深度学习之DeepLab用于语义分割
摘要
- 研究点:CNN做语义分割
- 工程主页:http://liangchiehchen.com/projects/DeepLab.html
- 主要贡献:
-
atrous conv: 可以控制参与卷积的feature的分辨率
Subsample -> Conv(kernel) 和 AtrousConv(kernel) -> Subsample 等价,且 AtrousConv(kernel) 平移不变。
参考博客:http://blog.csdn.net/u012759136/article/details/52434826#t9 -
atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) : 可以在不同的scale下分割物体。 -
定位物体边界更加精确!将 DCNN layer 最后的输出与 fully connected Conditional Random Field (CRF)结合,克服了DCNN中最大池化和下采样造成的定位精度不准的问题。
-
- 关键词: 语义分割;atrous convolution; CRF
1 Introduction
DCNN在语义分割这一块的局限性:
(1) 分辨率下降(max-pooling and downsampling 的stride引起)reduced feature resolution
引用了FCN做语义分割的[14] ,并指出其缺点是空间分辨率大大降低!作者为克服该问题,去掉了池化后几层的下采样操作,而在后续的几层卷积层中加入了上采样操作。
Use atrous convolution as a shorthand for convolution with upsampled filters
atrous convolution [3,6,16]
相比采用deconv(反卷积)的方法[13,14],作者采用的atrous conv+线性插值的方法也非常有效。
其优势在于:不需要增加参数的个数,而可以获得更大的感知野。
(2) 物体存在不同的尺度(existence of objects at multiple scales)
对这个问题,通常的做法是将同一幅图像的不同吃错的feature/score map聚合得到结果[6,17,18]。这方法的确可以增提高性能,但是增加量计算量。参考SPP的做法,作者提出了在卷积操作之前小对给定的feature layer用多种采样率进行 resample
即采用多个并行的不同采样率的atrous convolutional layers(ASPP)
(3) 定位不精确(reduced localization accuracy due to DCNN invariance)
这是由于物体检测时需要对空间变换具有不变性,因此限制了DCNN的空间精度。
解决该问题的一个办法是:skip-layers ,从多层提取出hyper-column features
作者则是提出了一个更为有效的方法:采用一个fully-connected CRF[22]
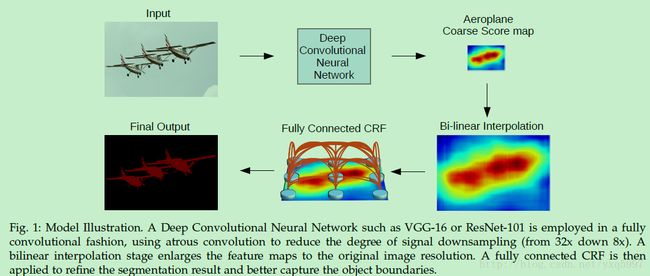
算法基本框架:
(1)基于VGG-16/ResNet-101(效果可能比VGG-16更好)进行变化:先将所有的全连接层换成卷积层 [14],然后通过atrous conv提高feature的分辨率(从32x到8x)
(2)Bi-linear interpolation : factor =8 这样把score map尺寸变回到原图像尺寸。
(3)结果送入CRF 来refine分割结果。
算法优点:
(1)速度快: 8FPS
(2)精度高:在PASCAL VOC 2012 semantic segmentation benchmark [34], PASCAL-Context [35], PASCALPersonPart [36], and Cityscapes [37]上取得了较好的成果。
(3)简单:主要由两部分组成:DCNN和CRF
2 相关工作
第一类:传统的方法
第二类:CNN提取特征做稠密的image labeling
[21] use skip layer-> pixel 分类
[51] pool 中间的feature maos by region proposals
第三类:直接用DCNN 得到抽魔的category-level pixel labels(甚至都不需要分割了),相关工作有[14,52], 将最后的全连接层替换为全卷积层。针对空间定位问题,[14]采用上采样并将中间过程的feature maps得到的score连接起来,而[52] 是将粗略的结果通过另一个DCNN进行refine.
近期进展:
- End-to-end training for structured prediction
[40], [59],[62], [64], [65]
[18], [68] combine semantic segmentation with edge detection.
- Weaker supervision
[49], [73] pursue instance segmentation, jointly tackling object detection and semantic segmentation.
atrous conv: 可以扩大filter的感知野
3 methods
3.1 atrous conv for dense feature extraction and field-of view enlargement
FCN【14】中对分辨率下降的补救方法是反卷积;作者采用的是atrous convolution
以1D为例,the output y[i] of atrous convolution 2 of a 1-D input signal x[i] with a filter w[k] of length K is defined as:
(见论文)
而在标准的卷积中,采样率r=1
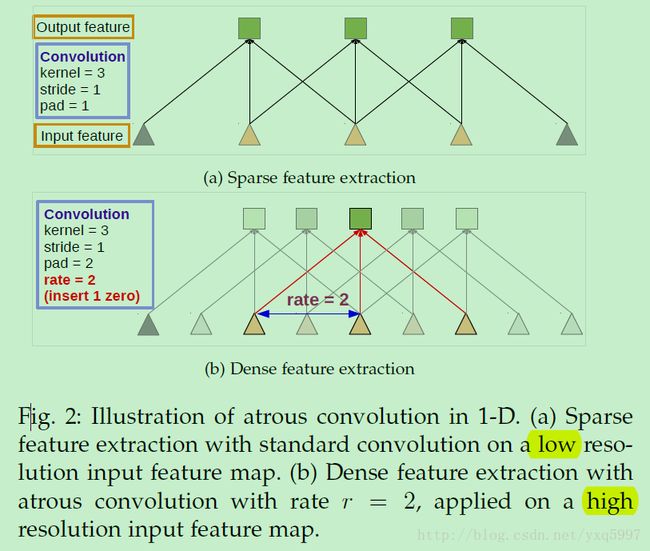
3.2 Multiscale Image Representations using Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling
受SPP的启发,一个任意尺寸的区域可以通过对一个固定尺度下的卷积特征进行resample
本文采用的是多个并行的不同采样率的atrous 卷积层,最后整合在一起。

3.3 Structured Prediction with Fully-Connected Conditional Random Fields for Accurate Boundary Recovery (物体边界定位)
解决方法:
1)[14] ,[21],[52] 将卷积网络不同层的信息进行合并。
2)[50] 采用super-pixel -> 变成一个low-level 分割问题。
作者采用的是CRF 并且不能用局部的,要用全局的[22]。
能量函数参考[22]:
4 实验
- 将最后一层的输出个数替换成需要分割的种类数(包括背景)。
- 损失函数为输出图的每个空间位置(输出是原输入图的1/8)的交叉熵之和。
- SGD
参考文献
[14] J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell, “Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation,” in CVPR, 2015.
[18] I. Kokkinos, “Pushing the boundaries of boundary detection using deep learning,” in ICLR, 2016.
[21] B. Hariharan, P. Arbel´aez, R. Girshick, and J. Malik, “Hypercolumns for object segmentation and fine-grained localization,” in CVPR, 2015.
[22] P. Kr¨ahenb ¨ uhl and V. Koltun, “Efficient inference in fully connected crfs with gaussian edge potentials,” in NIPS, 2011.
[51] J. Dai, K. He, and J. Sun, “Convolutional feature masking for joint object and stuff segmentation,” arXiv:1412.1283, 2014
[52] D. Eigen and R. Fergus, “Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture,”arXiv:1411.4734,2014.
[68] G. Bertasius, J. Shi, and L. Torresani, “High-for-low and low-forhigh: Efficient boundary detection from deep object features and its applications to high-level vision,” in ICCV, 2015.
