身份证识别项目(二)-- 3755个汉字的识别
目录标题
- 阶段目标
- 步骤
- 1 构建常用3755个字体
- 2 获取汉字label映射表
- 3 构建训练集
- 3 网络搭建
- 4 模型训练
- 7 接下来的难点
阶段目标
在opencv对图片预处理,截取相关文字信息后,需要对其进行识别,由于pytessact模块效果不好,所以选择使用tensorflow构建模型进行识别。
!!
本博客引自冠军的试炼:https://www.cnblogs.com/skyfsm/p/8436820.html
冠军的试炼模型构建:https://www.cnblogs.com/skyfsm/p/8443107.html#!comments
(本文仅对其技术做简单总结以记录项目进度,完成复现,并指出排除相应bug。版权归冠军的试炼所有,若有侵权请于本人联系,谢谢。)
!!
步骤
1 构建常用3755个字体
2 获取汉字label映射表
生成Chinese_labels文字映射文件,用两个字举例:
import pickle
import os
os.mknod('labels')
text = {1:'一', 2:'丁}
with open('labels','wb') as f:
i = pickle.dump(text,f,0)
print(i)
把汉字读入内存,建立一个字典,把这个关系记录下来,再使用pickle.dump存入文件保存。
3 构建训练集
收集常用的印刷体字体文件,用于文字的生成。
定义相应的一些参数:
def args_parse():
# 解析输入参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description=description, formatter_class=RawTextHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument('--out_dir', dest='out_dir',
default=None, required=True,
help='write a caffe dir')
parser.add_argument('--font_dir', dest='font_dir',
default=None, required=True,
help='font dir to to produce images')
parser.add_argument('--test_ratio', dest='test_ratio',
default=0.2, required=False,
help='test dataset size')
parser.add_argument('--width', dest='width',
default=None, required=True,
help='width')
parser.add_argument('--height', dest='height',
default=None, required=True,
help='height')
parser.add_argument('--no_crop', dest='no_crop',
default=True, required=False,
help='', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--margin', dest='margin',
default=0, required=False,
help='', )
parser.add_argument('--rotate', dest='rotate',
default=0, required=False,
help='max rotate degree 0-45')
parser.add_argument('--rotate_step', dest='rotate_step',
default=0, required=False,
help='rotate step for the rotate angle')
parser.add_argument('--need_aug', dest='need_aug',
default=False, required=False,
help='need data augmentation', action='store_true')
args = vars(parser.parse_args())
return args
# 实现汉字到ID的映射,用于后面的字体生成
# 将汉字的label读入,得到(ID:汉字)的映射表label_dict
label_dict = get_label_dict()
char_list=[] # 汉字列表
value_list=[] # label列表
for (value,chars) in label_dict.items():
print (value,chars)
char_list.append(chars)
value_list.append(value)
# 合并成新的映射关系表:(汉字:ID)
lang_chars = dict(zip(char_list,value_list))
font_check = FontCheck(lang_chars)
# 设置文字旋转范围:
if rotate < 0:
roate = - rotate
if rotate > 0 and rotate <= 45:
all_rotate_angles = []
for i in range(0, rotate+1, rotate_step):
all_rotate_angles.append(i)
for i in range(-rotate, 0, rotate_step):
all_rotate_angles.append(i)
#print(all_rotate_angles)
# 生成字体图像,原文是黑景白字,为更好识别opencv灰度二值化图像,接下来将采用白景黑字。
class Font2Image(object):
def __init__(self,
width, height,
need_crop, margin):
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.need_crop = need_crop
self.margin = margin
def do(self, font_path, char, rotate=0):
find_image_bbox = FindImageBBox()
# 黑色背景
img = Image.new("RGB", (self.width, self.height), "black")
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, int(self.width * 0.7),)
# 白色字体
draw.text((0, 0), char, (255, 255, 255),
font=font)
if rotate != 0:
img = img.rotate(rotate)
data = list(img.getdata())
sum_val = 0
for i_data in data:
sum_val += sum(i_data)
if sum_val > 2:
np_img = np.asarray(data, dtype='uint8')
np_img = np_img[:, 0]
np_img = np_img.reshape((self.height, self.width))
cropped_box = find_image_bbox.do(np_img)
left, upper, right, lower = cropped_box
np_img = np_img[upper: lower + 1, left: right + 1]
if not self.need_crop:
preprocess_resize_keep_ratio_fill_bg = \
PreprocessResizeKeepRatioFillBG(self.width, self.height,
fill_bg=False,
margin=self.margin)
np_img = preprocess_resize_keep_ratio_fill_bg.do(
np_img)
# cv2.imwrite(path_img, np_img)
return np_img
else:
print("img doesn't exist.")
# 写两个循环,外层循环是汉字列表,内层循环是字体列表,对于每个汉字会得到一个image_list列表,里面存储着这个汉字的所有图像:
for (char, value) in lang_chars.items(): # 外层循环是字
image_list = []
print (char,value)
#char_dir = os.path.join(images_dir, "%0.5d" % value)
for j, verified_font_path in enumerate(verified_font_paths): # 内层循环是字体
if rotate == 0:
image = font2image.do(verified_font_path, char)
image_list.append(image)
else:
for k in all_rotate_angles:
image = font2image.do(verified_font_path, char, rotate=k)
image_list.append(image)
# 将image_list中图像按照比例分为训练集和测试集存储
test_num = len(image_list) * test_ratio
random.shuffle(image_list) # 图像列表打乱
count = 0
for i in range(len(image_list)):
img = image_list[i]
#print(img.shape)
if count < test_num :
char_dir = os.path.join(test_images_dir, "%0.5d" % value)
else:
char_dir = os.path.join(train_images_dir, "%0.5d" % value)
if not os.path.isdir(char_dir):
os.makedirs(char_dir)
path_image = os.path.join(char_dir,"%d.png" % count)
cv2.imwrite(path_image,img)
count += 1
写好代码后,我们在cmd中执行如下指令,开始生成印刷体文字汉字集。
python gen_printed_char.py --out_dir ./dataset --font_dir ./chinese_fonts --width 30 --height 30 --margin 4 --rotate 30 --rotate_step 1
相应参数:
–out_dir 表示生成的汉字图像的存储目录
–font_dir 表示放置汉字字体文件的路径
–width --height 表示生成图像的高度和宽度
–margin 表示字体与边缘的间隔
–rotate 表示字体旋转的范围,[-rotate,rotate]
–rotate_step 表示每次旋转的间隔
最终会在dataset文件夹下有train和test两个文件夹,train和test文件夹下都有3755个子文件夹,每个子文件的名字就是该汉字对应的id。每个train文件夹中有634个文件,test中有139个。
3 网络搭建
构建一个较浅的网络(基于LeNet的改进)
#network: conv2d->max_pool2d->conv2d->max_pool2d->conv2d->max_pool2d->conv2d->conv2d->max_pool2d->fully_connected->fully_connected
具体代码相见附加博客
4 模型训练
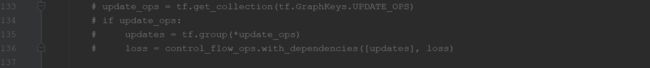
训练中遇到的问题,在loss不断下降的过程中,accuracy始终为零,本文给出解决方案:
注销相应代码:
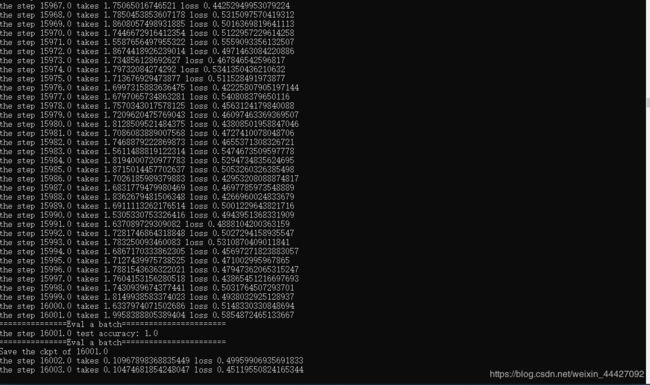
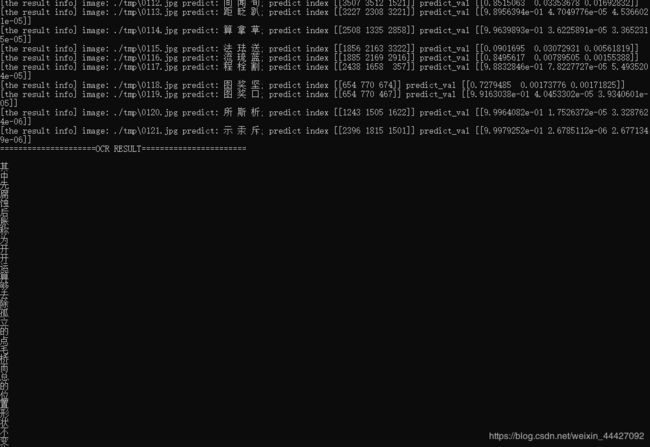
因有些小伙伴电脑较慢,附上模型链接,版权归原作者所有:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/12S8Cdo35Z3C93UH0T1SMVw
提取码:xfe5
7 接下来的难点
因身份证地址中是数字和汉字混合的情况,在进行单字分割后送入模型,需要在训练集后单独加入0-9数字集,完成训练。