yolov3-tiny原始weights模型转onnx模型并进行推理
时隔不知道多少天,我记起来我还有部分博客没写完(偷懒),所以不能偷懒把它完成!! 这篇博客的主要内容
- 将yolov3-tiny.weights模型转换到.onnx模型;
- 使用onnnxruntime-gpu(加速)模型推理;(不知道这里用加速形容是否合适)
- 照片推理测试;
- 视频文件推理测试;
(注:本文用的模型为本人日常测试的时候训练出来的一个小模型,能够检测车辆、行人、人脸,但是效果有限,仅限用于本文的博客内容测试使用)
接下来,我们就按照博客内容一步一步的来进行我们的学习(ctrl+c、ctrl+v)过程。
实验环境:(python3.5)
基础的cuda、cudnn、nvidian显卡驱动请自行装好
pip install pillow
pip install opencv-python
pip install onnx==1.4.1
pip install onnxruntime-gpu==1.1.0
测试硬件环境:
GTX 2060(laptop)-6G
i7-9750H
16g DDR4 2666MHz
一、yolov3-tiny.weights模型转.onnx模型
按照一贯的博客作风,直接上代码:yolov3_tiny_to_onnx.py
代码来源于论坛的大佬,我们直接学习(ctrl+c)使用
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import print_function
from collections import OrderedDict
import hashlib
import os.path
import wget
import onnx
from onnx import helper
from onnx import TensorProto
import numpy as np
import sys
class DarkNetParser(object):
"""Definition of a parser for DarkNet-based YOLOv3-608 (only tested for this topology)."""
def __init__(self, supported_layers):
"""Initializes a DarkNetParser object.
Keyword argument:
supported_layers -- a string list of supported layers in DarkNet naming convention,
parameters are only added to the class dictionary if a parsed layer is included.
"""
# A list of YOLOv3 layers containing dictionaries with all layer
# parameters:
self.layer_configs = OrderedDict()
self.supported_layers = supported_layers
self.layer_counter = 0
def parse_cfg_file(self, cfg_file_path):
"""Takes the yolov3.cfg file and parses it layer by layer,
appending each layer's parameters as a dictionary to layer_configs.
Keyword argument:
cfg_file_path -- path to the yolov3.cfg file as string
"""
with open(cfg_file_path, 'rb') as cfg_file:
remainder = cfg_file.read()
remainder = remainder.decode('utf-8')
print('remainder', remainder)
while remainder is not None:
layer_dict, layer_name, remainder = self._next_layer(remainder)
if layer_dict is not None:
self.layer_configs[layer_name] = layer_dict
return self.layer_configs
def _next_layer(self, remainder):
"""Takes in a string and segments it by looking for DarkNet delimiters.
Returns the layer parameters and the remaining string after the last delimiter.
Example for the first Conv layer in yolo.cfg ...
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=32
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
... becomes the following layer_dict return value:
{'activation': 'leaky', 'stride': 1, 'pad': 1, 'filters': 32,
'batch_normalize': 1, 'type': 'convolutional', 'size': 3}.
'001_convolutional' is returned as layer_name, and all lines that follow in yolo.cfg
are returned as the next remainder.
Keyword argument:
remainder -- a string with all raw text after the previously parsed layer
"""
remainder = remainder.split('[', 1)
if len(remainder) == 2:
remainder = remainder[1]
else:
return None, None, None
remainder = remainder.split(']', 1)
if len(remainder) == 2:
layer_type, remainder = remainder
else:
return None, None, None
if remainder.replace(' ', '')[0] == '#':
remainder = remainder.split('\n', 1)[1]
layer_param_block, remainder = remainder.split('\n\n', 1)
layer_param_lines = layer_param_block.split('\n')[1:]
layer_name = str(self.layer_counter).zfill(3) + '_' + layer_type
layer_dict = dict(type=layer_type)
if layer_type in self.supported_layers:
for param_line in layer_param_lines:
if param_line[0] == '#':
continue
param_type, param_value = self._parse_params(param_line)
layer_dict[param_type] = param_value
self.layer_counter += 1
return layer_dict, layer_name, remainder
def _parse_params(self, param_line):
"""Identifies the parameters contained in one of the cfg file and returns
them in the required format for each parameter type, e.g. as a list, an int or a float.
Keyword argument:
param_line -- one parsed line within a layer block
"""
param_line = param_line.replace(' ', '')
param_type, param_value_raw = param_line.split('=')
param_value = None
if param_type == 'layers':
layer_indexes = list()
for index in param_value_raw.split(','):
layer_indexes.append(int(index))
param_value = layer_indexes
elif isinstance(param_value_raw, str) and not param_value_raw.isalpha():
condition_param_value_positive = param_value_raw.isdigit()
condition_param_value_negative = param_value_raw[0] == '-' and \
param_value_raw[1:].isdigit()
if condition_param_value_positive or condition_param_value_negative:
param_value = int(param_value_raw)
else:
param_value = float(param_value_raw)
else:
param_value = str(param_value_raw)
return param_type, param_value
class MajorNodeSpecs(object):
"""Helper class used to store the names of ONNX output names,
corresponding to the output of a DarkNet layer and its output channels.
Some DarkNet layers are not created and there is no corresponding ONNX node,
but we still need to track them in order to set up skip connections.
"""
def __init__(self, name, channels):
""" Initialize a MajorNodeSpecs object.
Keyword arguments:
name -- name of the ONNX node
channels -- number of output channels of this node
"""
self.name = name
self.channels = channels
self.created_onnx_node = False
if name is not None and isinstance(channels, int) and channels > 0:
self.created_onnx_node = True
class ConvParams(object):
"""Helper class to store the hyper parameters of a Conv layer,
including its prefix name in the ONNX graph and the expected dimensions
of weights for convolution, bias, and batch normalization.
Additionally acts as a wrapper for generating safe names for all
weights, checking on feasible combinations.
"""
def __init__(self, node_name, batch_normalize, conv_weight_dims):
"""Constructor based on the base node name (e.g. 101_convolutional), the batch
normalization setting, and the convolutional weights shape.
Keyword arguments:
node_name -- base name of this YOLO convolutional layer
batch_normalize -- bool value if batch normalization is used
conv_weight_dims -- the dimensions of this layer's convolutional weights
"""
self.node_name = node_name
self.batch_normalize = batch_normalize
assert len(conv_weight_dims) == 4
self.conv_weight_dims = conv_weight_dims
def generate_param_name(self, param_category, suffix):
"""Generates a name based on two string inputs,
and checks if the combination is valid."""
assert suffix
assert param_category in ['bn', 'conv']
assert (suffix in ['scale', 'mean', 'var', 'weights', 'bias'])
if param_category == 'bn':
assert self.batch_normalize
assert suffix in ['scale', 'bias', 'mean', 'var']
elif param_category == 'conv':
assert suffix in ['weights', 'bias']
if suffix == 'bias':
assert not self.batch_normalize
param_name = self.node_name + '_' + param_category + '_' + suffix
return param_name
class UpsampleParams(object):
# Helper class to store the scale parameter for an Upsample node.
def __init__(self, node_name, value):
"""Constructor based on the base node name (e.g. 86_Upsample),
and the value of the scale input tensor.
Keyword arguments:
node_name -- base name of this YOLO Upsample layer
value -- the value of the scale input to the Upsample layer as a numpy array
"""
self.node_name = node_name
self.value = value
def generate_param_name(self):
"""Generates the scale parameter name for the Upsample node."""
param_name = self.node_name + '_' + "scale"
return param_name
class WeightLoader(object):
"""Helper class used for loading the serialized weights of a binary file stream
and returning the initializers and the input tensors required for populating
the ONNX graph with weights.
"""
def __init__(self, weights_file_path):
"""Initialized with a path to the YOLOv3 .weights file.
Keyword argument:
weights_file_path -- path to the weights file.
"""
self.weights_file = self._open_weights_file(weights_file_path)
def load_upsample_scales(self, upsample_params):
"""Returns the initializers with the value of the scale input
tensor given by upsample_params.
Keyword argument:
upsample_params -- a UpsampleParams object
"""
initializer = list()
inputs = list()
name = upsample_params.generate_param_name()
shape = upsample_params.value.shape
data = upsample_params.value
scale_init = helper.make_tensor(
name, TensorProto.FLOAT, shape, data)
scale_input = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
name, TensorProto.FLOAT, shape)
initializer.append(scale_init)
inputs.append(scale_input)
return initializer, inputs
def load_conv_weights(self, conv_params):
"""Returns the initializers with weights from the weights file and
the input tensors of a convolutional layer for all corresponding ONNX nodes.
Keyword argument:
conv_params -- a ConvParams object
"""
initializer = list()
inputs = list()
if conv_params.batch_normalize:
bias_init, bias_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'bias')
bn_scale_init, bn_scale_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'scale')
bn_mean_init, bn_mean_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'mean')
bn_var_init, bn_var_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'var')
initializer.extend(
[bn_scale_init, bias_init, bn_mean_init, bn_var_init])
inputs.extend([bn_scale_input, bias_input,
bn_mean_input, bn_var_input])
else:
bias_init, bias_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'conv', 'bias')
initializer.append(bias_init)
inputs.append(bias_input)
conv_init, conv_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'conv', 'weights')
initializer.append(conv_init)
inputs.append(conv_input)
return initializer, inputs
def _open_weights_file(self, weights_file_path):
"""Opens a YOLOv3 DarkNet file stream and skips the header.
Keyword argument:
weights_file_path -- path to the weights file.
"""
weights_file = open(weights_file_path, 'rb')
length_header = 5
np.ndarray(
shape=(length_header,), dtype='int32', buffer=weights_file.read(
length_header * 4))
return weights_file
def _create_param_tensors(self, conv_params, param_category, suffix):
"""Creates the initializers with weights from the weights file together with
the input tensors.
Keyword arguments:
conv_params -- a ConvParams object
param_category -- the category of parameters to be created ('bn' or 'conv')
suffix -- a string determining the sub-type of above param_category (e.g.,
'weights' or 'bias')
"""
param_name, param_data, param_data_shape = self._load_one_param_type(
conv_params, param_category, suffix)
initializer_tensor = helper.make_tensor(
param_name, TensorProto.FLOAT, param_data_shape, param_data)
input_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
param_name, TensorProto.FLOAT, param_data_shape)
return initializer_tensor, input_tensor
def _load_one_param_type(self, conv_params, param_category, suffix):
"""Deserializes the weights from a file stream in the DarkNet order.
Keyword arguments:
conv_params -- a ConvParams object
param_category -- the category of parameters to be created ('bn' or 'conv')
suffix -- a string determining the sub-type of above param_category (e.g.,
'weights' or 'bias')
"""
param_name = conv_params.generate_param_name(param_category, suffix)
channels_out, channels_in, filter_h, filter_w = conv_params.conv_weight_dims
if param_category == 'bn':
param_shape = [channels_out]
elif param_category == 'conv':
if suffix == 'weights':
param_shape = [channels_out, channels_in, filter_h, filter_w]
elif suffix == 'bias':
param_shape = [channels_out]
param_size = np.product(np.array(param_shape))
param_data = np.ndarray(
shape=param_shape,
dtype='float32',
buffer=self.weights_file.read(param_size * 4))
param_data = param_data.flatten().astype(float)
return param_name, param_data, param_shape
class GraphBuilderONNX(object):
"""Class for creating an ONNX graph from a previously generated list of layer dictionaries."""
def __init__(self, output_tensors):
"""Initialize with all DarkNet default parameters used creating YOLOv3,
and specify the output tensors as an OrderedDict for their output dimensions
with their names as keys.
Keyword argument:
output_tensors -- the output tensors as an OrderedDict containing the keys'
output dimensions
"""
self.output_tensors = output_tensors
self._nodes = list()
self.graph_def = None
self.input_tensor = None
self.epsilon_bn = 1e-5
self.momentum_bn = 0.99
self.alpha_lrelu = 0.1
self.param_dict = OrderedDict()
self.major_node_specs = list()
self.batch_size = 1
def build_onnx_graph(
self,
layer_configs,
weights_file_path,
verbose=True):
"""Iterate over all layer configs (parsed from the DarkNet representation
of YOLOv3-608), create an ONNX graph, populate it with weights from the weights
file and return the graph definition.
Keyword arguments:
layer_configs -- an OrderedDict object with all parsed layers' configurations
weights_file_path -- location of the weights file
verbose -- toggles if the graph is printed after creation (default: True)
"""
for layer_name in layer_configs.keys():
layer_dict = layer_configs[layer_name]
major_node_specs = self._make_onnx_node(layer_name, layer_dict)
if major_node_specs.name is not None:
self.major_node_specs.append(major_node_specs)
outputs = list()
for tensor_name in self.output_tensors.keys():
output_dims = [self.batch_size, ] + \
self.output_tensors[tensor_name]
output_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
tensor_name, TensorProto.FLOAT, output_dims)
outputs.append(output_tensor)
inputs = [self.input_tensor]
weight_loader = WeightLoader(weights_file_path)
initializer = list()
# If a layer has parameters, add them to the initializer and input lists.
for layer_name in self.param_dict.keys():
_, layer_type = layer_name.split('_', 1)
params = self.param_dict[layer_name]
if layer_type == 'convolutional':
initializer_layer, inputs_layer = weight_loader.load_conv_weights(
params)
initializer.extend(initializer_layer)
inputs.extend(inputs_layer)
elif layer_type == "upsample":
initializer_layer, inputs_layer = weight_loader.load_upsample_scales(
params)
initializer.extend(initializer_layer)
inputs.extend(inputs_layer)
del weight_loader
self.graph_def = helper.make_graph(
nodes=self._nodes,
name='YOLOv3-tiny-416', ##!!!!!!
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs,
initializer=initializer
)
if verbose:
print(helper.printable_graph(self.graph_def))
model_def = helper.make_model(self.graph_def,
producer_name='NVIDIA TensorRT sample')
return model_def
def _make_onnx_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Take in a layer parameter dictionary, choose the correct function for
creating an ONNX node and store the information important to graph creation
as a MajorNodeSpec object.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
layer_type = layer_dict['type']
if self.input_tensor is None:
if layer_type == 'net':
major_node_output_name, major_node_output_channels = self._make_input_tensor(
layer_name, layer_dict)
major_node_specs = MajorNodeSpecs(major_node_output_name,
major_node_output_channels)
else:
raise ValueError('The first node has to be of type "net".')
else:
node_creators = dict()
node_creators['convolutional'] = self._make_conv_node
node_creators['shortcut'] = self._make_shortcut_node
node_creators['route'] = self._make_route_node
node_creators['upsample'] = self._make_upsample_node
node_creators['maxpool'] = self._make_maxpool_node
if layer_type in node_creators.keys():
major_node_output_name, major_node_output_channels = \
node_creators[layer_type](layer_name, layer_dict)
major_node_specs = MajorNodeSpecs(major_node_output_name,
major_node_output_channels)
else:
print(
'Layer of type %s not supported, skipping ONNX node generation.' %
layer_type)
major_node_specs = MajorNodeSpecs(layer_name,
None)
return major_node_specs
def _make_input_tensor(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Create an ONNX input tensor from a 'net' layer and store the batch size.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
print(layer_dict)
batch_size = layer_dict['batch']
channels = layer_dict['channels']
height = layer_dict['height']
width = layer_dict['width']
self.batch_size = batch_size
input_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
str(layer_name), TensorProto.FLOAT, [
batch_size, channels, height, width])
self.input_tensor = input_tensor
return layer_name, channels
def _get_previous_node_specs(self, target_index=-1):
"""Get a previously generated ONNX node (skip those that were not generated).
Target index can be passed for jumping to a specific index.
Keyword arguments:
target_index -- optional for jumping to a specific index (default: -1 for jumping
to previous element)
"""
previous_node = None
for node in self.major_node_specs[target_index::-1]:
if node.created_onnx_node:
previous_node = node
break
assert previous_node is not None
return previous_node
def _make_conv_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Create an ONNX Conv node with optional batch normalization and
activation nodes.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
previous_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
inputs = [previous_node_specs.name]
previous_channels = previous_node_specs.channels
kernel_size = layer_dict['size']
stride = layer_dict['stride']
filters = layer_dict['filters']
batch_normalize = False
if 'batch_normalize' in layer_dict.keys(
) and layer_dict['batch_normalize'] == 1:
batch_normalize = True
kernel_shape = [kernel_size, kernel_size]
weights_shape = [filters, previous_channels] + kernel_shape
conv_params = ConvParams(layer_name, batch_normalize, weights_shape)
strides = [stride, stride]
dilations = [1, 1]
weights_name = conv_params.generate_param_name('conv', 'weights')
inputs.append(weights_name)
if not batch_normalize:
bias_name = conv_params.generate_param_name('conv', 'bias')
inputs.append(bias_name)
conv_node = helper.make_node(
'Conv',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
kernel_shape=kernel_shape,
strides=strides,
auto_pad='SAME_LOWER',
dilations=dilations,
name=layer_name
)
self._nodes.append(conv_node)
inputs = [layer_name]
layer_name_output = layer_name
if batch_normalize:
layer_name_bn = layer_name + '_bn'
bn_param_suffixes = ['scale', 'bias', 'mean', 'var']
for suffix in bn_param_suffixes:
bn_param_name = conv_params.generate_param_name('bn', suffix)
inputs.append(bn_param_name)
batchnorm_node = helper.make_node(
'BatchNormalization',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name_bn],
epsilon=self.epsilon_bn,
momentum=self.momentum_bn,
name=layer_name_bn
)
self._nodes.append(batchnorm_node)
inputs = [layer_name_bn]
layer_name_output = layer_name_bn
if layer_dict['activation'] == 'leaky':
layer_name_lrelu = layer_name + '_lrelu'
lrelu_node = helper.make_node(
'LeakyRelu',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name_lrelu],
name=layer_name_lrelu,
alpha=self.alpha_lrelu
)
self._nodes.append(lrelu_node)
inputs = [layer_name_lrelu]
layer_name_output = layer_name_lrelu
elif layer_dict['activation'] == 'linear':
pass
else:
print('Activation not supported.')
self.param_dict[layer_name] = conv_params
return layer_name_output, filters
def _make_shortcut_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Create an ONNX Add node with the shortcut properties from
the DarkNet-based graph.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
shortcut_index = layer_dict['from']
activation = layer_dict['activation']
assert activation == 'linear'
first_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
second_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs(
target_index=shortcut_index)
assert first_node_specs.channels == second_node_specs.channels
channels = first_node_specs.channels
inputs = [first_node_specs.name, second_node_specs.name]
shortcut_node = helper.make_node(
'Add',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(shortcut_node)
return layer_name, channels
def _make_route_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""If the 'layers' parameter from the DarkNet configuration is only one index, continue
node creation at the indicated (negative) index. Otherwise, create an ONNX Concat node
with the route properties from the DarkNet-based graph.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
route_node_indexes = layer_dict['layers']
if len(route_node_indexes) == 1:
split_index = route_node_indexes[0]
assert split_index < 0
# Increment by one because we skipped the YOLO layer:
split_index += 1
self.major_node_specs = self.major_node_specs[:split_index]
layer_name = None
channels = None
else:
inputs = list()
channels = 0
for index in route_node_indexes:
if index > 0:
# Increment by one because we count the input as a node (DarkNet
# does not)
index += 1
route_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs(
target_index=index)
inputs.append(route_node_specs.name)
channels += route_node_specs.channels
assert inputs
assert channels > 0
route_node = helper.make_node(
'Concat',
axis=1,
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(route_node)
return layer_name, channels
def _make_upsample_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Create an ONNX Upsample node with the properties from
the DarkNet-based graph.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
upsample_factor = float(layer_dict['stride'])
# Create the scales array with node parameters
scales = np.array([1.0, 1.0, upsample_factor, upsample_factor]).astype(np.float32)
previous_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
inputs = [previous_node_specs.name]
channels = previous_node_specs.channels
assert channels > 0
upsample_params = UpsampleParams(layer_name, scales)
scales_name = upsample_params.generate_param_name()
# For ONNX opset >= 9, the Upsample node takes the scales array as an input.
inputs.append(scales_name)
upsample_node = helper.make_node(
'Upsample',
mode='nearest',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(upsample_node)
self.param_dict[layer_name] = upsample_params
return layer_name, channels
def _make_maxpool_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
stride = layer_dict['stride']
kernel_size = layer_dict['size']
previous_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
inputs = [previous_node_specs.name]
channels = previous_node_specs.channels
kernel_shape = [kernel_size, kernel_size]
strides = [stride, stride]
assert channels > 0
maxpool_node = helper.make_node(
'MaxPool',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
kernel_shape=kernel_shape,
strides=strides,
auto_pad='SAME_UPPER',
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(maxpool_node)
return layer_name, channels
def generate_md5_checksum(local_path):
"""Returns the MD5 checksum of a local file.
Keyword argument:
local_path -- path of the file whose checksum shall be generated
"""
with open(local_path) as local_file:
data = local_file.read()
return hashlib.md5(data).hexdigest()
def download_file(local_path, link, checksum_reference=None):
"""Checks if a local file is present and downloads it from the specified path otherwise.
If checksum_reference is specified, the file's md5 checksum is compared against the
expected value.
Keyword arguments:
local_path -- path of the file whose checksum shall be generated
link -- link where the file shall be downloaded from if it is not found locally
checksum_reference -- expected MD5 checksum of the file
"""
if not os.path.exists(local_path):
print('Downloading from %s, this may take a while...' % link)
wget.download(link, local_path)
print()
if checksum_reference is not None:
checksum = generate_md5_checksum(local_path)
if checksum != checksum_reference:
raise ValueError(
'The MD5 checksum of local file %s differs from %s, please manually remove \
the file and try again.' %
(local_path, checksum_reference))
return local_path
def main():
"""Run the DarkNet-to-ONNX conversion for YOLOv3-tiny-416."""
img_size = 416 # !!!!!!
# Have to use python 2 due to hashlib compatibility
'''
if sys.version_info[0] > 2:
raise Exception("This script is only compatible with python2, please re-run this script with python2. The rest of this sample can be run with either version of python.")
'''
# Download the config for YOLOv3 if not present yet, and analyze the checksum:
cfg_file_path = './config/yolov3-tiny.cfg' # !!!!!
# These are the only layers DarkNetParser will extract parameters from. The three layers of
# type 'yolo' are not parsed in detail because they are included in the post-processing later:
supported_layers = ['net', 'convolutional', 'shortcut',
'route', 'upsample', 'maxpool']
# Create a DarkNetParser object, and the use it to generate an OrderedDict with all
# layer's configs from the cfg file:
parser = DarkNetParser(supported_layers)
layer_configs = parser.parse_cfg_file(cfg_file_path)
# We do not need the parser anymore after we got layer_configs:
del parser
# In above layer_config, there are three outputs that we need to know the output
# shape of (in CHW format):
output_tensor_dims = OrderedDict()
kernel_size_1 = int(img_size / 32)
kernel_size_2 = int(img_size / 16)
output_tensor_dims['016_convolutional'] = [24, kernel_size_1, kernel_size_1]
output_tensor_dims['023_convolutional'] = [24, kernel_size_2, kernel_size_2]
# Create a GraphBuilderONNX object with the known output tensor dimensions:
builder = GraphBuilderONNX(output_tensor_dims)
# We want to populate our network with weights later, that's why we download those from
# the official mirror (and verify the checksum):
weights_file_path = './yolov3-tiny-final.weights' # !!!!!!
# Now generate an ONNX graph with weights from the previously parsed layer configurations
# and the weights file:
yolov3_model_def = builder.build_onnx_graph(
layer_configs=layer_configs,
weights_file_path=weights_file_path,
verbose=True)
# Once we have the model definition, we do not need the builder anymore:
del builder
# Perform a sanity check on the ONNX model definition:
onnx.checker.check_model(yolov3_model_def)
# Serialize the generated ONNX graph to this file:
output_file_path = 'yolov3-tiny.onnx' # !!!!!!
onnx.save(yolov3_model_def, output_file_path)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
代码中有几个部分需要注意修改:
cfg_file_path = './config/yolov3-tiny.cfg' # 原始cfg文件位置
output_tensor_dims = OrderedDict()
kernel_size_1 = img_size/32
kernel_size_2 = img_size/16
output_tensor_dims['016_convolutional'] = [24, kernel_size_1, kernel_size_1]
output_tensor_dims['023_convolutional'] = [24, kernel_size_2, kernel_size_2]
这一部分中输出的参数需要我们对应调整: (24)nums = 3×(classes + 4 + 1)
weights_file_path = './yolov3-tiny-final.weights' # 原始模型位置
调整好后我们即可运行装换的脚本了:(python3)
python yolov3_tiny_to_onnx.py
装换成功后你可以看到这个输出:
二.进行模型推理测试
在推理之前,我们需要使用一些功能函数代码;这里称为darknet_api.py
# coding: utf-8
"""
YOlo相关的预处理api;
"""
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
# 加载label names;
def get_labels(names_file):
names = list()
with open(names_file, 'r') as f:
lines = f.read()
for name in lines.splitlines():
names.append(name)
f.close()
return names
# 照片预处理
def process_img(img_path, input_shape):
ori_img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = cv2.resize(ori_img, input_shape)
image = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose((2, 0, 1))
image = image[np.newaxis, :, :, :] / 255
image = np.array(image, dtype=np.float32)
return ori_img, ori_img.shape, image
# 视频预处理
def frame_process(frame, input_shape):
image = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image = cv2.resize(image, input_shape)
# image = cv2.resize(image, (640, 480))
image_mean = np.array([127, 127, 127])
image = (image - image_mean) / 128
image = np.transpose(image, [2, 0, 1])
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
image = image.astype(np.float32)
return image
# sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(x):
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-1 * x))
return s
# 获取预测正确的类别,以及概率和索引;
def get_result(class_scores):
class_score = 0
class_index = 0
for i in range(len(class_scores)):
if class_scores[i] > class_score:
class_index += 1
class_score = class_scores[i]
return class_score, class_index
# 通过置信度筛选得到bboxs
def get_bbox(feat, anchors, image_shape, confidence_threshold=0.25):
box = list()
for i in range(len(anchors)):
for cx in range(feat.shape[0]):
for cy in range(feat.shape[1]):
tx = feat[cx][cy][0 + 8 * i]
ty = feat[cx][cy][1 + 8 * i]
tw = feat[cx][cy][2 + 8 * i]
th = feat[cx][cy][3 + 8 * i]
cf = feat[cx][cy][4 + 8 * i]
cp = feat[cx][cy][5 + 8 * i:8 + 8 * i]
bx = (sigmoid(tx) + cx) / feat.shape[0]
by = (sigmoid(ty) + cy) / feat.shape[1]
bw = anchors[i][0] * np.exp(tw) / image_shape[0]
bh = anchors[i][1] * np.exp(th) / image_shape[1]
b_confidence = sigmoid(cf)
b_class_prob = sigmoid(cp)
b_scores = b_confidence * b_class_prob
b_class_score, b_class_index = get_result(b_scores)
if b_class_score >= confidence_threshold:
box.append([bx, by, bw, bh, b_class_score, b_class_index])
return box
# 采用nms算法筛选获取到的bbox
def nms(boxes, nms_threshold=0.6):
l = len(boxes)
if l == 0:
return []
else:
b_x = boxes[:, 0]
b_y = boxes[:, 1]
b_w = boxes[:, 2]
b_h = boxes[:, 3]
scores = boxes[:, 4]
areas = (b_w + 1) * (b_h + 1)
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = list()
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(b_x[i], b_x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(b_y[i], b_y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(b_x[i] + b_w[i], b_x[order[1:]] + b_w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(b_y[i] + b_h[i], b_y[order[1:]] + b_h[order[1:]])
# 相交面积,不重叠时面积为0
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
# 相并面积,面积1+面积2-相交面积
union = areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter
# 计算IoU:交 /(面积1+面积2-交)
IoU = inter / union
# 保留IoU小于阈值的box
inds = np.where(IoU <= nms_threshold)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
final_boxes = [boxes[i] for i in keep]
return final_boxes
# 绘制预测框
def draw_box(boxes, img, img_shape):
label = ["background", "car", "pedestrian", "face"]
for box in boxes:
x1 = int((box[0] - box[2] / 2) * img_shape[1])
y1 = int((box[1] - box[3] / 2) * img_shape[0])
x2 = int((box[0] + box[2] / 2) * img_shape[1])
y2 = int((box[1] + box[3] / 2) * img_shape[0])
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(img, label[int(box[5])] + ":" + str(round(box[4], 3)), (x1 + 5, y1 + 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1)
print(label[int(box[5])] + ":" + "概率值:%.3f" % box[4])
# 获取预测框
def get_boxes(prediction, anchors, img_shape, confidence_threshold=0.25, nms_threshold=0.6):
boxes = []
for i in range(len(prediction)):
feature_map = prediction[i][0].transpose((2, 1, 0))
box = get_bbox(feature_map, anchors[i], img_shape, confidence_threshold)
boxes.extend(box)
Boxes = nms(np.array(boxes), nms_threshold)
return Boxes
其中,筛选预选框这部分函数需要根据自己模型输出类别数而调整:
tx = feat[cx][cy][0 + 8 * i]
ty = feat[cx][cy][1 + 8 * i]
tw = feat[cx][cy][2 + 8 * i]
th = feat[cx][cy][3 + 8 * i]
cf = feat[cx][cy][4 + 8 * i]
cp = feat[cx][cy][5 + 8 * i:8 + 8 * i]
里面的参数8 = classes + 4 + 1 (因为在本篇博客内容中检测模型检测的类别维度数为3)
接下来我们写代码来测试转换好的模型进行本地MP4文件的推理,推理代码:onnx_inference.py
# -*-coding: utf-8-*-
import cv2
import time
import logging
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime
from lib.darknet_api import get_boxes
# load onnx model
def load_model(onnx_model):
sess = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(onnx_model)
in_name = [input.name for input in sess.get_inputs()][0]
out_name = [output.name for output in sess.get_outputs()]
logging.info("输入的name:{}, 输出的name:{}".format(in_name, out_name))
return sess, in_name, out_name
# process frame
def frame_process(frame, input_shape=(416, 416)):
img = cv2.resize(frame, input_shape)
image = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose((2, 0, 1))
image = image[np.newaxis, :, :, :] / 255
image = np.array(image, dtype=np.float32)
return image
# 视屏预处理
def stream_inference():
# 基本的参数设定
label = ["background", "car", "pedestrian", "face"]
anchors_yolo_tiny = [[(81, 82), (135, 169), (344, 319)], [(10, 14), (23, 27), (37, 58)]]
# anchors_yolo = [[(116, 90), (156, 198), (373, 326)], [(30, 61), (62, 45), (59, 119)],
# [(10, 13), (16, 30), (33, 23)]]
session, in_name, out_name = load_model(onnx_model='./yolov3-tiny.onnx')
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('test.mp4')
while True:
_, frame = cap.read()
input_shape = frame.shape
s = time.time()
test_data = frame_process(frame, input_shape=(416, 416))
logging.info("process per pic spend time is:{}ms".format((time.time() - s) * 1000))
s1 = time.time()
prediction = session.run(out_name, {in_name: test_data})
s2 = time.time()
print("prediction cost time: %.3fms" % (s2 - s1))
fps = 1 / (s2 - s1)
boxes = get_boxes(prediction=prediction,
anchors=anchors_yolo_tiny,
img_shape=(416, 416))
print("get box cost time:{}ms".format((time.time() - s2) * 1000))
for box in boxes:
x1 = int((box[0] - box[2] / 2) * input_shape[1])
y1 = int((box[1] - box[3] / 2) * input_shape[0])
x2 = int((box[0] + box[2] / 2) * input_shape[1])
y2 = int((box[1] + box[3] / 2) * input_shape[0])
logging.info(label[int(box[5])] + ":" + str(round(box[4], 3)))
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 1)
cv2.putText(frame, label[int(box[5])] + ":" + str(round(box[4], 3)),
(x1 + 5, y1 + 10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.5,
(0, 0, 255),
1)
cv2.putText(frame, str('FPS:%.3f' % fps), (5, 100),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
1, (0, 255, 255), 2)
frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.7, fy=0.7)
cv2.imshow("Results", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
stream_inference()
【注意:记得修改你转换好的模型文件所在位置】
session, in_name, out_name = load_model(onnx_model='./yolov3-tiny.onnx')
好了,运行到这里你应该能够看到你想要的结果了,我这里经过同学的允许,用他的自拍视频测试了一下效果,(好像不能本地文件传视频, 好尴尬,那就截图吧):
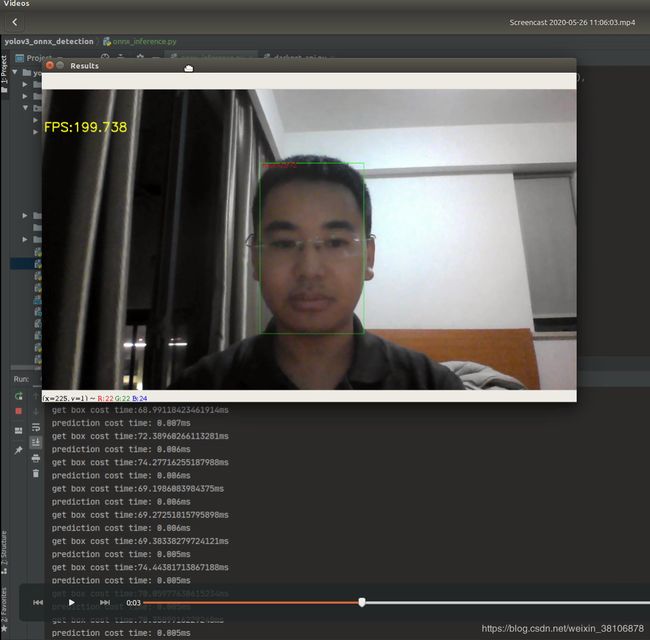 可以看到检测还是很妥的。上面有个fps你看到没,199 哈哈哈哈哈。。。我差点就信了。。。
可以看到检测还是很妥的。上面有个fps你看到没,199 哈哈哈哈哈。。。我差点就信了。。。
解释一下这个fps是怎么来的,在计算fps时只考虑了模型前向推理的时间,没有把各种骚操作(画框,resize等)耗时考虑进去, 所以这个fps飞起来了。。测试的时候平均fps在170上下。。。
对了,照片的推理代码可以自己写,应该很简单了吧。。。
- 总结
老规矩,总结一下:
- 最近在弄tx2,所以就多多少少接触到了部分相关的模型量化的知识技能,学到的东西就拉出来记录一下,顺便大家共同学习,共同进步;
- ps:话说nvidia板子说的推理速度贼快,是不是都是指的是前向推理时间,不包括其他操作。
- 不足之处还请各位多多指点!!!