二叉树
文章目录
- 前序遍历
- 144. 二叉树的前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 145. 二叉树的后序遍历
- 层次遍历
- 102. 二叉树的层次遍历
- 二叉树高度
- 104. 二叉树的最大深度
- 111. 二叉树的最小深度
- 直观地打印一棵二叉树
- 后继节点
- 285 二叉搜索树中的中序后继
- 前驱节点
- 序列化与反序列化
- 297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
- 平衡二叉树
- 110. 平衡二叉树
- 完全二叉树
- 958. 二叉树的完全性检验
- 222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
- 路径
- 112. 路径总和
- 437. 路径总和 III
- 687. 最长同值路径
- 其他
- 543. 二叉树的直径
- 226. 翻转二叉树
- 617. 合并二叉树
- 572. 另一个树的子树
- 101. 对称二叉树
- 404. 左叶子之和
- 337. 打家劫舍 III
- 671. 二叉树中第二小的节点 (简单)
- 637. 二叉树的层平均值
- 513. 找树左下角的值 (中等)
- 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
前序遍历
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
- 递归
JAVA代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
return help(root, res);
}
public List<Integer> help (TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if (root != null) {
list.add(root.val);
help(root.left, list);
help(root.right, list);
}
return list;
}
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null) return new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
stack.push(root);
//访问栈节点并弹出,先右孩子入栈,后左孩子入栈
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
res.add(top.val);
if (top.right!=null){
stack.push(top.right);
}
if (top.left!=null){
stack.push(top.left);
}
}
return res;
}
}
中序遍历
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- 递归
JAVA代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
res = help(root, res);
return res;
}
public List<Integer> help(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if (root!=null){
help(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val);
help(root.right, list);
return list;
}
return list;
}
}
- 访问左侧链的最后一个节点 (左侧链节点入栈)
- 转向该节点的右子树
- 访问该子树上左侧链的最后一个节点 (右子树左侧链节点入栈)
JAVA代码
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
//左侧链入栈:左孩子不为空则入栈
if (root.left != null){
root = root.left;
stack.push(root);
}
else{ //否则访问左侧链最后一个节点,即栈顶元素
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
res.add(top.val);
if (top.right!=null){
root = top.right;
stack.push(root);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
后序遍历
左右中
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
- 递归
JAVA代码
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
res = help(root, res);
return res;
}
public List<Integer> help(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if (root!=null){
help(root.left,list);
help(root.right, list);
list.add(root.val);
}
return list;
}
}
- 迭代
由于前序 (中左右) 和中序 (左中右) 遍历要求每个节点要访问两遍,因此可以用栈实现。
后序遍历要求每个节点访问三次,因此需要借用两个栈。
根右左 的逆序是 左右根, 即为后序遍历。
而前序遍历为 根左右,只要前序遍历的过程改为先访问右孩子再访问左孩子,即为根右左.
因此可以考虑按照 根右左 的顺序访问节点,将访问的节点装入另一个栈中再弹出,顺序即为左右根.
注意的地方:由于需要得到 根右左 的顺序,因此入栈顺序为先入左孩子后入右孩子。
JAVA代码
//迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root==null) return res;
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>(); //根右左: 因此入栈顺序为先左孩子入栈,后右孩子入栈
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
stack1.add(root);
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
root = stack1.pop();
stack2.add(root);
if(root.left!=null){ //左孩子入栈
stack1.add(root.left);
}
if(root.right!=null){ //右孩子入栈
stack1.add(root.right);
}
}
while(!stack2.isEmpty()){
res.add(stack2.pop().val);
}
return res;
}
}
层次遍历
利用队列:先进先出
若访问当前节点,若左孩子存在,左孩子入栈;若右孩子存在,右孩子入栈.

JAVA代码
public class BTree_LevelOrder {
public List<Integer> levelOrder(TreeNode root){
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
root = queue.poll();
res.add(root.val);
if (root.left!=null) queue.offer(root.left); //若左孩子不为空,左孩子入队
if (root.right!=null) queue.offer(root.right); //若右孩子不为空,右孩子入队
}
return res;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
102. 二叉树的层次遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回其按层次遍历的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
例如:
给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
题解:
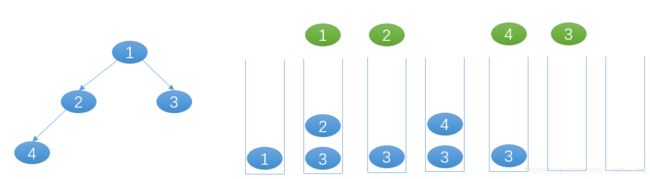
- 思路一
递归:先序遍历
借用一个help递归函数,传的值为:当前节点,当前节点的层数
- 根节点为空,返回空的 List
- 第0层只包含一个根节点 root.
- 若当前节点的层数大于 list 的个数,则增加一个空的 list
- 当前节点位于第几层就将该节点放进第几个list中.
- 递归当前节点的左孩子和右孩子,此时层数增 1
JAVA代码
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null) return res;
help(root, 0);
return res;
}
public void help(TreeNode root, int level){
if (res.size()-1<level){ //若最高层数小于当前层数,则res中再增加一个列表来装这一层的节点值
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
res.get(level).add(root.val); //对应的list装对应层的节点值
if (root.left!=null){
help(root.left, level+1);
}
if (root.right!=null){
help(root.right, level+1);
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度: O(n) 输出的数组包含n个值
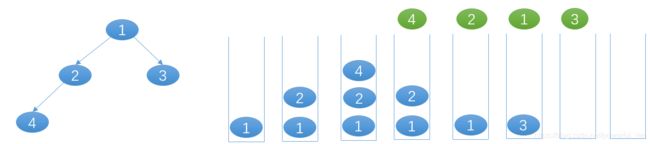
- 思路二
BFS迭代,借用队列
- 根节点为空时,返回空数组
- 根节点不空时,初始节点为root,入队,层数为0
- 每到新的一层增加一个新的空数组
- 当前层的节点即为当前队列中的所有节点,将队列中的节点逐一弹出并放入数组中,并将当前节点的左孩子右孩子放入队列中,level+1
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root==null) return res;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int level = 0; //初始时root为第0层
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
//当前层节点即为队列中的节点
int len = queue.size();
//当前层节点加入数组
for (int i=0; i<len; i++){
root = queue.poll();
res.get(level).add(root.val);
if (root.left!=null) queue.offer(root.left);
if (root.right!=null) queue.offer(root.right);
}
level++;
}
return res;
}
}
二叉树高度
二叉树任一节点高度,都等于其孩子节点的最大高度+1.
104. 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
题解:
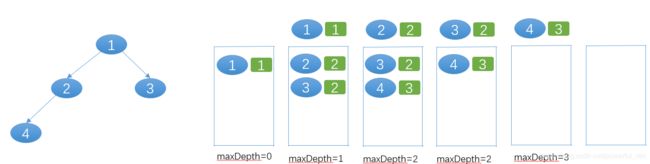
- 思路一
递归
根节点的深度等于左右子树中最深子树的高度 +1
JAVA代码
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
2. 思路二
BFS迭代:层次遍历,借用队列
队列的每个元素记录了:key:当前节点,value: 当前节点距离根节点的距离
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
Queue<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //队列形式{"节点","距离根节点的距离"}
if (root==null) return 0;
queue.offer(new Pair(root,1));
int max = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Pair<TreeNode,Integer> current = queue.poll();//当前节点
root = current.getKey();
int depth = current.getValue(); //当前节点距离根节点的距离
max = Math.max(max, depth);
if (root.left!=null)
queue.offer(new Pair(root.left,depth+1));
if (root.right!=null)
queue.offer(new Pair(root.right, depth+1));
}
return max;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
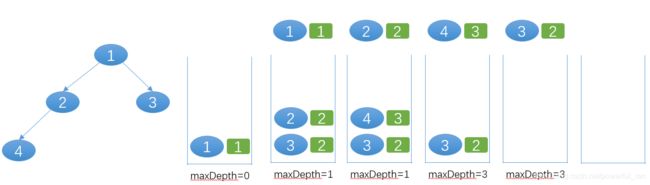
- 思路三
DFS 迭代:先序遍历,利用栈
栈的每个元素记录了:key:当前节点,value: 当前节点距离根节点的距离
//DFS: 先序遍历
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
Stack<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> stack = new Stack<>(); //队列形式{"节点","距离根节点的距离"}
if (root==null) return 0;
stack.push(new Pair(root,1));
int max = 1;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
Pair<TreeNode,Integer> current = stack.pop();//当前节点
root = current.getKey();
int depth = current.getValue(); //当前节点距离根节点的距离
max = Math.max(max, depth);
if (root.right!=null)
stack.push(new Pair(root.right,depth+1));
if (root.left!=null)
stack.push(new Pair(root.left, depth+1));
}
return max;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:完全不平衡时最坏O(n) ,完全平衡时最好O(logn)
111. 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最小深度 2.
题解:
- 递归
分三种情况:
- 当前节点只有左子树,返回左子树的高度+1
- 当前节点只有右子树,返回右子树的高度+1
- 当前节点又有左子树又有右子树,返回矮的那棵树的高度+1
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
//如果只有右子树,返回右子树的高度+1
if (root.left==null && root.right!=null) return minDepth(root.right)+1;
//如果只有左子树,返回左子树的高度+1
if (root.right==null && root.left!=null) return minDepth(root.left)+1;
//既有左子树又有右子树,返回左子树和右子树中较矮的高度+1
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left),minDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:最好O(logn),最坏O(logn)
2. DFS先序迭代,类似104
3. BFS队列,类似104
直观地打印一棵二叉树
福利函数
后继节点
285 二叉搜索树中的中序后继
【题目】 现在有一种新的二叉树节点类型如下:
public class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int data) { this.value = data; }
}
该结构比普通二叉树节点结构多了一个指向父节点的parent指针。
假设有一 棵Node类型的节点组成的二叉树,
树中每个节点的parent指针都正确地指向自己的父节点,
头节点的parent指向null。只给一个在二叉树中的某个节点 node,
请实现返回node的后继节点的函数。在二叉树的中序遍历的序列中,node的下一个节点叫作node的后继节。
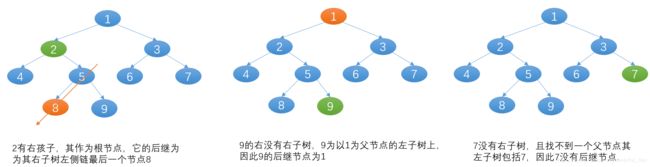
- 后继节点:按照中序遍历的顺序 左根右
- 若当前节点有右孩子,那么它的后继节点为右子树左侧链的最后一个节点
- 若当前节点没有右孩子,那么一直找父节点,节点在父节点的左子树中,则该父节点为其后继节点。
注意的地方:查看某一结点是否是某父节点左子树的中的节点,只需设一个临时指针p,初始时p为当前节点,然后查看p的父节点的左孩子是否为p, 若是,则该父节点为后继,否则p指向该父节点,继续找下一个父节点,知道找到根节点。
前驱节点
- 若该节点有左孩子,则前驱为左子树最右的节点
- 若该节点没有左孩子,那么一直往上找一个父节点,节点在父节点的右子树中,该父节点为其前驱节点。
序列化与反序列化
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
序列化是将一个数据结构或者对象转换为连续的比特位的操作,进而可以将转换后的数据存储在一个文件或者内存中,同时也可以通过网络传输到另一个计算机环境,采取相反方式重构得到原数据。
请设计一个算法来实现二叉树的序列化与反序列化。这里不限定你的序列 / 反序列化算法执行逻辑,你只需要保证一个二叉树可以被序列化为一个字符串并且将这个字符串反序列化为原始的树结构。
示例:
你可以将以下二叉树:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
序列化为 "[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]"
提示: 这与 LeetCode 目前使用的方式一致,详情请参阅 LeetCode 序列化二叉树的格式。你并非必须采取这种方式,你也可以采用其他的方法解决这个问题。
说明: 不要使用类的成员 / 全局 / 静态变量来存储状态,你的序列化和反序列化算法应该是无状态的。
解答:
- 思路一:
先序遍历方式,遇到空时,将空字符也加入序列。
public class BinaryTree_Serialize_Deserialize {
/******************二叉树 => 字符串*********************/
public static String serialize(TreeNode root){
if (root==null) return "null,";
String str = Integer.toString(root.val)+",";
str += serialize(root.left);
str += serialize(root.right);
return str;
}
/*******************字符串 => 二叉树*******************/
public TreeNode deserialize(String data){
String[] data_array = data.split(","); //按照"," 切分
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//将元素装入队列
for (int i=0; i<data_array.length; i++){
queue.offer(data_array[i]);
}
return deserialize_preOrder(queue);
}
//中序方式将字符串转化为二叉树
public TreeNode deserialize_preOrder(Queue<String> queue){
String val = queue.poll();
if (val.equals("null")) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(val));
root.left = deserialize_preOrder(queue);
root.right = deserialize_preOrder(queue);
return root;
}
}
- 思路二:
中序遍历方式、后序遍历
3.思路三:
层序遍历
平衡二叉树
110. 平衡二叉树
树形动态规划
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
示例 1:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回 true 。
解答:
- 思路一
自底向下
(1) 判断左子数是否平衡,若不是直接返回 false
(2)判断右子树是否平衡,若不是直接返回 false
(3)左子树的高度
(4)右子树的高度
若左平衡,右平衡, 且左子树的高度与右子树的高度差1, 则该子树平衡.
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return recur(root) != -1;
}
public int recur(TreeNode root){
if (root == null) return 0; //根节点若为空,则返回高度为0
int left = recur(root.left);
if (left == -1) return -1; //若左子树不平衡,返回-1
int right = recur(root.right);
if (right == -1) return -1; //若右子树不平衡,返回-1
//若左右平衡且高度相差小于2,则整颗树平衡,高度为较高子树高度+1,
//若左右平衡且高度相差小于2,则整棵树不平衡,返回-1
return Math.abs(left-right)<2? Math.max(left, right)+1: -1;
}
}
时间复杂度 O(n)
空间复杂度 O(n)
- 思路二
自顶向下
每一个节点左子树高度与右子树高度差都小于2,则整棵树为平衡树。
需要求每个节点的高度,造成冗余。
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null) return true;
return Math.abs(depth(root.left)-depth(root.right))<2 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
public int depth(TreeNode root){
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(depth(root.left),depth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
空间复杂度:O(n)
完全二叉树
958. 二叉树的完全性检验
给定一个二叉树,确定它是否是一个完全二叉树。
百度百科中对完全二叉树的定义如下:
若设二叉树的深度为 h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第 h 层所有的结点都连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。(注:第 h 层可能包含 1~ 2h 个节点。)
示例 1:

输入:[1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:true
解释:最后一层前的每一层都是满的(即,结点值为 {1} 和 {2,3} 的两层),且最后一层中的所有结点({4,5,6})都尽可能地向左。
题解:
按层遍历
-
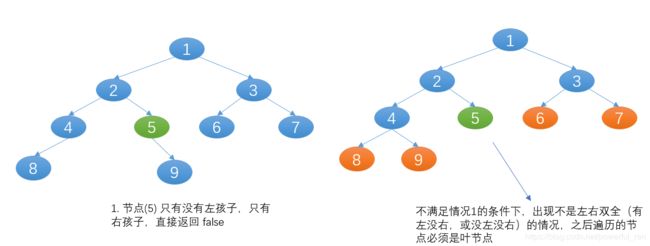
- 一个节点没有左孩子,有右孩子,一定不是完全二叉树,直接返回
false
- 一个节点没有左孩子,有右孩子,一定不是完全二叉树,直接返回
class Solution {
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
boolean leaf = false;
//层遍历
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
root = queue.poll();
//3. 前面出现左右孩子双全的节点,若当前节点不是叶子,返回false
//2. 或者当前节点没有左孩子,但有右孩子,返回false
if ((leaf && (root.left!=null || root.right!=null)) //
||(root.left==null && root.right!=null)){
return false;
}
if (root.left!=null) queue.offer(root.left);
if (root.right != null) queue.offer(root.right);
else leaf = true; //1. 当不是左右孩子双全时,后面遍历的节点必须是叶子的情况开启
}
return true;
}
}
时间复杂度:每个节点访问一下 O(n)
空间复杂度:树的最大宽度O(w)
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
说明:
完全二叉树的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例:
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ /
4 5 6
输出: 6
题解:
来自左chengyun的思路
- 求出树高
h:只需遍历左侧链 - 求出右子树的高度:
- 等于
h-1:- 左子树是完全二叉树,左子树+根节点个数:
2^(h-1) -1+1 - 右子树递归计算节点个数
- 左子树是完全二叉树,左子树+根节点个数:
- 等于
h-2:- 右子树是完全二叉树,右子树+根节点个数:
2^(h-2) -1+1 - 左子树递归计算节点个数
- 右子树是完全二叉树,右子树+根节点个数:
递归函数bfs: root-当前子树根节点,level- 当前子树根节点层数,h-树总高,返回当前子树总节点数。
计算子树高度函数leLftLevel

JAVA代码
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int h = leftLevel(root, 1);
return bfs(root, 1, h);
}
public int bfs(TreeNode root, int level, int h){
if (level == h) return 1; //注意的点
//左子树完全二叉
if (leftLevel(root.right, level+1) == h){
return (1<<(h-level)) + bfs(root.right, level+1, h);
}
else { //右子树完全二叉
return (1<<(h-level-1))+bfs(root.left, level+1, h);
}
}
//遍历左侧链,得到子树高度
public static int leftLevel(TreeNode root, int level){
while (root!=null){
level++;
root = root.left;
}
return level-1;
}
}
路径
112. 路径总和
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
解答:
- DFS递归:先序
- 当根节点为空时,返回false
- 当根节点为空时,
- 当前节点不为叶子,对左、右孩子调用
hasPathSum函数:通过递归left || right,其中sum值减去当前节点的权值。 - 当前节点为叶子,且sum值为0时,为有效路径。否则路径无效。
- 当前节点不为叶子,对左、右孩子调用
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root==null) return false;
sum -=root.val;
if (root.left==null&& root.right==null && sum==0)
return true;
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum);
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:最坏O(n), 最好O(logn)
- DFS迭代
借用栈,栈元素:{root, sum-val}
栈中存放节点及对应的sum,当前节点为叶子且sum值为0时,为有效路径。
- 根节点为空时,返回false
- 根节点不为空时,
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return false;
Stack<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> stack = new Stack<>();
sum = sum - root.val;
stack.push(new Pair(root,sum));
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
Pair<TreeNode, Integer> current = stack.pop();
root = current.getKey();
sum = current.getValue();
if (root.left==null && root.right==null && sum==0){
return true;
}
if (root.right!=null) stack.push(new Pair(root.right, sum-root.right.val));
if (root.left!=null) stack.push(new Pair(root.left, sum-root.left.val));
}
return false;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:最坏O(n), 最好O(logn)
437. 路径总和 III
给定一个二叉树,它的每个结点都存放着一个整数值。
找出路径和等于给定数值的路径总数。
路径不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
二叉树不超过1000个节点,且节点数值范围是 [-1000000,1000000] 的整数。
示例:
root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], sum = 8
10
/ \
5 -3
/ \ \
3 2 11
/ \ \
3 -2 1
返回 3。和等于 8 的路径有:
1. 5 -> 3
2. 5 -> 2 -> 1
3. -3 -> 11
题解:
递归方法:
由于路径不一定从根节点开始,任何一个节点都可能开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束。
情况分为包括当前根节点的路径和不包括根节点的路径。
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
int num = 0;
if (root == null) return num;
if (root.val == sum) num +=1;
//与root无关的路径
num += pathSum(root.left, sum);
num += pathSum(root.right, sum);
//与root有关的路径,不能直接递归pathSum, 会出现断路的情况
num += pathSum_root(root.left, sum-root.val);
num += pathSum_root(root.right, sum-root.val);
return num;
}
public int pathSum_root(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int num = 0;
if (root.val == sum) num += 1;
//与root无关的路径
num += pathSum_root(root.left, sum-root.val);
num += pathSum_root(root.right, sum-root.val);
return num;
}
}
【自我总结(不一定正确)】
时间复杂度:每个节点都要作为起点计算一次路径 O(n), 每个节点计算路径时间复杂度O(logn)
所以时间复杂度为 O(nlogn)
空间复杂度: O(n)
“需要进一步看题解,现在看不懂,后面再看”
687. 最长同值路径
给定一个二叉树,找到最长的路径,这个路径中的每个节点具有相同值。 这条路径可以经过也可以不经过根节点。
注意:两个节点之间的路径长度由它们之间的边数表示。
示例 1:
输入:
5
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
1 1 5
输出:
2
示例 2:
输入:
1
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
4 4 5
输出:
2
还有其他路径题,别忘了。
其他
543. 二叉树的直径
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
示例 :
给定二叉树
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
返回 3, 它的长度是路径 [4,2,1,3] 或者 [5,2,1,3]。
注意:两结点之间的路径长度是以它们之间边的数目表示。
// 一条路径的长度为该路径经过的节点数减一
//最长路径:max{左子树最长路径,右子树最长路径,经过根节点的最长路径}
//=》最长路径:max{左子树最长路径,右子树最长路径,左子树深度+右子树深度}
class Solution {
int diameter = 0; //使用全局变量保存访问过的节点中的最长路径
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root==null) return 0;
depth(root);
return diameter;
}
//求当前子树高度
public int depth(TreeNode root){
if (root==null) return 0;
int left = depth(root.left);
int right = depth(root.right);
diameter = Math.max(left+right, diameter);
return 1+Math.max(left,right);
}
}
226. 翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
示例:
输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
617. 合并二叉树
给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠。
你需要将他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
示例 1:
输入:
Tree 1 Tree 2
1 2
/ \ / \
3 2 1 3
/ \ \
5 4 7
输出:
合并后的树:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
5 4 7
注意: 合并必须从两个树的根节点开始。
572. 另一个树的子树
给定两个非空二叉树 s 和 t,检验 s 中是否包含和 t 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。s 的一个子树包括 s 的一个节点和这个节点的所有子孙。s 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
示例 1:
给定的树 s:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
给定的树 t:
4
/ \
1 2
返回 true,因为 t 与 s 的一个子树拥有相同的结构和节点值。
示例 2:
给定的树 s:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
/
0
给定的树 t:
4
/ \
1 2
101. 对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
说明:
如果你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题,会很加分。
404. 左叶子之和
计算给定二叉树的所有左叶子之和。
示例:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
在这个二叉树中,有两个左叶子,分别是 9 和 15,所以返回 24
337. 打家劫舍 III
在上次打劫完一条街道之后和一圈房屋后,小偷又发现了一个新的可行窃的地区。这个地区只有一个入口,我们称之为“根”。 除了“根”之外,每栋房子有且只有一个“父“房子与之相连。一番侦察之后,聪明的小偷意识到“这个地方的所有房屋的排列类似于一棵二叉树”。 如果两个直接相连的房子在同一天晚上被打劫,房屋将自动报警。
计算在不触动警报的情况下,小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,3,null,3,null,1]
3
/ \
2 3
\ \
3 1
输出: 7
解释: 小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额 = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
示例 2:
输入: [3,4,5,1,3,null,1]
3
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
1 3 1
输出: 9
解释: 小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额 = 4 + 5 = 9.
671. 二叉树中第二小的节点 (简单)
给定一个非空特殊的二叉树,每个节点都是正数,并且每个节点的子节点数量只能为 2 或 0。如果一个节点有两个子节点的话,那么这个节点的值不大于它的子节点的值。
给出这样的一个二叉树,你需要输出所有节点中的第二小的值。如果第二小的值不存在的话,输出 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:
2
/ \
2 5
/ \
5 7
输出: 5
说明: 最小的值是 2 ,第二小的值是 5 。
示例 2:
输入:
2
/ \
2 2
输出: -1
说明: 最小的值是 2, 但是不存在第二小的值。
637. 二叉树的层平均值
给定一个非空二叉树, 返回一个由每层节点平均值组成的数组.
示例 1:
输入:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输出: [3, 14.5, 11]
解释:
第0层的平均值是 3, 第1层是 14.5, 第2层是 11. 因此返回 [3, 14.5, 11].
注意:节点值的范围在32位有符号整数范围内。
题解:
1. 思路一:DFS递归
递归遍历二叉树,用两个数组分别记录每一层的总值和节点的总个数.
需要一个新的递归函数来完成:help(),参数有:
root:当前节点值
sum: 每一层的总值,第i层的值累加到第i个元素中
count: 每一层节点总个数,第i层的个数累加到第i个元素中
i:当前节点所在层数,每次向下遍历层数增1.
class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
List<Double> res = new ArrayList<>();
//List sum = new ArrayList<>(); //节省一个变量空间
List<Integer> count = new ArrayList<>();
help(root, 0, res, count);
for (int i=0; i<res.size(); i++){
res.set(i, res.get(i)/count.get(i));
}
return res;
}
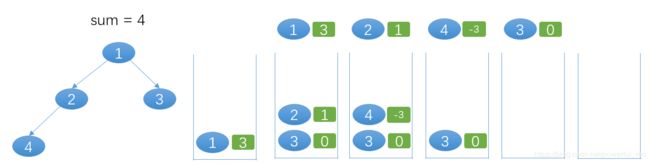
public void help(TreeNode root, int i, List<Double> sum, List<Integer> count){
if (root==null) return ;
if (i < sum.size()){
sum.set(i, sum.get(i) + root.val);
count.set(i, count.get(i) + 1);
}else{
sum.add(1.0*root.val);
count.add(1);
}
help(root.left, i+1, sum, count); //向下遍历,层数+1
help(root.right, i+1, sum, count); //向下遍历,层数+1
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(h)
2. BFS:借用队列
使用两个队列:一个队列存放当前层节点,一个临时队列存放下一层节点。
下一次层节点时,即访问临时队列中存放的节点。
class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
List<Double> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return null;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){ //当前层节点不空
int count = 0;
long sum = 0; //注意:sum为长整型
Queue<TreeNode> temp = new LinkedList<>(); //装下一层节点的队列
while(!queue.isEmpty()){ //当前层节点不空
root = queue.poll();
sum += root.val;
count++;
//下一层节点入临时队列
if (root.left!=null) temp.offer(root.left);
if (root.right!=null) temp.offer(root.right);
}
//当前层平均值
res.add(1.0*sum/count);
//开始遍历下一层
queue = temp;
}
return res;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(w)
513. 找树左下角的值 (中等)
给定一个二叉树,在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。
示例 1:
输入:
2
/ \
1 3
输出:
1
示例 2:
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
/ / \
4 5 6
/
7
输出:
7
注意: 您可以假设树(即给定的根节点)不为 NULL。
题解:
1. 思路一:DFS递归
借助一个二维数组,每一行元素保存对应层的所有结点,最后一行元素的第一个结点即为最后一层的最左结点。
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
List<List<TreeNode>> array = new ArrayList<>();
List<TreeNode> subArray = new ArrayList<>();
help(root, 0, array, subArray);
return array.get(array.size()-1).get(0).val;
}
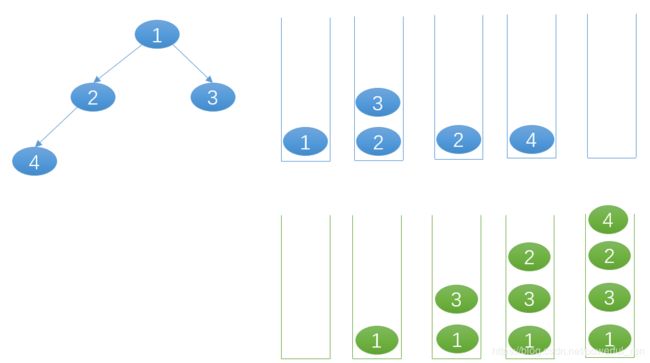
public void help(TreeNode root, int i, List<List<TreeNode>> array, List<TreeNode> subArray){
if (root==null) return;
if (i<array.size()){
subArray.add(root);
}else{
subArray = new ArrayList<>();
subArray.add(root);
array.add(subArray);
}
help(root.left, i+1, array, subArray);
help(root.right, i+1, array, subArray);
}
}
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(n)
2.思路二:DFS
记录深度达到最大时的第一个结点:当到达的深度大于目前的最大深度时,为第一次到达该最大深度,最大深度更新。
class Solution {
int maxLevel = -1;
int leftVal = 0;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
help (root, 0);
return leftVal;
}
public void help(TreeNode root, int i){
if (root==null) return;
if (i>maxLevel){
maxLevel = i;
leftVal = root.val;
}
help(root.left, i+1);
help(root.right, i+1);
}
}
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(h)
3. 思路三:BFS
利用队列,每一层从右向左遍历,最后遍历到的最后一个结点即为最后一层最左的结点。
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
root = queue.poll();
if (root.right!=null){
queue.offer(root.right);
}
if (root.left!=null){
queue.offer(root.left);
}
}
return root.val;
}
}
时间复杂度O(n)
时间复杂度O(w)
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
1. 思路一: DFS递归
- 当前左子树有
p和q,则在左子树找 - 当前右子树有
p和q,则在右子树找 - 否则当前节点就是最近公共祖先节点
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (hasNode(root.left,p) && hasNode(root.left,q)) //左子树有节点p和q,则最近祖先在左子树找
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
else if (hasNode(root.right,p) && hasNode(root.right,q)) //右子树有节点p和q,则最近祖先在右子树找
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
return root; //否则当前节点为最近祖先节点
}
//子树中是否存在节点t
public boolean hasNode(TreeNode node, TreeNode t){
if (node == null) return false;
if (node.val == t.val) return true;
return help(node.left,t) || help(node.right,t);
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n^2)
空间复杂度:O(h)
- 思路二:
这个函数的功能有三个:给定两个节点 p 和 q
如果 p 和 q都存在,则返回它们的公共祖先;
如果只存在一个,则返回存在的一个;
如果 p和 q都不存在,则返回NULL
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left == null) return right;
if (right == null) return left;
if (left!=null && right!=null) return root;
return null;
}
}
时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复复杂度:O(h)