CentOS环境下安装MySQL8.0以上版本、远程授权和开机启动
目录
1、卸载已经安装的数据库
2、安装MySQL数据库
2.1、下载mysql软件安装包,下载地址:https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/
2.2、上传软件包到Linux系统中,并解压,执行命令:
2.3、添加软连接,执行命令:ln -s 源文件 目标文件(锦上添花的操作,可以不执行)
2.4、在当前系统中添加mysql用户,执行命令:
2.5、初始化数据库
2.6、验证安装是否成功
2.6.4 修改mysql数据库密码,执行命令:
3、授权远程连接(重点)
4、开放防火墙端口:
4.1、查看启停防火墙状态
4.2、开放指定端口:
4.3、重启防火墙:
4.4、查看端口号
5、设置mysql开机启动
5.1、将服务文件复制一份到/etc/init.d下,并重命名为mysql或者mysqld,执行命令:
5.2、对文件赋予执行权限,执行命令:
5.3、增加mysql服务
5.4、查询mysqld服务情况
5.5、重启服务器验证:reboot
MySQL8.0以上版本安装对比低版本发生了一些细微的变化,具体细节在安装步骤中会特别说明,从安装到远程连接总共需要操作以下几个步骤:
1、卸载已经安装的数据库
1.1、检查linux是否安装了mariadb数据库,新安装的centos系统会自带mariadb数据库,mariadb数据库是MySQL的分支,执行命令:
yum list installed | grep mariadb1.2、若linux中安装了mariadb数据库,先卸载掉,mariadb数据库可能与安装mysql发生冲突,执行命令:
yum -y remove mariadb*.*(其中mariadb*.*是第1.1步搜索出来的mariadb软件包,不同机器可能不一样)
2、安装MySQL数据库
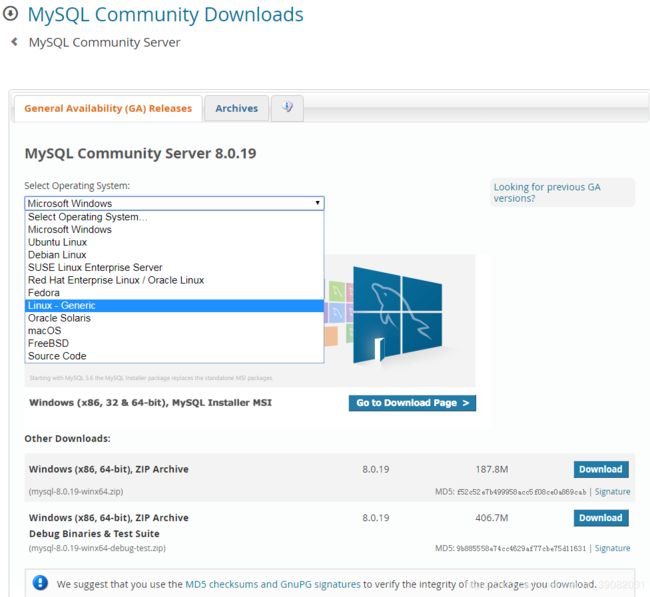
2.1、下载mysql软件安装包,下载地址:https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/
2.1.1 选择软件包,英文不好的建议浏览器安装自动翻译插件,谷歌自带的翻译插件就很好用。本人习惯用.tar格式或者.tar.xz格式的软件安装包安装软件,所以在此选择了Linux-Genetic操作系统。
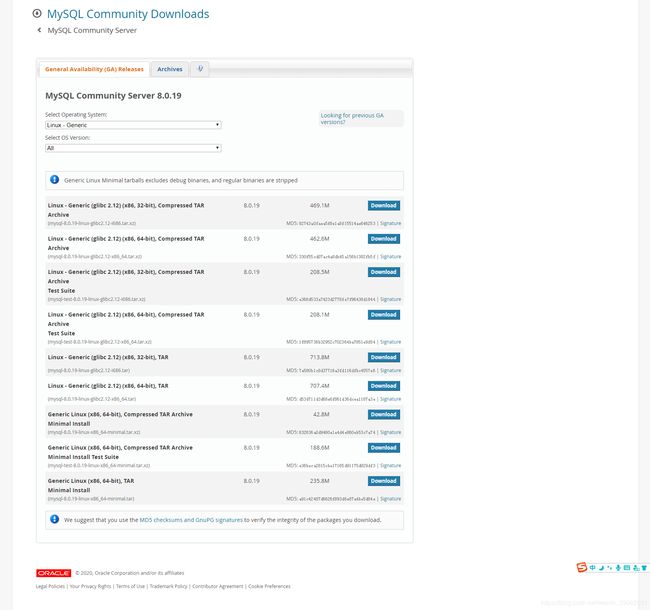
2.1.2 选择合适的操作系统版本的软件压缩包
我的电脑操作系统是64位的,所以选择的是mysql-8.0.19-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.xz。
2.2、上传软件包到Linux系统中,并解压,执行命令:
xz -d mysql-8.0.19-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.xz得到的是mysql-8.0.19-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar软件包,这个命令是将.tar.xz格式的文件先转为.tar格式的文件。再执行命令:
tar -xvf mysql-8.0.19-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar -C /usr/local其中,-C /usr/local 是指定解压到哪个目录下去,如果不加这个参数,则解压到当前所在的目录,此时压缩格式的软件安装包完全解压。切换目录到解压后的目录再次执行命令:
mv mysql-8.0.19-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 mysql-8.0.19将文件夹重命名,建议保留版本号。
2.3、添加软连接,执行命令:ln -s 源文件 目标文件(锦上添花的操作,可以不执行)
ln -s /usr/local/mysql-8.0.19/ /mysql该命令是在根目录下创建mysql指向/usr/local/mysql8.0.19/的软连接,linux中的软连接就类似于Windows中的快捷方式。
2.4、在当前系统中添加mysql用户,执行命令:
useradd mysql 或者 adduser mysql具体是使用useradd命令还是使用adduser命令,结合操作系统根据个人喜好来选择,useradd命令和adduser命令的区别参考:https://blog.csdn.net/beitiandijun/article/details/41678251
2.5、初始化数据库
2.5.1 在mysql目录下创建data文件夹,执行命令:mkdir data
2.5.2 切换到mysql/bin目录下执行命令:
./mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --datadir=/usr/local/mysql-8.0.19/data --basedir=/usr/local/mysql-8.0.19在执行上面命令后,会生成一个临时的mysql数据库root用户的密码,类似于以下这行内容:
[Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: sol%rzWwo5H(其中,root@localhost: 后面跟的是mysql数据库登录的临时密码,各人安装生成的临时密码不一样,请先拷贝出来记住,后续第一次登录mysql需要使用。
2.5.3 切换到mysql/bin目录下执行命令:
./mysql_ssl_rsa_setup --datadir=/usr/local/mysql-8.0.19/data2.6、验证安装是否成功
2.6.1 启动数据库服务:切换到mysql/bin目录下执行命令./mysqld_safe &后台启动mysql服务。
2.6.2 登录数据库:切换到mysql/bin目录下执行命令./mysql -uroot -p,输入2.5.2步生成的临时密码,进入数据库。
2.6.3 、执行sql语句 show databases; 第一次使用将会提示修改mysql的root用户密码:
mysql> show databases;
ERROR 1820 (HY000): You must reset your password using ALTER USER statement before executing this statement.2.6.4 修改mysql数据库密码,执行命令:
alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by '123456';密码修改之后退出数据库,执行命令exit,然后重新进入数据库,这次需要输入的密码是刚设置的123456。
3、授权远程连接(重点)
此操作与低版本的有区别,低版本的只要分别执行以下命令一般就可以解决远程连接权限问题:
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to root@'%' identified by '123456';
mysql> flush privileges; 8.0以上的版本,需要执行以下命令:
第一步:开放root用户的权限
mysql> update user set Host="%" where User="root";
第二步:刷新权限
mysql> flush privileges;
第三步:还原密码验证插件,将MySQL8的密码认证插件由caching_sha2_password更换成mysql_native_password
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '123456';
第四步:刷新权限
mysql> flush privileges;4、开放防火墙端口:
4.1、查看启停防火墙状态
systemctl [参数] firewalld
其中,参数可以是: status---查看防火墙状态
start----启动防火墙
stop-----关闭防火墙4.2、开放指定端口:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp --permanent
命令含义:
--zone #作用域
--add-port=3306/tcp #添加端口,格式为:端口/通讯协议
--permanent #永久生效,没有此参数重启后失效4.3、重启防火墙:
firewall-cmd --reload
4.4、查看端口号
netstat -ntlp //查看当前所有tcp端口·
netstat -ntulp |grep 3306 //查看所有3306端口使用情况·5、设置mysql开机启动
5.1、将服务文件复制一份到/etc/init.d下,并重命名为mysql或者mysqld,执行命令:
cp /mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysql5.2、对文件赋予执行权限,执行命令:
chmod +x /etc/init.d/mysql 或 chmod 777 /etc/init.d/mysql5.3、增加mysql服务
执行命令:chkconfig --add mysql
5.4、查询mysqld服务情况
执行命令:chkconfig --list mysql,mysql服务运行状态如下:
mysql 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
默认的运行级别为2,3,4,5为on,如果3,4,5 为off:则执行命令:chkconfig --level 345 mysql on
5.5、重启服务器验证:reboot
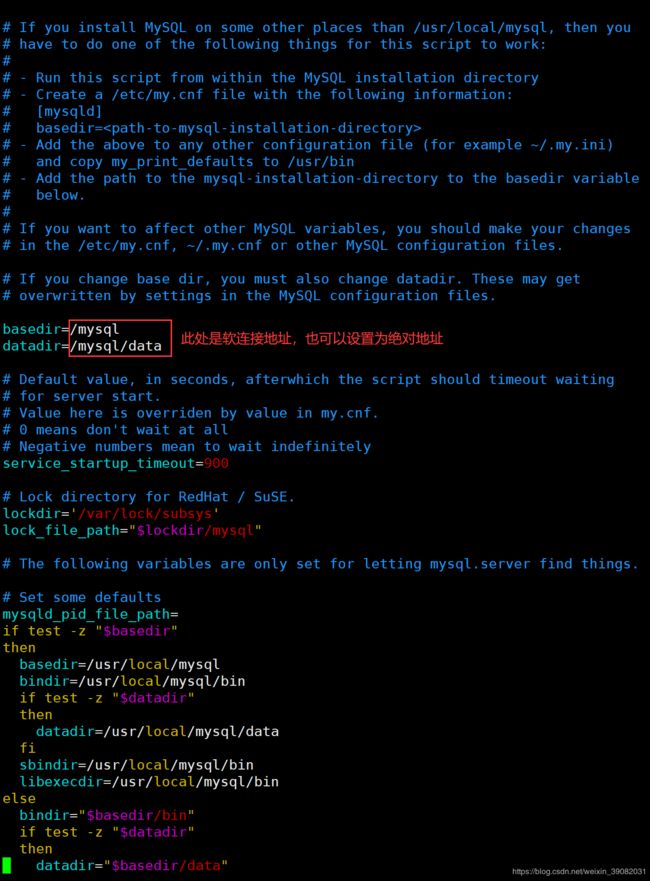
重启之后,发现服务启动了,但是mysql没有启动,经过排查,找到原因是启动文件没有修改配置,因为本人的basedir和datadir都不是mysql默认的/usr/local/mysql和/usr/local/mysql/data。根据配置文件里面的提示有四种方法可以解决,提示内容如下:
# If you install MySQL on some other places than /usr/local/mysql, then you
# have to do one of the following things for this script to work:
#
# - Run this script from within the MySQL installation directory
# - Create a /etc/my.cnf file with the following information:
# [mysqld]
# basedir=
# - Add the above to any other configuration file (for example ~/.my.ini)
# and copy my_print_defaults to /usr/bin
# - Add the path to the mysql-installation-directory to the basedir variable
# below.
#
# If you want to affect other MySQL variables, you should make your changes
# in the /etc/my.cnf, ~/.my.cnf or other MySQL configuration files.
# If you change base dir, you must also change datadir. These may get
# overwritten by settings in the MySQL configuration files. 方法1:- Run this script from within the MySQL installation directory。在mysql安装目录内运行。
方法2:- Create a /etc/my.cnf file with the following information:创建my.cnf文件
[mysqld]
basedir=
方法3:- Add the above to any other configuration file (for example ~/.my.ini) and copy my_print_defaults to /usr/bin
将方法2中的内容复制到别的文件中(例如~/.my.ini),并且把mysql/bin目录下的my_print_defaults文件复制到 /usr/bin目录下。
方法4:- Add the path to the mysql-installation-directory to the basedir variable below.修改下面的dasedir变量,将mysql的路径赋值给下面的basedir。(此方法即下述方法)。
编辑/etc/init.d/目录下的mysql文件,将其中的basedir=和datadir=改为basedir=/mysql或者/usr/local/mysql-8.0.19和datadir=mysql/data或者/usr/local/mysql-8.0.19/data,因为我在根目录下加了mysql的软连接,所以可以直接改为/mysql或者/mysql/data,如图所示:
修改前:
修改后: