Spring
- 1.Spring是什么?有什么好处?
- 2.IOC是什么?有什么好处?简单过程?
- 3.DI是什么?
- 4.IOC和DI的关系?
- 5.bean标签的属性有哪些?
- 6.IOC创建对象有哪几种方式?
- 7.Spring是如何实现IOC的?也就是如何创建对象的?
- 8.Spring Bean的生命周期?
- 9.依赖注入DI的方式有几种?
- 10.注解实现IOC和DI的准备工作有哪些?
- 11.有哪些注解?分别表示什么含义?
- 12.谈谈你对Spring AOP的理解?
- 13.XML方式实现AOP的通知有几种?
- 14.注解实现AOP的过程?
- 15.更改多个切面类的执行顺序的方法有几种?
- 16.Spring有哪些主要模块?
- 17.Spring中的bean是线程安全的吗?
- 18.Spring支持几种bean的作用域?
- 19.Spring JDBC的实现过程?
- 20.事务的概念是什么?
- 21.事务的特性有几个?
- 22.数据库操作时可能存在的问题有哪些?
- 23.什么是事务的隔离级别?事务的隔离级别有几个?
- 24.Spring中事务的传播行为有几种?
- 25.Spring 声明式事务的实现?
- 26.Spring 事务失效的场景有哪些?
- 27.@Transactional(readOnly = true)的理解?
- 28.Spring支持的事务管理类型有哪些?
- 29.@Transactional(timeout= 2)的理解?
- 30.Spring读取properties文件的方式
1.Spring是什么?有什么好处?
- 概念: SPring是一个支持控制反转(IOC)和面向切面编程(AOP)的容器框架。
- 好处: 两降低>>>两支持>>>两方便
- ①降低了耦合性,提高了开发速度。
- ②降低了JAVAEE API的使用难度。
- ③支持AOP和IOC。
- ④支持声明式事务。
- ⑤方便程序测试。
- ⑥方便集成其他框架。、
2.IOC是什么?有什么好处?简单过程?
- IOC: 是Inverse of Control(控制反转)的简写。
- 好处: 通过IOC,直接把对象创建的权力反转给Spring容器,降低了对象之间的耦合性。
- 简单过程: 程序读取Spring的XML配置文>>>获取需要创建对象的bean>>>通过反射机制创建对象的实例。
3.DI是什么?
- DI: Dependency Injection(依赖注入)的简写。
- 创建对象实例时,同时为对象注入它所依赖的属性,相当于把每个bean和bean之间的关系交给Spring容器来管理。
4.IOC和DI的关系?
- 控制反转(IOC)和依赖注入(DI)是从不同角度描述同一件事情,利用依赖关系注入的方式,实现对像之间的解耦。
- 耦合性(耦合度):是对模块间关联程度的度量。模块之间联系越紧密,其耦合性就越高,模块之间越独立则越低。
5.bean标签的属性有哪些?
- ① id (唯一标识)
- ② name(获取bean的键)
- ③ class(指定bean对应类的全路径)
- ④ scope(单例或者多例设计模式)
- ⑤ lazy-init(延时加载,默认值:false):设置false时,只有调用getBean方法才会创建对象
- ⑥ init-method(指定:监听对象创建的方法)
- ⑦ destroy-method(指定:监听对象销毁的方法)
6.IOC创建对象有哪几种方式?
- ①无参构造
- ②有参构造
- ③静态工厂模式(1个bean标签)
- ④非静态工厂模式(2个bean标签)
//1.无参构造
<bean id="user" class="com.wpq.pojo.User">bean>
//在bean标签内部使用property标签,相当于调用set方法. name:要赋值的属性的属性名 value:值
<bean id="user" class="com.wpq.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="zs">property>
<property name="password" value="123">property>
bean>
//2.有参构造
<bean id="user" class="com.wpq.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" name="name" value="张三">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" type="java.lang.String" name="password" value="123">constructor-arg>
bean>
//3.静态工厂模式--createPerson()为静态方法
<bean name="personFactory" class="com.wpq.factory.PersonFactory" factory-method="createPerson"/>
//4.工厂模式
<bean name="personFactory" class="com.wpq.factory.PersonFactory"/>
<bean name="person" factory-bean="personFactory" factory-method="instancePerson"/>
7.Spring是如何实现IOC的?也就是如何创建对象的?
<!--0.对象创建原理:xml解析+反射-->
<!--1.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext根据xml的路径和名称加载xml;-->
<!--2.对该xml文件进行解析-->
<!--3.根据class属性,获取class属性的值:com.wpq.domain.Person-->
<!--4.反射:获取字节码的方式,Class clazz=Class.forName("全路径");p.getClass();Person.class-->
<!--5.根据字节码创建对象:Person p=clazz.newInstance()-->
<!--6.给对象里的属性赋值:Fields[] fields=clazz.getDeclaredFields();-->
<!--7.遍历属性数组:for(Field field : fields){ field.setAccessable(true);field.set(30)}-->
<bean id="person" class="com.wpq.domain.Person">
<property name="name" value="zs"/>
<property name="age" value="30"/>
</bean>
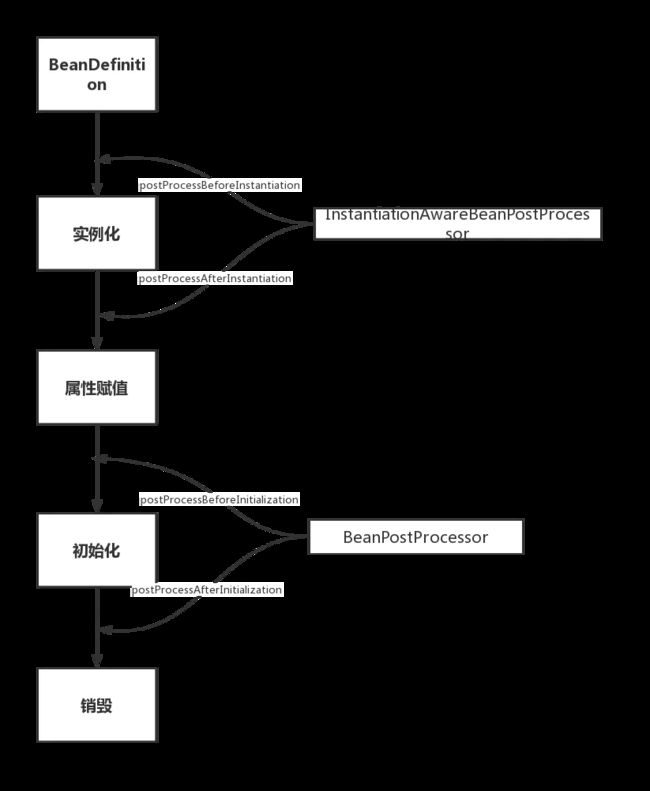
8.Spring Bean的生命周期?
- ①实例化 Instantiation
- ②属性赋值 Populate
- ③初始化 Initialization
- ④销毁 Destruction
9.依赖注入DI的方式有几种?
<bean id="user" class="com.wpq.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="zs">property>
<property name="password" value="123">property>
bean>
<bean id="user" class="com.wpq.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" name="name" value="张三">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" type="java.lang.String" name="password" value="123">constructor-arg>
bean>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean name="car" class="com.wpq.domain.Car" p:logo="马车" p:color="黑色"/>
<bean name="person" class="com.wpq.domain.Person" p:name="阮小二" p:age="40" p:car-ref="car"/>
beans>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean name="car" class="com.syc.spring.domain.Car">
<property name="logo" value="劳斯莱斯"/>
<property name="color" value="黑色"/>
bean>
<bean name="person" class="com.wpq.domain.Person">
<property name="name" value="#{car.logo}"/>
bean>
beans>
package com.wpq.domain;
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionBean {
private Object[] arr;
private List list;
private Map map;
private Set set;
private Properties props;
public Object[] getArr() {
return arr;
}
public void setArr(Object[] arr) {
this.arr = arr;
}
public List getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Map getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Set getSet() {
return set;
}
public void setSet(Set set) {
this.set = set;
}
public Properties getProps() {
return props;
}
public void setProps(Properties props) {
this.props = props;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CollectionBean{" +
"arr=" + Arrays.toString(arr) +
", list=" + list +
", map=" + map +
", set=" + set +
", props=" + props +
'}';
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean name="cb2" class="com.wpq.domain.CollectionBean">
<property name="arr">
<array>
<value>李师师value>
<value>柳如是value>
<value>苍老师value>
array>
property>
bean>
<bean name="cb3" class="com.wpq.domain.CollectionBean">
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>大乔value>
<value>小乔value>
<value>金莲value>
list>
property>
bean>
<bean name="cb4" class="com.wpq.domain.CollectionBean">
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="name" value="三胖"/>
<entry key="age" value="30"/>
<entry key="job" value="boss"/>
map>
property>
bean>
<bean name="cb5" class="com.wpq.domain.CollectionBean">
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>大乔value>
<value>小乔value>
<value>金莲value>
set>
property>
bean>
<bean name="cb6" class="com.wpq.domain.CollectionBean">
<property name="props">
<props>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db01prop>
<prop key="driver">com.jdbc.mysql.Driverprop>
<prop key="username">rootprop>
<prop key="password">rootprop>
props>
property>
bean>
beans>
10.注解实现IOC和DI的准备工作有哪些?
- ① 在XML文件中引入Context的约束
- ② 配置组件扫描器
- ③使用注解
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.wpq.domain,com.wpq.web,com.wpq.service,com.wpq.dao"/>
beans>
11.有哪些注解?分别表示什么含义?
- ①注解实现IOC
- @Component:组件注解,用来创建一个对象,等同于在xml中写了bean标签。
- ②注解实现DI
- @Value("…"): 只能给简单类型注入值,不能给引用类型注入值,使用在成员变量上或set方法上 (简单类型=String+8种基本类型)
- 注意:该注解可以引入配置文件中的变量。 语法: @Value("${age}")
实现步骤: 1. 创建conf.properties配置文件(age=11,name=wpq)
2. XML中配置property-placeholder加载配置文件
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:conf.properties"/>
- @Autowired: 自动装载对象,默认情况下是按照类型来进行匹配。
- @Qualifier: 该注解一般要结合@Autowired的一起使用,当@Autowired根据类型无法匹配对象的时候,进行辅助,根据名称进行依赖注入.解决无法根据类型进行唯一性对象匹配的问题.
- @Resource: 等同于@Autowired+@Qualifier,该注解是Java原生的注解,既可以根据类型,又可以根据名称进行依赖注入.
- ③ Bean标签的属性对应的注解
- 作用域: @Scope(scopeName=“单例/多例”)
- 延迟加载:@Lazy: 等同于中的lazy-init属性 ,设置是否延迟加载
- 创建对象监听:@PostConstruct 指定监听对象创建的方法
- 销毁对象监听:@PreDestroy 指定监听对象销毁的方法
- ④ 组件注解
- @Component:组件注解
- @Controller:组件注解,一般用于web层对象的创建
- @Service:组件注解,一般用于service层对象的创建
- @Repository:组件注解,一般用于dao层对象的创建
- ⑤ 测试注解
- @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) :括号内指定完成测试工作的类
- @ContextConfiguration(“classpath:appication-Collection.xml”) : 指定要加载的XML配置文件
- @Test :写在测试方法上
- ⑥ 元注解
- @Target(ElementType.FIELD):定义注解的作用范围
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME):定义注解的生命周期(保留策略)
- 自定义注解:必须带上面两个元注解
12.谈谈你对Spring AOP的理解?
- ① 概念:是Aspect Oriented Programming的简写,翻译过来就是面向切面编程。
- ② 核心思想:AOP把系统分为核心关注点和横切关注点两个部分,将应用程序中的业务逻辑同为其提供支持的通用服务进行分离。
- 核心关注点:就是业务处理的主要流程(纵向的业务逻辑处理)
- 横切关注点:就是出现在每个业务逻辑处理模块中的大量重复代码,比如说权限认证,日志,事务处理。
- ③ AOP解决的问题:避免了出现大量的重复性代码,提高了代码的复用性。
- ④ AOP底层使用的两种机制:JDK的动态代理和Java类库的CGLIB代理。
- 如果我们类实现了接口,Spring底层实现AOP就会调用动态代理,否则就调用CGLIB代理。
13.XML方式实现AOP的通知有几种?
- ① 前置通知 before
- ② 环绕通知 around
- ③ 后置通知 after-Returning
- ④ 异常通知 after-Throwing
- ⑤ 最终通知 after
14.注解实现AOP的过程?
1.配置Spring XML文件
开启自动代理 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> :声明自动为spring容器中那些配置@Aspect切面的bean创建代理,织入切面
开启组件扫描 <context:component-scan base-package="com.wpq.Spring"/>
2.创建切面类:给类上面添加@Aspect注解
3.切面类中配置切入点 :@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.wpq.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public void pointCut() {}
4.在切面类不同的方法中添加注解:
前置:@Before(value=“pointCut()”)
环绕: @Around(value=“pointCut()”)
后置: @AfterReturning(value=“pointCut()”)
异常: @AfterThrowing(value=“pointCut()”)
最终: @After(value=“pointCut()”)
15.更改多个切面类的执行顺序的方法有几种?
- ① 默认按照类的首字母来执行,a-z/A-Z
- ② 给切面类添加 @Order(v) 注解,v越小,优先级越高
- ③ 切面类实现Order接口,重写getOrder()方法
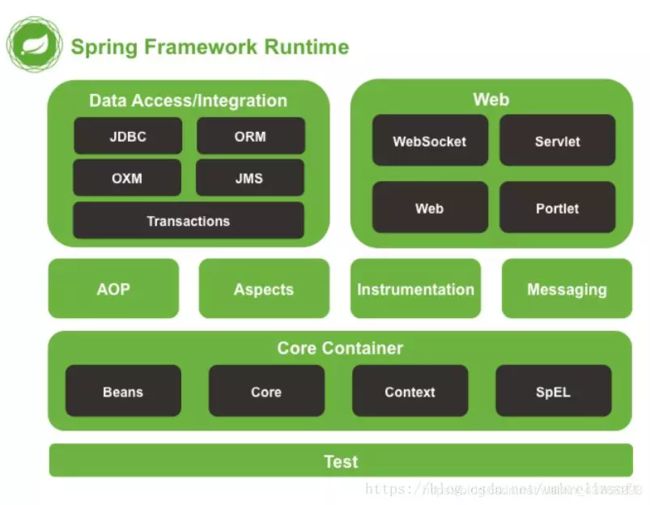
16.Spring有哪些主要模块?
- Spring框架至今已经集成了20多个模块。主要是核心容器、数据访问/集成、Web、AOP、工具、消息和测试模块。
17.Spring中的bean是线程安全的吗?
- Spring容器中的Bean是否线程安全,容器本身并没有提供Bean的线程安全策略,因此可以说spring容器中的Bean本身不具备线程安全的特性,但是还是要结合具体的scope的Bean去研究。
18.Spring支持几种bean的作用域?
- ① singleton 单例模式 (Scope默认):@Scope(value = “singleton”)
- ② prototype 多例模式:每次获取Bean的时候会有一个新的实例
- ③ request: request表示该针对每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的bean,同时该bean仅在当前HTTP request内有效
- ④ session:该作用域表示该针对每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的bean,同时该bean仅在当前HTTP session内有效
- ⑤ global session:该作用域类似于标准的HTTP Session作用域,不过它仅仅在基于portlet的web应用中才有意义。Portlet规范定义了全局Session的概念,它被所有构成某个 portlet web应用的各种不同的portlet所共享。在global session作用域中定义的bean被限定于全局portlet Session的生命周期范围内。如果你在web中使用global session作用域来标识bean,那么web会自动当成session类型来使用。
19.Spring JDBC的实现过程?
- ① 添加spring-orm依赖包(SpringJDBC、mybatis、hibernate的必须依赖包)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-ormartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
1.封装一个xxxDao(UserDao)类,在类中直接通过自动装配注解注入
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; <先创建对象>
2.创建Spring XML配置文件 <把创建JdbcTemplate对象的权利交给Spring>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.wpq.dao"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="xxx.properties" />
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"/>
<property name="user" value=" ${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
bean>
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
beans>
package com.wpq.dao.impl;
import com.wpq.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate template;
@Override
public void subMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
System.out.println("账户:" + id + ",减钱了..." + money);
String sql = "update tb_account set money=money - ? where id=?";
template.update(sql, money, id);
}
@Override
public void addMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
System.out.println("账户:" + id + ",加钱了..." + money);
String sql = "update tb_account set money=money + ? where id=?";
template.update(sql, money, id);
}
}
20.事务的概念是什么?
- 事务是一组原子性的SQL查询,或者说是一个独立的工作单位。(要么全部成功,要么全部失败)
21.事务的特性有几个?
- ① 原子性(atomicity):指处于同一个事务中的多条SQL查询是不可分割的,要么全部提交成功,要么全部提交失败回滚。
- ② 一致性(consistency):事务必须使数据库从一个一致性状态变换到另外一个一致性状态。比如转账,转账前两个账户余额之和为2k,转账之后也应该是2K。
- ③ 隔离性(isolation):指多线程环境下,一个事务所做的修改在最终提交以前,对其它事务是不可见的。
- ④ 持久性(durability):事务一旦提交,则其所做的修改就会永久保存到数据库中。
22.数据库操作时可能存在的问题有哪些?
- ① 脏读:指一个线程中的事务读取到了另外一个线程中事务未提交的数据。
- ② 不可重复读:指一个线程中的事务读取到了另外一个线程中事务提交的update的数据,读取到之前查询一次,读取到之后查询一次,两次查询结果不一样。
- ③ 幻读:指的是当A事务在读取某个范围内的记录时,B事务又在该范围内插入了新的记录,当A事务再次读取该范围的记录时,会产生幻行(指一个线程中的事务读取到了另外一个线程中事务提交的insert数据)。
23.什么是事务的隔离级别?事务的隔离级别有几个?
- 概念: 指的是一个事务对数据的修改与另一个并发的事务的隔离程度。当多个事务同时访问相同数据时,如果没有采取必要的隔离机制,就可能发生脏读,不可重复读和幻读的问题。
- ① READ UNCOMMITTED 未提交读(最低级别)
- ② READ COMMITTED 提交读–>解决了脏读
- ③ REPEATABLE READ 可重复读 (MySQL的默认) -->解决了脏读和不可重复读
- ④ SERIALIZABLE 可串行化 (最高级别) -->解决了脏读,不可重复读和幻读
24.Spring中事务的传播行为有几种?
- ① PROPAGATION_REQUIRED(默认) :表示当前方法必须运行在事务中
- ② PROPAGATION_REQUIRED_NEW:表示当前方法必须运行在它自己的事务中
- ③ PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS :表示当前方法不需要事务上下文,但是如果存在当前事务的话,那么该方法会在这个事务中运行
- ④ PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED: 表示该方法不应该运行在事务中
- ⑤ PROPAGATION_NEVER: 表示当前方法不应该运行在事务上下文中
- ⑥ PROPAGATION_NESTED: 表示如果当前已经存在一个事务,那么该方法将会在嵌套事务中运行
- ⑦ PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:表示该方法必须在事务中运行,如果当前事务不存在,则会抛出一个异常
25.Spring 声明式事务的实现?
- ① 传统事务实现方案:利用JDBC通过手动编写事务相关代码来实现。
try{
beginTransaction();
业务代码;
commit();
}catch (Exception e){
rollback();
}
- ② Spring实现声明式事务的原理:AOP
- ③ XML方式实现声明式事务
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.wpq"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="xxx.properties" />
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"/>
<property name="user" value=" ${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
bean>
1.配置一个事务管理器
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
2.配置一个事务切面类,配置事务规则
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transfer**" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="add**"/>
<tx:method name="delete**"/>
<tx:method name="update**"/>
<tx:method name="select**" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
3.把目标类和切面类整合在一起
<aop:congfig>
<aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* com.wpq.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointCut"/>
aop:config>
4.实现自己的service层业务代码
beans>
package com.wpq.domain;
@Data
public class Account {
private Integer from;
private Integer to;
private Double money;
}
package com.wpq.dao.impl;
import com.wpq.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate template;
@Override
public void subMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
System.out.println("账户:" + id + ",减钱了..." + money);
String sql = "update tb_account set money=money - ? where id=?";
template.update(sql, money, id);
}
@Override
public void addMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
System.out.println("账户:" + id + ",加钱了..." + money);
String sql = "update tb_account set money=money + ? where id=?";
template.update(sql, money, id);
}
}
package com.wpq.service.impl;
import com.wpq.dao.AccountDao;
import com.wpq.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void transfer(Integer from, Integer to, Double money) {
System.out.println("service层...转账业务...");
accountDao.subMoney(from, money);
accountDao.addMoney(to, money);
}
}
package com.wpq.web;
import com.wpq.domain.Account;
import com.wpq.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class AccountController {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@RequestMapping("/trans")
public void transfer(Account account) {
System.out.println("web层...转账接口...");
accountService.transfer(account.getFrom(), account.getTo(), account.getMoney());
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.wpq"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="xxx.properties" />
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"/>
<property name="user" value=" ${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
bean>
1.XML中配置一个事务管理器
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
2.XML中开启事务的注解功能
<tx:annotation-driven/>
3.在业务类或者业务方法上面添加注解
@Transactional(isolation =Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
beans>
package com.wpq.service.impl;
import com.wpq.dao.AccountDao;
import com.wpq.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@Transactional(isolation =Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void transfer(Integer from, Integer to, Double money) {
System.out.println("service层...转账业务...");
accountDao.subMoney(from, money);
accountDao.addMoney(to, money);
}
}
26.Spring 事务失效的场景有哪些?
- 1.业务方法中异常被try-catch掉,导致异常没有抛出,没有触发回滚,事务失效
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
@Override
public int batchAdd(List<Role> roleList) {
int i = roleMapper.insertList(roleList);
try {
Integer a = null;
a.toString();
}catch (Exception e){
}
return i;
}
- 2.在非public修饰的业务方法上使用事务注解,会导致事务失效
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
protected int batchAdd(List<Role> roleList) {
int i = roleMapper.insertList(roleList);
Integer a = null;
a.toString();
return i;
}
- 3.数据库引擎不支持事务
- MySQL的MyISAM引擎是不支持事务操作的,InnoDB引擎才支持事务。
- 4.打上事务注解的方法所在的类并没有交给spring的IOC容器管理,同样会导致事务失效
public class RoleServiceImpl implements RoleService {
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int batchAdd(List<Role> roleList) {
int i = roleMapper.insertList(roleList);
Integer a = null;
a.toString();
return i;
}
}
- 5.业务方法中的运行时异常被try-catch之后,在catch里面抛出的异常类型不是运行时异常,同样会导致事务失败,因为如果不在事务注解中声明触发回滚类型,默认的是RuntimeException
@Transactional
@Override
public int batchAdd(List<Role> roleList) throws MyException {
int i = 0;
try {
i = roleMapper.insertList(roleList);
Integer a = null;
a.toString();
}catch (Exception e){
throw new MyException("xxx错误");
}
return i;
}
- 6.自身调用问题,业务层自身非事务方法调用事务方法,会导致不经过Spring的代理类。默认只有在外部调用事务方法,事务才会生效
@Service
public class RoleServiceImpl implements RoleService {
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int batchAdd(List<Role> roleList) {
int i = roleMapper.insertList(roleList);
Integer a = null;
a.toString();
return i;
}
public int testBatchAdd(List<Role> roleList){
return batchAdd(roleList);
}
}
class Test{
@Autowired
RoleServiceImpl service;
@Test
public void test() {
Role role = new Role();
role.setRoleName("sss");
role.setRemark("哈哈哈");
Role role2 = new Role();
role.setRoleName("bbb");
role.setRemark("嘿嘿嘿");
List<Role> roleList = new ArrayList<>();
roleList.add(role);
roleList.add(role2);
int i = service.testBatchAdd(roleList);
}
}
27.@Transactional(readOnly = true)的理解?
- 某个事务被指定只读属性为true的时候,相当于在该事务执行期间,把数据库设置成了只读数据库,换句话说就是该事务在执行期间,是看不见其它事务提交的数据的。
28.Spring支持的事务管理类型有哪些?
- 声明式事务
- 编程式事务(TransactionTemplate ,PlatformTransactionManager)
29.@Transactional(timeout= 2)的理解?
- 从事务开始得两秒钟后,数据库还未返回结果,Spring就会抛出TransactionTimedOutException。
@SpringBootTest(classes = {UserServiceApp.class})
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class TTT {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
@Transactional(timeout = 2)
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(2000);
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectAll();
System.out.println("userList = " + userList);
}
}
30.Spring读取properties文件的方式
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("conf/db.properties");
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
String o = properties.getProperty("jdbc.url");


