有序二维数组查找的两种方法:从左上角(递归)和右上角(非递归)出发
有序二维数组查找
这道题是在学习剑指offer这本书看到的,原题如下所示:
在一个二维数组中,每行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
分块治之
在拿到题目的时候,我并没有找到右上角那么优秀的特征,所以我选择二分查找的有序数组的思想,最初的想法是从最小值(左上角)到最大值(右下角)进行扇形搜索。
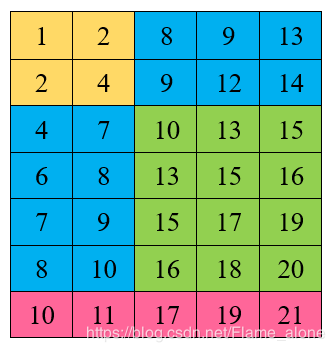
例如上边的这个数组,但是发现该数组并不具备这样的条件,因为扇形搜索的话,同半径下的元素,例如9,9,7,6这四个元素并不相等,但是发现一个有趣的规律,假如我沿着该矩阵左上角最大最小值这样的对角线,针对7这个元素进行搜索,搜索到绿色区域10这个元素时,绿色部分均大于等于10,进而大于7,而黄色部分均小于7,这样便可以将黄,绿两个区域进行排除,只搜索蓝色区域即可,同时针对蓝色区域同样执行一样的搜索模式,这样的话便可以分块递归处理了。同时为了处理不对称情况作出了以下处理:
- 只针对矩阵中从左上角出发最大的正形矩阵进行搜索,剩下的矩阵(粉红区域)下一步搜索
- 对于当前搜索矩阵,当在对角线搜索到目标值时,返回当前搜索区域已搜索到目标值
- 当前搜索矩阵左上角第一个元素大于目标值时,返回当前搜索区域无目标值
- 当前搜索矩阵右下角第一个元素小于目标值时,返回当前搜索区域无目标值
- 当前搜索矩阵对角线中部存在大于目标值元素时,搜索进一步该元素的蓝色区域
学过数据结构与算法的同学一样就可以看出这个算法的弊端,当这个二维数组退化为一维数组时,本算法的时间复杂度也会退化成 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。不过作为脑海中的第一种实现方法,我还是打算把它记录下来。代码如下 :
template <typename item>
bool _FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopLeft(item *array, item value, int startx, int starty, int endx, int endy,
int column) {
assert(startx <= endx && starty <= endy);
int currentrow = endx - startx;
int currentcolumn = endy - starty;
int count = currentrow < currentcolumn ? currentrow : currentcolumn;
// std::cout << startx << "," \
// << starty << "-->"\
// << endx << ","\
// << endy << "\n";
item currentItem = 0;
int currentX = startx;
int currentY = starty;
for (int i = 0; i <= count; ++i, ++currentX, ++currentY) {
currentItem = array[currentX * column + currentY];
if (currentItem == value) {
return true;
} else if (currentItem > value) {
if (i == 0) return false;
else {
if (_FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopLeft(array, value, currentX, starty, endx, currentY - 1,
column)) return true;
return _FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopLeft(array, value, startx, currentY, currentX - 1, endy,
column);
}
}
}
currentX --;
currentY --;
if (currentrow > currentcolumn) {
if (currentX == endx) return false;
else
return _FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopLeft(array, value, currentX + 1, starty, endx, endy, column);
} else {
if (currentY == endy) return false;
else
return _FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopLeft(array, value, startx, currentY + 1, endx, endy, column);
}
}
template <typename item>
bool FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopLeft(item *array, item value, int row, int column){
return _FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopLeft(array, value, 0, 0, row - 1, column - 1, column);
}
剑指offer解法
当然从右上角搜索是更为优化的一种算法了,因为这个算法是利用单列最小这个特性所以跟矩阵形状无关,如下图所示,直接从右上角对该矩阵进行搜索,当右上角元素大于目标元素时,直接排除其所在这一列(绿色区域),当右上角元素小于目标元素,直接排除这一行(蓝色区域),这样的话每一步搜索都可以对一行(列)进行排除,搜索效率较高。

template <typename item>
bool FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopRight(item *matrix, item number, int rows, int columns)
{
bool found = false;
if(matrix != nullptr && rows > 0 && columns > 0)
{
int row = 0;
int column = columns - 1;
while(row < rows && column >=0)
{
// std::cout << row << "," \
// << column << "-->"\
// << rows-1 << ","\
// << 0 << "\n";
if(matrix[row * columns + column] == number)
{
found = true;
break;
}
else if(matrix[row * columns + column] > number)
-- column;
else
++ row;
}
}
return found;
}
编写的自动化测试代码如下:
template <typename T>
void test_find_sorted_matrix(const std::string &findName, bool (*find)(T *, T, int, int), T *array, int value,
int rows, int columns, bool expect, int count = 10000000) {
clock_t startTime, endTime;
startTime = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
assert(find(array, value, rows, columns)==expect);
}
endTime = clock();
std::cout<<findName << " : "<<(double)(endTime-startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" s."<<std::endl;
}
void test_all_find_sorted_matrix(int n,int m,int count = 1){
assert(n < 21 && m < 21);
int array[n][m];
for (int k = 0; k < m; ++k) {
array[0][k] = k;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
array[i][j] = array[i-1][j] + array[i-1][m-1];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
std::cout << array[i][j] << "\t";
}
std::cout << "\n";
}
int value = array[rand()%n][rand()%m];
test_find_sorted_matrix("Find Top Right Corner", flame::CodingInterviewChinese::FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopRight<int>, (int *) array,
value, n, m,true, count);
test_find_sorted_matrix("Find Top Left Corner", flame::CodingInterviewChinese::FindInPartiallySortedMatrixTopLeft<int>, (int *) array,
value, n, m, true,count);
}
}
性能测试
经测试从左上角搜索,只针对对角线元素性能较优(2-3倍),从右上角搜索整体较优(2-3倍),感兴趣的朋友可以运行测试一下。