在linux下跟着教材写的需要注意的是在多线程编程中引用了线程的头文件,这个库不是linux的标准库,所以在编译时要手动加上,格式为:gcc 文件.c -lpthread -o 输出.out
- 服务器端
#include
#include
#include
#include //pthread_t , pthread_attr_t and so on.
#include
#include //structure sockaddr_in
#include //Func : htonl; htons; ntohl; ntohs
#include //Func :assert
#include //Func :memset
#include //Func :close,write,read
#define SOCK_PORT 9988
#define BUFFER_LENGTH 1024
#define MAX_CONN_LIMIT 10 //MAX connection limit
static void Data_handle(void * sock_fd); //Only can be seen in the file
int main()
{
int sockfd_server;
int sockfd;
int fd_temp;
struct sockaddr_in s_addr_in;
struct sockaddr_in s_addr_client;
int client_length;
sockfd_server = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); //ipv4,TCP
assert(sockfd_server != -1);
//before bind(), set the attr of structure sockaddr.
memset(&s_addr_in,0,sizeof(s_addr_in));
s_addr_in.sin_family = AF_INET;
s_addr_in.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); //trans addr from uint32_t host byte order to network byte order.
s_addr_in.sin_port = htons(SOCK_PORT); //trans port from uint16_t host byte order to network byte order.
fd_temp = bind(sockfd_server,(struct scokaddr *)(&s_addr_in),sizeof(s_addr_in));
if(fd_temp == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"bind error!\n");
exit(1);
}
fd_temp = listen(sockfd_server,MAX_CONN_LIMIT);
if(fd_temp == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"listen error!\n");
exit(1);
}
while(1)
{
printf("waiting for new connection...\n");
pthread_t thread_id;
client_length = sizeof(s_addr_client);
//Block here. Until server accpets a new connection.
sockfd = accept(sockfd_server,(struct sockaddr_*)(&s_addr_client),(socklen_t *)(&client_length));
if(sockfd == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Accept error!\n");
continue; //ignore current socket ,continue while loop.
}
printf("A new connection occurs!\n");
if(pthread_create(&thread_id,NULL,(void *)(&Data_handle),(void *)(&sockfd)) == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create error!\n");
break; //break while loop
}
}
//Clear
int ret = shutdown(sockfd_server,SHUT_WR); //shut down the all or part of a full-duplex connection.
assert(ret != -1);
printf("Server shuts down\n");
return 0;
}
static void Data_handle(void * sock_fd)
{
int fd = *((int *)sock_fd);
int i_recvBytes;
char data_recv[BUFFER_LENGTH];
const char * data_send = "Server has received your request!\n";
while(1)
{
printf("waiting for request...\n");
//Reset data.
memset(data_recv,0,BUFFER_LENGTH);
i_recvBytes = read(fd,data_recv,BUFFER_LENGTH);
if(i_recvBytes == 0)
{
printf("Maybe the client has closed\n");
break;
}
if(i_recvBytes == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"read error!\n");
break;
}
if(strcmp(data_recv,"quit")==0)
{
printf("Quit command!\n");
break; //Break the while loop.
}
printf("read from client : %s\n",data_recv);
if(write(fd,data_send,strlen(data_send)) == -1)
{
break;
}
}
//Clear
printf("terminating current client_connection...\n");
close(fd); //close a file descriptor.
pthread_exit(NULL); //terminate calling thread!
}
- 客户端
#include
#include
#include //pthread_t , pthread_attr_t and so on.
#include
#include //structure sockaddr_in
#include //Func : htonl; htons; ntohl; ntohs
#include //Func :assert
#include //Func :memset
#include //Func :close,write,read
#define SOCK_PORT 9988
#define BUFFER_LENGTH 1024
int main()
{
int sockfd;
int tempfd;
struct sockaddr_in s_addr_in;
char data_send[BUFFER_LENGTH];
char data_recv[BUFFER_LENGTH];
memset(data_send,0,BUFFER_LENGTH);
memset(data_recv,0,BUFFER_LENGTH);
sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); //ipv4,TCP
if(sockfd == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"socket error!\n");
exit(1);
}
//before func connect, set the attr of structure sockaddr.
memset(&s_addr_in,0,sizeof(s_addr_in));
s_addr_in.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1"); //trans char * to in_addr_t
s_addr_in.sin_family = AF_INET;
s_addr_in.sin_port = htons(SOCK_PORT);
tempfd = connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *)(&s_addr_in),sizeof(s_addr_in));
if(tempfd == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Connect error! \n");
exit(1);
}
while(1)
{
printf("Please input something you wanna say(input \"quit\" to quit):\n");
gets(data_send);
//scanf("%[^\n]",data_send); //or you can also use this
tempfd = write(sockfd,data_send,BUFFER_LENGTH);
if(tempfd == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"write error\n");
exit(0);
}
if(strcmp(data_send,"quit") == 0) //quit,write the quit request and shutdown client
{
break;
}
else
{
tempfd = read(sockfd,data_recv,BUFFER_LENGTH);
assert(tempfd != -1);
printf("%s\n",data_recv);
memset(data_send,0,BUFFER_LENGTH);
memset(data_recv,0,BUFFER_LENGTH);
}
}
int ret = shutdown(sockfd,SHUT_WR); //or you can use func close()-- to close the fd
assert(ret != -1);
return 0;
}
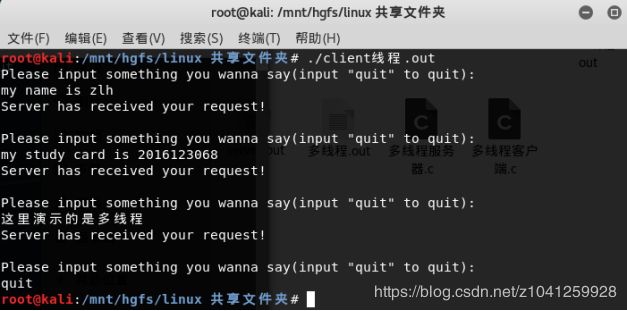
- 运行结果
服务器端: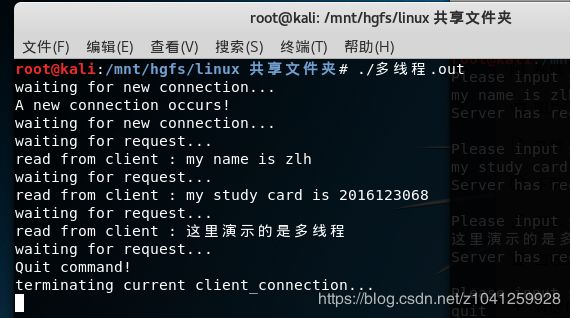
客户端: