在其子类中
protected void layoutChildren() {
}ListView 的 layoutChildren
@Override
protected void layoutChildren() {
final boolean blockLayoutRequests = mBlockLayoutRequests;
if (blockLayoutRequests) {
return;
}
mBlockLayoutRequests = true;
try {
super.layoutChildren();
invalidate();
if (mAdapter == null) {
resetList();
invokeOnItemScrollListener();
return;
}
final int childrenTop = mListPadding.top;
final int childrenBottom = mBottom - mTop - mListPadding.bottom;
// 一开始获取 count = 0;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
int index = 0;
int delta = 0;
View sel;
View oldSel = null;
View oldFirst = null;
View newSel = null;
// Remember stuff we will need down below
switch (mLayoutMode) {
case LAYOUT_SET_SELECTION:
index = mNextSelectedPosition - mFirstPosition;
if (index >= 0 && index < childCount) {
newSel = getChildAt(index);
}
break;
case LAYOUT_FORCE_TOP:
case LAYOUT_FORCE_BOTTOM:
case LAYOUT_SPECIFIC:
case LAYOUT_SYNC:
break;
case LAYOUT_MOVE_SELECTION:
default:
// Remember the previously selected view
index = mSelectedPosition - mFirstPosition;
if (index >= 0 && index < childCount) {
oldSel = getChildAt(index);
}
// Remember the previous first child
oldFirst = getChildAt(0);
if (mNextSelectedPosition >= 0) {
delta = mNextSelectedPosition - mSelectedPosition;
}
// Caution: newSel might be null
newSel = getChildAt(index + delta);
}
boolean dataChanged = mDataChanged;
if (dataChanged) {
handleDataChanged();
}
// Handle the empty set by removing all views that are visible
// and calling it a day
if (mItemCount == 0) {
resetList();
invokeOnItemScrollListener();
return;
} else if (mItemCount != mAdapter.getCount()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The content of the adapter has changed but "
+ "ListView did not receive a notification. Make sure the content of "
+ "your adapter is not modified from a background thread, but only from "
+ "the UI thread. Make sure your adapter calls notifyDataSetChanged() "
+ "when its content changes. [in ListView(" + getId() + ", " + getClass()
+ ") with Adapter(" + mAdapter.getClass() + ")]");
}
setSelectedPositionInt(mNextSelectedPosition);
AccessibilityNodeInfo accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreNode = null;
View accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView = null;
int accessibilityFocusPosition = INVALID_POSITION;
// Remember which child, if any, had accessibility focus. This must
// occur before recycling any views, since that will clear
// accessibility focus.
final ViewRootImpl viewRootImpl = getViewRootImpl();
if (viewRootImpl != null) {
final View focusHost = viewRootImpl.getAccessibilityFocusedHost();
if (focusHost != null) {
final View focusChild = getAccessibilityFocusedChild(focusHost);
if (focusChild != null) {
if (!dataChanged || isDirectChildHeaderOrFooter(focusChild)
|| (focusChild.hasTransientState() && mAdapterHasStableIds)) {
// The views won't be changing, so try to maintain
// focus on the current host and virtual view.
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView = focusHost;
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreNode = viewRootImpl
.getAccessibilityFocusedVirtualView();
}
// If all else fails, maintain focus at the same
// position.
accessibilityFocusPosition = getPositionForView(focusChild);
}
}
}
View focusLayoutRestoreDirectChild = null;
View focusLayoutRestoreView = null;
// Take focus back to us temporarily to avoid the eventual call to
// clear focus when removing the focused child below from messing
// things up when ViewAncestor assigns focus back to someone else.
final View focusedChild = getFocusedChild();
if (focusedChild != null) {
// TODO: in some cases focusedChild.getParent() == null
// We can remember the focused view to restore after re-layout
// if the data hasn't changed, or if the focused position is a
// header or footer.
if (!dataChanged || isDirectChildHeaderOrFooter(focusedChild)
|| focusedChild.hasTransientState() || mAdapterHasStableIds) {
focusLayoutRestoreDirectChild = focusedChild;
// Remember the specific view that had focus.
focusLayoutRestoreView = findFocus();
if (focusLayoutRestoreView != null) {
// Tell it we are going to mess with it.
focusLayoutRestoreView.dispatchStartTemporaryDetach();
}
}
requestFocus();
}
// Pull all children into the RecycleBin.
// These views will be reused if possible
//mFirstPosition是ListView的成员变量,存储着第一个显示的child所对应的adapter的position
final int firstPosition = mFirstPosition;
final RecycleBin recycleBin = mRecycler;
if (dataChanged) {
//如果数据发生了变化,那么就把ListView的所有子View都放入到RecycleBin的mScrapViews数组中
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
//addScrapView方法会传入一个View,以及这个View所对应的position
recycleBin.addScrapView(getChildAt(i), firstPosition+i);
}
} else {
//如果数据没发生变化,那么把ListView的所有子View都放入到RecycleBin的mActiveViews数组中
recycleBin.fillActiveViews(childCount, firstPosition);
}
// Clear out old views
detachAllViewsFromParent();
recycleBin.removeSkippedScrap();
// mLayoutMode的值来决定布局模式,默认情况下都是普通模式LAYOUT_NORMAL
switch (mLayoutMode) {
case LAYOUT_SET_SELECTION:
if (newSel != null) {
sel = fillFromSelection(newSel.getTop(), childrenTop, childrenBottom);
} else {
sel = fillFromMiddle(childrenTop, childrenBottom);
}
break;
case LAYOUT_SYNC:
sel = fillSpecific(mSyncPosition, mSpecificTop);
break;
case LAYOUT_FORCE_BOTTOM:
sel = fillUp(mItemCount - 1, childrenBottom);
adjustViewsUpOrDown();
break;
case LAYOUT_FORCE_TOP:
mFirstPosition = 0;
sel = fillFromTop(childrenTop);
adjustViewsUpOrDown();
break;
case LAYOUT_SPECIFIC:
final int selectedPosition = reconcileSelectedPosition();
sel = fillSpecific(selectedPosition, mSpecificTop);
/**
* When ListView is resized, FocusSelector requests an async selection for the
* previously focused item to make sure it is still visible. If the item is not
* selectable, it won't regain focus so instead we call FocusSelector
* to directly request focus on the view after it is visible.
*/
if (sel == null && mFocusSelector != null) {
final Runnable focusRunnable = mFocusSelector
.setupFocusIfValid(selectedPosition);
if (focusRunnable != null) {
post(focusRunnable);
}
}
break;
case LAYOUT_MOVE_SELECTION:
sel = moveSelection(oldSel, newSel, delta, childrenTop, childrenBottom);
break;
default:
if (childCount == 0) {
if (!mStackFromBottom) {
final int position = lookForSelectablePosition(0, true);
setSelectedPositionInt(position);
sel = fillFromTop(childrenTop);
} else {
final int position = lookForSelectablePosition(mItemCount - 1, false);
setSelectedPositionInt(position);
sel = fillUp(mItemCount - 1, childrenBottom);
}
} else {
if (mSelectedPosition >= 0 && mSelectedPosition < mItemCount) {
sel = fillSpecific(mSelectedPosition,
oldSel == null ? childrenTop : oldSel.getTop());
} else if (mFirstPosition < mItemCount) {
sel = fillSpecific(mFirstPosition,
oldFirst == null ? childrenTop : oldFirst.getTop());
} else {
sel = fillSpecific(0, childrenTop);
}
}
break;
}
// Flush any cached views that did not get reused above
recycleBin.scrapActiveViews();
// remove any header/footer that has been temp detached and not re-attached
removeUnusedFixedViews(mHeaderViewInfos);
removeUnusedFixedViews(mFooterViewInfos);
if (sel != null) {
// The current selected item should get focus if items are
// focusable.
if (mItemsCanFocus && hasFocus() && !sel.hasFocus()) {
final boolean focusWasTaken = (sel == focusLayoutRestoreDirectChild &&
focusLayoutRestoreView != null &&
focusLayoutRestoreView.requestFocus()) || sel.requestFocus();
if (!focusWasTaken) {
// Selected item didn't take focus, but we still want to
// make sure something else outside of the selected view
// has focus.
final View focused = getFocusedChild();
if (focused != null) {
focused.clearFocus();
}
positionSelector(INVALID_POSITION, sel);
} else {
sel.setSelected(false);
mSelectorRect.setEmpty();
}
} else {
positionSelector(INVALID_POSITION, sel);
}
mSelectedTop = sel.getTop();
} else {
final boolean inTouchMode = mTouchMode == TOUCH_MODE_TAP
|| mTouchMode == TOUCH_MODE_DONE_WAITING;
if (inTouchMode) {
// If the user's finger is down, select the motion position.
final View child = getChildAt(mMotionPosition - mFirstPosition);
if (child != null) {
positionSelector(mMotionPosition, child);
}
} else if (mSelectorPosition != INVALID_POSITION) {
// If we had previously positioned the selector somewhere,
// put it back there. It might not match up with the data,
// but it's transitioning out so it's not a big deal.
final View child = getChildAt(mSelectorPosition - mFirstPosition);
if (child != null) {
positionSelector(mSelectorPosition, child);
}
} else {
// Otherwise, clear selection.
mSelectedTop = 0;
mSelectorRect.setEmpty();
}
// Even if there is not selected position, we may need to
// restore focus (i.e. something focusable in touch mode).
if (hasFocus() && focusLayoutRestoreView != null) {
focusLayoutRestoreView.requestFocus();
}
}
// Attempt to restore accessibility focus, if necessary.
if (viewRootImpl != null) {
final View newAccessibilityFocusedView = viewRootImpl.getAccessibilityFocusedHost();
if (newAccessibilityFocusedView == null) {
if (accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView != null
&& accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView.isAttachedToWindow()) {
final AccessibilityNodeProvider provider =
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView.getAccessibilityNodeProvider();
if (accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreNode != null && provider != null) {
final int virtualViewId = AccessibilityNodeInfo.getVirtualDescendantId(
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreNode.getSourceNodeId());
provider.performAction(virtualViewId,
AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS, null);
} else {
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView.requestAccessibilityFocus();
}
} else if (accessibilityFocusPosition != INVALID_POSITION) {
// Bound the position within the visible children.
final int position = MathUtils.constrain(
accessibilityFocusPosition - mFirstPosition, 0,
getChildCount() - 1);
final View restoreView = getChildAt(position);
if (restoreView != null) {
restoreView.requestAccessibilityFocus();
}
}
}
}
// Tell focus view we are done mucking with it, if it is still in
// our view hierarchy.
if (focusLayoutRestoreView != null
&& focusLayoutRestoreView.getWindowToken() != null) {
focusLayoutRestoreView.dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach();
}
mLayoutMode = LAYOUT_NORMAL;
mDataChanged = false;
if (mPositionScrollAfterLayout != null) {
post(mPositionScrollAfterLayout);
mPositionScrollAfterLayout = null;
}
mNeedSync = false;
setNextSelectedPositionInt(mSelectedPosition);
updateScrollIndicators();
if (mItemCount > 0) {
checkSelectionChanged();
}
invokeOnItemScrollListener();
} finally {
if (mFocusSelector != null) {
mFocusSelector.onLayoutComplete();
}
if (!blockLayoutRequests) {
mBlockLayoutRequests = false;
}
}
}看到这个 layoutChildren()这么复杂,这里找重要的类去分析:
一开始还没有设置数据源, getChildCount 的值等于0;
之后会判断数据源是否变化, 分别使用RecyclerBin 的 addScrapView fillActiveViews 对数据进行缓存和删除处理.
之后根据mLayoutMode 的值判定布局模式, 一般会进入default 中处理,由于默认的布局顺序是从上往下,所以会进入fillFromTop 方法
private View fillFromTop(int nextTop) {
mFirstPosition = Math.min(mFirstPosition, mSelectedPosition);
mFirstPosition = Math.min(mFirstPosition, mItemCount - 1);
if (mFirstPosition < 0) {
mFirstPosition = 0;
}
return fillDown(mFirstPosition, nextTop);
}从 fillFromTop 方法可以看出主要方法是在filDown方法中,接下来再看filDown中是什么…
private View fillDown(int pos, int nextTop) {
View selectedView = null;
int end = (mBottom - mTop);
if ((mGroupFlags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) {
end -= mListPadding.bottom;
}
while (nextTop < end && pos < mItemCount) {
// is this the selected item?
boolean selected = pos == mSelectedPosition;
View child = makeAndAddView(pos, nextTop, true, mListPadding.left, selected);
nextTop = child.getBottom() + mDividerHeight;
if (selected) {
selectedView = child;
}
pos++;
}
setVisibleRangeHint(mFirstPosition, mFirstPosition + getChildCount() - 1);
return selectedView;
}fillDown 方法通过一个while循环,主要的是makeAndAddView
private View makeAndAddView(int position, int y, boolean flow, int childrenLeft,
boolean selected) {
if (!mDataChanged) {
// Try to use an existing view for this position.
final View activeView = mRecycler.getActiveView(position);
if (activeView != null) {
// Found it. We're reusing an existing child, so it just needs
// to be positioned like a scrap view.
setupChild(activeView, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, true);
return activeView;
}
}
// Make a new view for this position, or convert an unused view if
// possible.
final View child = obtainView(position, mIsScrap);
// This needs to be positioned and measured.
setupChild(child, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, mIsScrap[0]);
return child;
}ListView 中的View的创建以及复用主要是在obtainView中实现
View obtainView(int position, boolean[] outMetadata) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "obtainView");
outMetadata[0] = false;
// Check whether we have a transient state view. Attempt to re-bind the
// data and discard the view if we fail.
final View transientView = mRecycler.getTransientStateView(position);
if (transientView != null) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) transientView.getLayoutParams();
// If the view type hasn't changed, attempt to re-bind the data.
if (params.viewType == mAdapter.getItemViewType(position)) {
final View updatedView = mAdapter.getView(position, transientView, this);
// If we failed to re-bind the data, scrap the obtained view.
if (updatedView != transientView) {
setItemViewLayoutParams(updatedView, position);
mRecycler.addScrapView(updatedView, position);
}
}
outMetadata[0] = true;
// Finish the temporary detach started in addScrapView().
transientView.dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach();
return transientView;
}
final View scrapView = mRecycler.getScrapView(position);
final View child = mAdapter.getView(position, scrapView, this);
if (scrapView != null) {
if (child != scrapView) {
// Failed to re-bind the data, return scrap to the heap.
mRecycler.addScrapView(scrapView, position);
} else if (child.isTemporarilyDetached()) {
outMetadata[0] = true;
// Finish the temporary detach started in addScrapView().
child.dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach();
}
}
if (mCacheColorHint != 0) {
child.setDrawingCacheBackgroundColor(mCacheColorHint);
}
if (child.getImportantForAccessibility() == IMPORTANT_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY_AUTO) {
child.setImportantForAccessibility(IMPORTANT_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY_YES);
}
setItemViewLayoutParams(child, position);
if (AccessibilityManager.getInstance(mContext).isEnabled()) {
if (mAccessibilityDelegate == null) {
mAccessibilityDelegate = new ListItemAccessibilityDelegate();
}
if (child.getAccessibilityDelegate() == null) {
child.setAccessibilityDelegate(mAccessibilityDelegate);
}
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
return child;
}obtainView 方法中 从 RecyclerBin中getScrapView 在数据展示过程中第一次读取的时候一定是null,因为第一屏数据还没有展示完全,不会缓存数据; 之后就调用adapter中的getView那去child,getView就是我们在自定义Adapter时重写的getView方法,最后通过调用LayoutInflater的inflate()方法来去加载一个布局。拿到View之后,将回到makeAndAddView方法中,之后将child传入到setupChild中。
private void setupChild(View child, int position, int y, boolean flowDown, int childrenLeft,
boolean selected, boolean isAttachedToWindow) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "setupListItem");
final boolean isSelected = selected && shouldShowSelector();
final boolean updateChildSelected = isSelected != child.isSelected();
final int mode = mTouchMode;
final boolean isPressed = mode > TOUCH_MODE_DOWN && mode < TOUCH_MODE_SCROLL
&& mMotionPosition == position;
final boolean updateChildPressed = isPressed != child.isPressed();
final boolean needToMeasure = !isAttachedToWindow || updateChildSelected
|| child.isLayoutRequested();
// Respect layout params that are already in the view. Otherwise make
// some up...
AbsListView.LayoutParams p = (AbsListView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (p == null) {
p = (AbsListView.LayoutParams) generateDefaultLayoutParams();
}
p.viewType = mAdapter.getItemViewType(position);
p.isEnabled = mAdapter.isEnabled(position);
// Set up view state before attaching the view, since we may need to
// rely on the jumpDrawablesToCurrentState() call that occurs as part
// of view attachment.
if (updateChildSelected) {
child.setSelected(isSelected);
}
if (updateChildPressed) {
child.setPressed(isPressed);
}
if (mChoiceMode != CHOICE_MODE_NONE && mCheckStates != null) {
if (child instanceof Checkable) {
((Checkable) child).setChecked(mCheckStates.get(position));
} else if (getContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
>= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {
child.setActivated(mCheckStates.get(position));
}
}
if ((isAttachedToWindow && !p.forceAdd) || (p.recycledHeaderFooter
&& p.viewType == AdapterView.ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER)) {
attachViewToParent(child, flowDown ? -1 : 0, p);
// If the view was previously attached for a different position,
// then manually jump the drawables.
if (isAttachedToWindow
&& (((AbsListView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).scrappedFromPosition)
!= position) {
child.jumpDrawablesToCurrentState();
}
} else {
p.forceAdd = false;
if (p.viewType == AdapterView.ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER) {
p.recycledHeaderFooter = true;
}
addViewInLayout(child, flowDown ? -1 : 0, p, true);
// add view in layout will reset the RTL properties. We have to re-resolve them
child.resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
}
if (needToMeasure) {
final int childWidthSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(mWidthMeasureSpec,
mListPadding.left + mListPadding.right, p.width);
final int lpHeight = p.height;
final int childHeightSpec;
if (lpHeight > 0) {
childHeightSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(lpHeight, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightSpec = MeasureSpec.makeSafeMeasureSpec(getMeasuredHeight(),
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
}
child.measure(childWidthSpec, childHeightSpec);
} else {
cleanupLayoutState(child);
}
final int w = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int h = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final int childTop = flowDown ? y : y - h;
if (needToMeasure) {
final int childRight = childrenLeft + w;
final int childBottom = childTop + h;
child.layout(childrenLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom);
} else {
child.offsetLeftAndRight(childrenLeft - child.getLeft());
child.offsetTopAndBottom(childTop - child.getTop());
}
if (mCachingStarted && !child.isDrawingCacheEnabled()) {
child.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true);
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}setupChild 方法主要是调用addViewInLayout 将 view 添加到ListView中,这样通过fillDown的循环,就依次填满ListView 一屏的数据。 这样第一次新建View 添加到ListView 相对来说比较耗时,但之后将通过RecyclerBin回收和缓冲机制来展示LsitView。
在之后绘制过程中,从上面提到的layoutChildren 方法中的getChildCount将不是0,而是ListView中一屏可以显示的子View数量, 之前我们会在fillActiveViews方法中存储我们目前屏幕中展示的View; 之后又调用了调用了detachAllViewsFromParent()方法,这个方法会将所有ListView当中的子View全部清除掉,从而保证第二次Layout过程不会产生一份重复的数据。那有的朋友可能会问了,这样把已经加载好的View又清除掉,待会还要再重新加载一遍,这不是严重影响效率吗?不用担心,还记得我们刚刚调用了RecycleBin的fillActiveViews()方法来缓存子View吗,待会儿将会直接使用这些缓存好的View来进行加载,而并不会重新执行一遍inflate过程,因此效率方面并不会有什么明显的影响。
之后的分居布局模式判断将走进default的else中,执行fillSpecific方法, 不过其实它和fillUp()、fillDown()方法功能也是差不多的,主要的区别在于,fillSpecific()方法会优先将指定位置的子View先加载到屏幕上,然后再加载该子View往上以及往下的其它子View。那么由于这里我们传入的position就是第一个子View的位置,于是fillSpecific()方法的作用就基本上和fillDown()方法是差不多的了,这里我们就不去关注太多它的细节,而是将精力放在makeAndAddView()方法上面。再次回到makeAndAddView()方法;
之后会从RecycleBin当中获取Active View,然而这次就一定可以获取到了,因为前面我们调用了RecycleBin的fillActiveViews()方法来缓存子View。那么既然如此,就不会再进入到obtainView()方法,而是会直接进入setupChild()方法当中,setupChild()方法的最后一个参数传入的是true,这个参数表明当前的View是之前被回收过的;
setupChild()方法的最后一个参数是isAttachedToWindow,然后在第32行会对这个变量进行判断,由于isAttachedToWindow现在是true,所以会执行attachViewToParent()方法,而第一次Layout过程则是执行的else语句中的addViewInLayout()方法。这两个方法最大的区别在于,如果我们需要向ViewGroup中添加一个新的子View,应该调用addViewInLayout()方法,而如果是想要将一个之前detach的View重新attach到ViewGroup上,就应该调用attachViewToParent()方法。那么由于前面在layoutChildren()方法当中调用了detachAllViewsFromParent()方法,这样ListView中所有的子View都是处于detach状态的,所以这里attachViewToParent()方法是正确的选择。
这一部分的分析是参考 郭神的博客分析的,这是郭神原创
ListView的onDraw过程和其他View类似。
下一篇将会分析 ListView 剩余的 5,6,7部分