DbUtils源码分析系列(二)
今天分析一下QueryRunner这个DbUtils核心类,它
利用可插拨的策略执行SQL查询来处理ResultSets。QueryRunner类图如下所示:
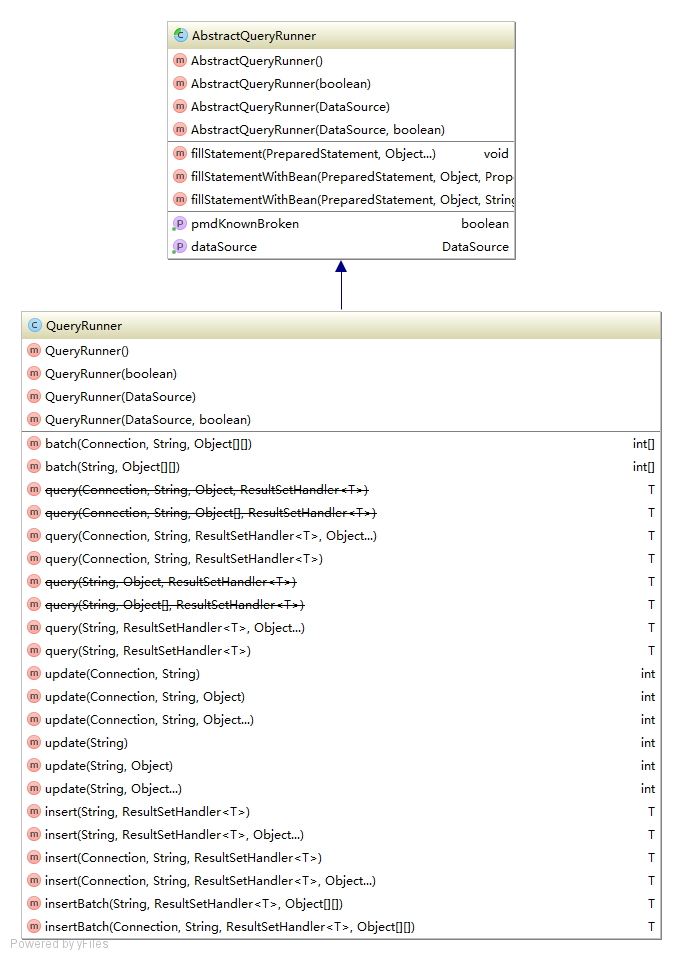
从类图中我们可以看出它继承AbstractQueryRunner。
QueryRunner构造器有多个重载方法:
public AbstractQueryRunner() {
ds = null;
}
/**
* Constructor to control the use of ParameterMetaData.
*
* @param pmdKnownBroken
* Some drivers don't support
* {@link ParameterMetaData#getParameterType(int) }; if
* pmdKnownBroken is set to true, we won't even try
* it; if false, we'll try it, and if it breaks, we'll remember
* not to use it again.
*/
public AbstractQueryRunner(boolean pmdKnownBroken) {
this.pmdKnownBroken = pmdKnownBroken;
ds = null;
}
/**
* Constructor to provide a DataSource. Methods that do not
* take a Connection parameter will retrieve connections from
* this DataSource.
*
* @param ds
* The DataSource to retrieve connections from.
*/
public AbstractQueryRunner(DataSource ds) {
this.ds = ds;
}
/**
* Constructor to provide a DataSource and control the use of
* ParameterMetaData. Methods that do not take a
* Connection parameter will retrieve connections from this
* DataSource.
*
* @param ds
* The DataSource to retrieve connections from.
* @param pmdKnownBroken
* Some drivers don't support
* {@link ParameterMetaData#getParameterType(int) }; if
* pmdKnownBroken is set to true, we won't even try
* it; if false, we'll try it, and if it breaks, we'll remember
* not to use it again.
*/
public AbstractQueryRunner(DataSource ds, boolean pmdKnownBroken) {
this.pmdKnownBroken = pmdKnownBroken;
this.ds = ds;
}构造函数中有两个成员变量:boolean类型的pmdKnownBroken和DataSource类型的ds。
有些情况下,你需要在PreparedStatement中设置空值,这个时候如果你还使用设置具体类型的方法,如setInt(1,null),程序会毫不留情的报出空指针异常,所以你需要做的是使用setNull(index, type)方法来代替你原来的方法。例如
stmt.setNull(1,Types.INTEGER);第二个参数为java.sql.Types中具体的类型值,你可以通过Types查找到你需要的具体类型。通过这个方法,就可以完成在PreparedStatement设置null值,前提当然是你的数据库字段允许null值。
pmdKnownBroken这个变量,源码的解释是这样的:有些数据库驱动程序不支持ParameterMetaData.getParameterType方法,如果pmdKnownBroken设置为false,在调用fillStatement进行SQL参数填充的时候,如果某个参数值为NULL,我们则会尝试着使用ParameterMetaData.getParameterType方法来获取参数类型,如果有异常抛出,则将pmdKnownBroken值置为 true,以后不再使用。如果pmdKnownBroken设置为true,不进行getParameterType尝试处理。
pmdKnownBroken被定义为volatile类型原因是为了保证这个类的线程安全性。它可以用来确保变量的更新操作通知到其他线程。需要注意的是volatile变量只能保证可见性,在当且仅当满足以下条件的时候才应该使用它:
- 在访问变量时不需要加锁
- 对变量的写入操作不会依赖变量的当前值,或者确保只有当个线程更新变量值
- 该变量不会和其他状态变量一起纳入不变性条件中
显然pmdKnownBroken满足以上使用条件。它只是某个状态标记。
private volatile boolean pmdKnownBroken = false;
/**
* Fill the PreparedStatement replacement parameters with the
* given objects.
*
* @param stmt
* PreparedStatement to fill
* @param params
* Query replacement parameters; null is a valid
* value to pass in.
* @throws SQLException
* if a database access error occurs
*/
public void fillStatement(PreparedStatement stmt, Object... params)
throws SQLException {
// check the parameter count, if we can
ParameterMetaData pmd = null;
if (!pmdKnownBroken) {
pmd = stmt.getParameterMetaData();
int stmtCount = pmd.getParameterCount();
int paramsCount = params == null ? 0 : params.length;
if (stmtCount != paramsCount) {
throw new SQLException("Wrong number of parameters: expected "
+ stmtCount + ", was given " + paramsCount);
}
}
// nothing to do here
if (params == null) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
if (params[i] != null) {
stmt.setObject(i + 1, params[i]);
} else {
// VARCHAR works with many drivers regardless
// of the actual column type. Oddly, NULL and
// OTHER don't work with Oracle's drivers.
int sqlType = Types.VARCHAR;
if (!pmdKnownBroken) {
try {
/*
* It's not possible for pmdKnownBroken to change from
* true to false, (once true, always true) so pmd cannot
* be null here.
*/
sqlType = pmd.getParameterType(i + 1);
} catch (SQLException e) {
pmdKnownBroken = true;
}
}
stmt.setNull(i + 1, sqlType);
}
}
}DataSource是用来获取数据库连接的,如何获取DataSource对象呢,这得需要借助于commons里的dbcp和pool这两个组件。
QueryRunner中剩下的方法就是数据库的CRUD操作接口了。
分类说明一下:
- query
执行SELECT查询语句,返回结果集Handler生成的对象 - update
执行 INSERT, UPDATE, 或者 DELETE 语句,返回影响的行数 - insert/insertBatch
执行INSERT语句,并返回生成的键值 - batch
执行批量INSERT, UPDATE, 或者 DELETE 语句,返回影响的行数数组int[]
当需要向数据库发送一批SQL语句执行时,应避免向数据库一条条的发送执行,而应采用JDBC的批处理机制,以提升执行效率。实现批处理有两种方式:
- 采用Statement.addBatch(sql)方式实现批量静态的SQL。优点:可以向数据库发送多条不同的SQL语句。缺点:SQL语句没有预编译。当向数据库发送多条语句相同,但仅参数不同的SQL语句时,需重复写上很多条SQL语句。
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//连续添加多条静态SQL
stmt.addBatch("insert into testdb.book (kind, name) values ('java', 'java in aciton')");
stmt.addBatch("insert into testdb.book (kind, name) values ('c', 'c in aciton')");
stmt.addBatch("delete from testdb.book where kind ='C#'");
stmt.addBatch("update testdb.book set kind = 'JAVA' where kind='java'");
// stmt.addBatch("select count(*) from testdb.book"); //批量执行不支持Select语句
//执行批量执行
stmt.executeBatch(); - 采用PreparedStatement.addBatch()批量执行预定义模式的SQL 。优点:发送的是预编译后的SQL语句,执行效率高。缺点:只能应用在SQL语句相同,但参数不同的批处理中。因此此种形式的批处理经常用于在同一个表中批量插入数据,或批量更新表的数据。
String sql = "insert into testdb.book (kind, name) values (?,?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, "java");
pstmt.setString(2, "java in action");
pstmt.addBatch(); //添加一次预定义参数
pstmt.setString(1, "c");
pstmt.setString(2, "c in action");
pstmt.addBatch(); //再添加一次预定义参数
//批量执行预定义SQL
pstmt.executeBatch(); QueryRunner中的批处理方法batch/insertBatch采用的是第二种方式。
/**
* Calls update after checking the parameters to ensure nothing is null.
* @param conn The connection to use for the batch call.
* @param closeConn True if the connection should be closed, false otherwise.
* @param sql The SQL statement to execute.
* @param params An array of query replacement parameters. Each row in
* this array is one set of batch replacement values.
* @return The number of rows updated in the batch.
* @throws SQLException If there are database or parameter errors.
*/
private int[] batch(Connection conn, boolean closeConn, String sql, Object[][] params) throws SQLException {
if (conn == null) {
throw new SQLException("Null connection");
}
if (sql == null) {
if (closeConn) {
close(conn);
}
throw new SQLException("Null SQL statement");
}
if (params == null) {
if (closeConn) {
close(conn);
}
throw new SQLException("Null parameters. If parameters aren't need, pass an empty array.");
}
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
int[] rows = null;
try {
stmt = this.prepareStatement(conn, sql);
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
this.fillStatement(stmt, params[i]);
stmt.addBatch();
}
rows = stmt.executeBatch();
} catch (SQLException e) {
this.rethrow(e, sql, (Object[])params);
} finally {
close(stmt);
if (closeConn) {
close(conn);
}
}
return rows;
}具体来说明一下QueryRunner父类中的fillStatementWithBean这个方法,它可以为SQL语句参数指定bean变量值,也就是JavaBean与特定数据表的映射了。Hibernate、JPA等框架能够自动完成对象与关系型数据库的映射,底层的实现也诸如此类吧!
/**
* Fill the PreparedStatement replacement parameters with the
* given object's bean property values.
*
* @param stmt
* PreparedStatement to fill
* @param bean
* A JavaBean object
* @param propertyNames
* An ordered array of property names (these should match the
* getters/setters); this gives the order to insert values in the
* statement
* @throws SQLException
* If a database access error occurs
*/
public void fillStatementWithBean(PreparedStatement stmt, Object bean,
String... propertyNames) throws SQLException {
PropertyDescriptor[] descriptors;
try {
descriptors = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean.getClass())
.getPropertyDescriptors();
} catch (IntrospectionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Couldn't introspect bean "
+ bean.getClass().toString(), e);
}
PropertyDescriptor[] sorted = new PropertyDescriptor[propertyNames.length];
for (int i = 0; i < propertyNames.length; i++) {
String propertyName = propertyNames[i];
if (propertyName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("propertyName can't be null: "
+ i);
}
boolean found = false;
for (int j = 0; j < descriptors.length; j++) {
PropertyDescriptor descriptor = descriptors[j];
if (propertyName.equals(descriptor.getName())) {
sorted[i] = descriptor;
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
throw new RuntimeException("Couldn't find bean property: "
+ bean.getClass() + " " + propertyName);
}
}
fillStatementWithBean(stmt, bean, sorted);
}基本过程是这样的:
1. 通过内省机制获取指定bean实例的PropertyDescriptor[]数组,这样呢,就有了对bean属性的直接操作能力了;
2. 根据指定的参数名数组propertyNames,实例化一个PropertyDescriptor[]数组,这个数组,主要的呢,就是存储PreparedStatement指定的参数名对应bean实例中的属性的PropertyDescriptor对象;
3. 将propertyNames与Bean的属性进行比较,确保为每个属性名找到在bean中对应的PropertyDescriptor实例 。
4. 执行fillStatementWithBean的重载方法通过指定stmt中参数的bean实例对应的属性描述数组,进行参数填充。
/**
* Fill the PreparedStatement replacement parameters with the
* given object's bean property values.
*
* @param stmt
* PreparedStatement to fill
* @param bean
* a JavaBean object
* @param properties
* an ordered array of properties; this gives the order to insert
* values in the statement
* @throws SQLException
* if a database access error occurs
*/
public void fillStatementWithBean(PreparedStatement stmt, Object bean,
PropertyDescriptor[] properties) throws SQLException {
Object[] params = new Object[properties.length];
for (int i = 0; i < properties.length; i++) {
PropertyDescriptor property = properties[i];
Object value = null;
Method method = property.getReadMethod();
if (method == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No read method for bean property "
+ bean.getClass() + " " + property.getName());
}
try {
value = method.invoke(bean, new Object[0]);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Couldn't invoke method: " + method,
e);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Couldn't invoke method with 0 arguments: " + method, e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Couldn't invoke method: " + method,
e);
}
params[i] = value;
}
fillStatement(stmt, params);
}这个方法遍历给定的bean属性描述数组PropertyDescriptor[],获取属性对应的getter方法,
Method method = property.getReadMethod();通过反射调用getter方法获取属性值 。
value = method.invoke(bean, new Object[0]);
将获取到的属相值保存到 Object[] 数组中,
params[i] = value;最后调用fillStatement(stmt, params)填充参数。
fillStatement(stmt, params);