卡片式控件CardView&源码分析
前言
CardView作为卡片控件是在Android5.0系统引入的,继承于FragmentLayout布局在里面添加圆角阴影的效果,Google在5.0中引入了MD设计Elevation和Z轴位移,目的就是突出不同元素之间的层次关系,在显示列表或者网格时候更加的炫酷,说到这里便有跃跃欲试的感觉,Let's go!
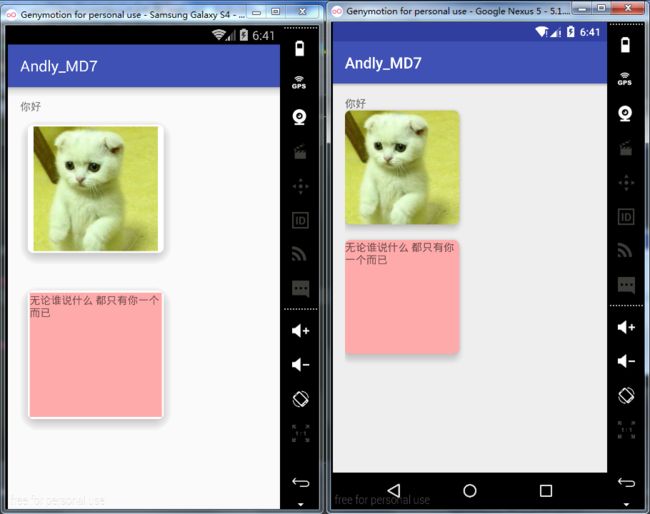
效果~
Part 1、CardView卡片的简单应用
配置
dependencies {
compile fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2', {
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'support-annotations'
})
compile 'com.android.support:cardview-v7:25.0.1'
}代码:
1、Space : 空格控件
2、app:cardCornerRadius="" : 设置卡片圆角的半径
3、app:cardElevation="" : Z轴的值
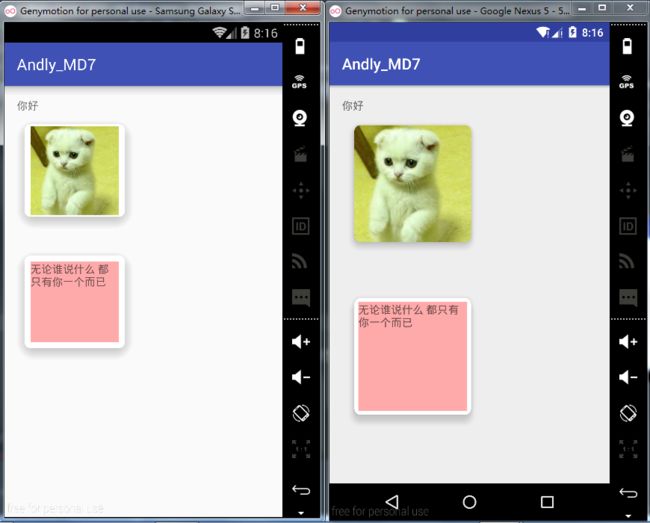
效果~
上面的坑:
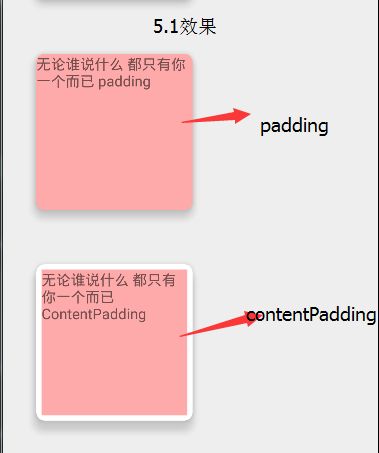
1、相同cardElevation值,阴影效果4.4要强于5.1
2、5.1中文字紧贴着圆角,不美观
解决方案:
1、在低版本中设置CardElevation之后CardView会自动留出空间供阴影显示,而Lollipop之后需要手动进行设置Margin边距来预留空间,这里我们定义两套布局(当然你也可以写两个dimen.xml)。
在低版本设置
android:layout_margin="0dp" android:layout_margin="16dp" 从上面可知需要进行设置contentPadding,但这里注意的是因为5.0以上会自动图片进行裁剪已经很美观了不需要在设置contentPadding。
接下来为CardView设置水波纹效果
android:clickable="true"
android:foreground="?attr/selectableItemBackground"最后为CardView设置动画(这里只是点击让它阴影变大)
android:stateListAnimator="@drawable/state_animator"
-
-
效果~
附上设置基本属性
app:cardBackgroundColor这是设置背景颜色
app:cardCornerRadius这是设置圆角大小
app:cardElevation这是设置z轴的阴影
app:cardMaxElevation这是设置z轴的最大高度值
app:cardUseCompatPadding是否使用CompatPadding
app:cardPreventCornerOverlap是否使用PreventCornerOverlap
app:contentPadding 设置内容的padding
app:contentPaddingLeft 设置内容的左padding
app:contentPaddingTop 设置内容的上padding
app:contentPaddingRight 设置内容的右padding
app:contentPaddingBottom 设置内容的底padding
Part 2、CardView源码分析
public class CardView extends FrameLayout {CardView继承FrameLayout,也就有了FrameLayout层次结构的特点
private static final CardViewImpl IMPL;
static {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 21) {
IMPL = new CardViewApi21();
} else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 17) {
IMPL = new CardViewJellybeanMr1();
} else {
IMPL = new CardViewGingerbread();
}
IMPL.initStatic();
}一初始化便对版本进行判断,来定义不同的实现类
final Rect mContentPadding = new Rect();
final Rect mShadowBounds = new Rect();进而进入构造方法
private void initialize(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CardView, defStyleAttr,
R.style.CardView);
ColorStateList backgroundColor;
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.CardView_cardBackgroundColor)) {
backgroundColor = a.getColorStateList(R.styleable.CardView_cardBackgroundColor);
} else {
// There isn't one set, so we'll compute one based on the theme
final TypedArray aa = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(COLOR_BACKGROUND_ATTR);
final int themeColorBackground = aa.getColor(0, 0);
aa.recycle();查看onMesure方法
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (!(IMPL instanceof CardViewApi21)) {
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
switch (widthMode) {
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
final int minWidth = (int) Math.ceil(IMPL.getMinWidth(mCardViewDelegate));
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Math.max(minWidth,
MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)), widthMode);
break;
}
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
switch (heightMode) {
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
final int minHeight = (int) Math.ceil(IMPL.getMinHeight(mCardViewDelegate));
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Math.max(minHeight,
MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec)), heightMode);
break;
}
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}这里来进入CardViewApi21类
class CardViewApi21 implements CardViewImpl {
@Override
public void initialize(CardViewDelegate cardView, Context context,
ColorStateList backgroundColor, float radius, float elevation, float maxElevation) {
final RoundRectDrawable background = new RoundRectDrawable(backgroundColor, radius);//圆角矩形
cardView.setCardBackground(background);//为CardView设置圆角
View view = cardView.getCardView();//得到CardView控件
view.setClipToOutline(true);//进行裁剪
view.setElevation(elevation);//设置阴影大小
setMaxElevation(cardView, maxElevation);//设置最大阴影大小
} @Override
public void updatePadding(CardViewDelegate cardView) {
if (!cardView.getUseCompatPadding()) {
cardView.setShadowPadding(0, 0, 0, 0);
return;
}
float elevation = getMaxElevation(cardView);
final float radius = getRadius(cardView);
int hPadding = (int) Math.ceil(RoundRectDrawableWithShadow
.calculateHorizontalPadding(elevation, radius, cardView.getPreventCornerOverlap()));
int vPadding = (int) Math.ceil(RoundRectDrawableWithShadow
.calculateVerticalPadding(elevation, radius, cardView.getPreventCornerOverlap()));
cardView.setShadowPadding(hPadding, vPadding, hPadding, vPadding);
} private final CardViewDelegate mCardViewDelegate = new CardViewDelegate() {
private Drawable mCardBackground; public void setShadowPadding(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
mShadowBounds.set(left, top, right, bottom);
CardView.super.setPadding(left + mContentPadding.left, top + mContentPadding.top,
right + mContentPadding.right, bottom + mContentPadding.bottom);
}那为什么设置padding没有效果呢?
@Override
public void setPadding(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
// NO OP
}
public void setPaddingRelative(int start, int top, int end, int bottom) {
// NO OP
}