python读取excel并导入mysql
python读取excel
如果Excel文件内的数据是这样的:
| id | name | age | birthday |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | kate | 11 | 2008-2-2 |
| 2 | mike | 22 | 1997-4-4 |
| 3 | tom | 33 | 1986-5-5 |
首先,导入python包xlrd,以及它的一个方法 xldate_as_tuple。
import xlrd
from xlrd import xldate_as_tuple # 用于转换时间格式
from datetime import date,datetime # 也是用于标准化时间
book = xlrd.open_workbook("pxbdata.xlsx") # 打开excel文件
sheet = book.sheets()[0] # 获取文件中的第一个表
std = [] #定义一个空列表,准备存放后面将要读到的数据
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows): # 一行一行遍历数据,sheet.nrows为excel中数据的总行数
# 因为数据被读取后,数据的格式会发生变化,所以下面要先把数据的格式转换一下。
temp = sheet.row_values(i) # 获取到第i行数据
temp[0]=int(temp[0]) # 把这一行的第1个数据转换为整型,因为读取之后已经变成了浮点型
temp[2]=int(temp[2]) # 把这一行的第3个数据转换为整形,理由一样
# 下面这行比较复杂了。temp[3]在原表里是时间,读入之后变成一个浮点数。
# 那么先用xldate_as_tuple()的方法,把temp[3]转换成一个时间元组,
# 在取这个元组的前3个数字,用date()方法变成时间,
# 再把这个时间通过.strftime(),转换成标准格式,最后得到的时间格式是str
temp[3]=date(*xldate_as_tuple(temp[3],book.datemode)[:3]).strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
std.append(tuple(temp)) # 最后把转换后的一组数据添加到列表中
std
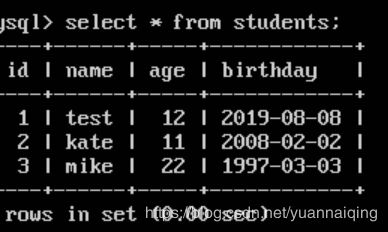
最后得到的std的结果是:
[(1, ‘kate’, 11, ‘2008-02-02’),
(2, ‘mike’, 22, ‘1997-04-04’),
(3, ‘tom’, 33, ‘1986-05-05’)]
连接mysql并导入数据
可以在Ubuntu中先把表创建好。
create database test816; # 创建数据库
use test816; #使用数据库
#创建数据表
create table students(
-> id int not null auto_increment,
-> name varchar(100) not null,
-> age int not null,
-> birthday date,
-> primary key(id)
-> );
连接mysql
安装pymysql包
Ubuntu中,用命令:pip3 install pymysql
导入包
import pymysql
创建连接:
conn = pymysql.connect(host = 'localhost', user = 'root', passwd = '2', db = 'test816', charset = 'utf8')
创建游标,给数据库发送sql语句指令:
cur = conn.cursor()
导入数据
准备好数据:
std = [(1, 'kate', 11, '2008-02-02'),
(2, 'mike', 22, '1997-04-04'),
(3, 'tom', 33, '1986-05-05')]
编写sql指令:
sql = 'insert into students values(%s, %s, %s, %s);'
传入数据:
cur.executemany(sql, std) # 执行多行插入
最后提交并关闭游标和连接:
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
import xlrd
from xlrd import xldate_as_tuple
from datetime import date,datetime
def read_excel(file_path):
'''读取excel,返回数据列表'''
book = xlrd.open_workbook(file_path)
sheet = book.sheets()[0]
std = []
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
temp = sheet.row_values(i)
temp[0]=int(temp[0])
temp[2]=int(temp[2])
temp[3]=date(*xldate_as_tuple(temp[3],book.datemode)[:3]).strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
std.append(tuple(temp))
return std
import pymysql
def insert_data(std):
'''数据导入mysql'''
conn = pymysql.connect(host = 'localhost', user = 'root', passwd = '2', db = 'test816', charset = 'utf8')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = 'insert into students values(%s, %s, %s, %s);'
cur.executemany(sql, std) # 执行多行插入
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()