Linux上安装NetCat
简述:
在网络工具中有“瑞士军刀”美誉的NetCat(以下简称nc),在我们用了N年了至今仍是爱不释手。因为它短小精悍(这个用在它身上很适合,现在有人已经将其修改成大约10K左右,而且功能不减少)。
一个简单而有用的工具,透过使用TCP或UDP协议的网络连接去读写数据。它被设计成一个稳定的后门工具,能够直接由其它程序和脚本轻松驱动。
安装方式一:yum安装
yum install -y netcat
或者
yum install -y nc
安装方式二:编译安装
1.下载
https://download.csdn.net/download/z1941563559/10577879
2.上传到linux服务器并解压
进入netcat-0.7.1.tar.gz所在目录,并执行下面的命令:
tar -zxvf netcat-0.7.1.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
3.编译并安装netcat
进入解压之后的目录
cd /usr/local/netcat-0.7.1/
执行编译安装的命令:
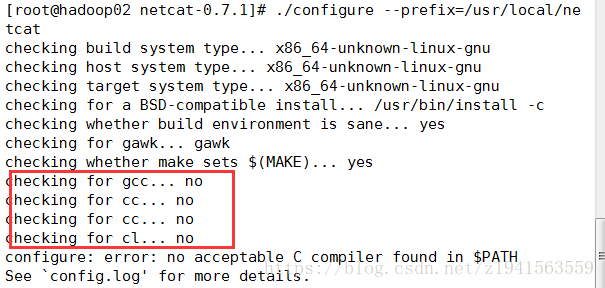
[root@hadoop02 netcat-0.7.1]# ./configure –prefix=/usr/local/netcat
错误出现原因是没有gcc编译器,使用yum安装gcc即可
[root@hadoop02 netcat-0.7.1]# yum install -y gcc
重新执行
[root@hadoop02 netcat-0.7.1]# ./configure –prefix=/usr/local/netcat
编译和安装
[root@hadoop02 netcat-0.7.1]# make && make install
编译安装成功,进入netcat目录:
[root@hadoop02 netcat-0.7.1]# cd /usr/local/netcat
[root@hadoop02 netcat]# ll
total 16
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Aug 1 20:40 bin
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Aug 1 20:40 info
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Aug 1 20:40 man
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Aug 1 20:40 share
注:此处的/usr/local/netcat−0.7.1/相当于源码文件,安装成功的文件是/usr/local/netcat,这里可以将/usr/local/netcat−0.7.1/删除 注 : 此 处 的 / u s r / l o c a l / n e t c a t − 0.7.1 / 相 当 于 源 码 文 件 , 安 装 成 功 的 文 件 是 / u s r / l o c a l / n e t c a t , 这 里 可 以 将 / u s r / l o c a l / n e t c a t − 0.7.1 / 删 除
4.配置环境变量
[root@hadoop02 netcat]# vi /etc/profile
export NETCAT_HOME=/usr/local/netcat
export PATH=$PATH:$NETCAT_HOME/bin重新载入配置文件:
[root@hadoop02 netcat]# source /etc/profile
5.测试是否安装成功
nc –help
或 netcat –help
安装成功的效果:
[root@hadoop02 netcat]# nc --help
GNU netcat 0.7.1, a rewrite of the famous networking tool.
Basic usages:
connect to somewhere: nc [options] hostname port [port] ...
listen for inbound: nc -l -p port [options] [hostname] [port] ...
tunnel to somewhere: nc -L hostname:port -p port [options]
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
Options:
-c, --close close connection on EOF from stdin
-e, --exec=PROGRAM program to exec after connect
-g, --gateway=LIST source-routing hop point[s], up to 8
-G, --pointer=NUM source-routing pointer: 4, 8, 12, ...
-h, --help display this help and exit
-i, --interval=SECS delay interval for lines sent, ports scanned
-l, --listen listen mode, for inbound connects
-L, --tunnel=ADDRESS:PORT forward local port to remote address
-n, --dont-resolve numeric-only IP addresses, no DNS
-o, --output=FILE output hexdump traffic to FILE (implies -x)
-p, --local-port=NUM local port number
-r, --randomize randomize local and remote ports
-s, --source=ADDRESS local source address (ip or hostname)
-t, --tcp TCP mode (default)
-T, --telnet answer using TELNET negotiation
-u, --udp UDP mode
-v, --verbose verbose (use twice to be more verbose)
-V, --version output version information and exit
-x, --hexdump hexdump incoming and outgoing traffic
-w, --wait=SECS timeout for connects and final net reads
-z, --zero zero-I/O mode (used for scanning)
Remote port number can also be specified as range. Example: '1-1024'