C++11多线程异步操作std::future
本博客参考自https://thispointer.com/c11-tutorial/
C++多线程的在某些场景需要实现异步操作,由std::futer 和std::asych, std::packaged_task, std::promise搭配使用。
目录
1.std::future
2.std::promise
3.std::asych
4.std::packaged_task
1.std::future
std::future是一个类模板,它的模板类可访问“未来”的值,从而实现异步访问。
创建语法:
与std::futer 和std::asych, std::packaged_task, std::promise搭配使用对应的创建语法如下
std::future futureObj = promiseObj.get_future(); std::future resultFromDB = std::async(std::launch::async, fetchDataFromDB, "Data"); std::future result = task.get_future(); 调用语法:
获取future结果有三种方式:get、wait、wait_for,其中get等待异步操作结束并返回结果,wait只是等待异步操作完成,没有返回值,wait_for是超时等待返回结果(参考自https://blog.csdn.net/daaikuaichuan/article/details/81173303)
std::cout<
2.std::promise
创建语法:
std::promise promiseObj; 调用语法:
promObj->set_value(35);完整代码:
#include
#include
#include
void initiazer(std::promise * promObj)
{
std::cout<<"Inside Thread"<set_value(35);
}
int main()
{
std::promise promiseObj;
std::future futureObj = promiseObj.get_future();
std::thread th(initiazer, &promiseObj);
std::cout< 3.std::asych
创建语法:
std::asych直接在创建时就与future变量关联,并且创建对应的线程。与普通的多线程不同的是它可以通过future得到该线程函数的结果。
std::future resultFromDB = std::async(std::launch::async, fetchDataFromDB, "Data");
完整代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std::chrono;
std::string fetchDataFromDB(std::string recvdData)
{
// Make sure that function takes 5 seconds to complete
std::this_thread::sleep_for(seconds(5));
//Do stuff like creating DB Connection and fetching Data
return "DB_" + recvdData;
}
std::string fetchDataFromFile(std::string recvdData)
{
// Make sure that function takes 5 seconds to complete
std::this_thread::sleep_for(seconds(5));
//Do stuff like fetching Data File
return "File_" + recvdData;
}
int main()
{
// Get Start Time
system_clock::time_point start = system_clock::now();
std::future resultFromDB = std::async(std::launch::async, fetchDataFromDB, "Data");
//Fetch Data from File
std::string fileData = fetchDataFromFile("Data");
//Fetch Data from DB
// Will block till data is available in future object.
std::string dbData = resultFromDB.get();
// Get End Time
auto end = system_clock::now();
auto diff = duration_cast < std::chrono::seconds > (end - start).count();
std::cout << "Total Time Taken = " << diff << " Seconds" << std::endl;
//Combine The Data
std::string data = dbData + " :: " + fileData;
//Printing the combined Data
std::cout << "Data = " << data << std::endl;
return 0;
} 4.std::packaged_task
创建语法:
输入模板是函数原型std::packaged_task
std::packaged_task task(getDataFromDB); 调用语法:
这时packaged_task对象就相当于普通的回调函数,传入thread对象实现多线程,与普通的多线程不同的是它可以通过future得到该线程函数的结果。
// Fetch the associated future<> from packaged_task<>
std::future result = task.get_future();
// Pass the packaged_task to thread to run asynchronously
std::thread th(std::move(task), "Arg"); 完整代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
// Fetch some data from DB
std::string getDataFromDB( std::string token)
{
// Do some stuff to fetch the data
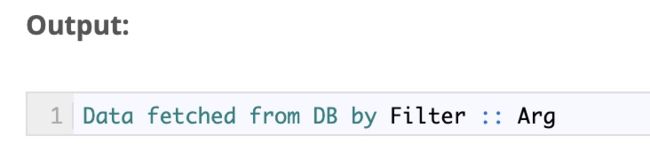
std::string data = "Data fetched from DB by Filter :: " + token;
return data;
}
int main()
{
// Create a packaged_task<> that encapsulated the callback i.e. a function
std::packaged_task task(getDataFromDB);
// Fetch the associated future<> from packaged_task<>
std::future result = task.get_future();
// Pass the packaged_task to thread to run asynchronously
std::thread th(std::move(task), "Arg");
// Join the thread. Its blocking and returns when thread is finished.
th.join();
// Fetch the result of packaged_task<> i.e. value returned by getDataFromDB()
std::string data = result.get();
std::cout << data << std::endl;
return 0;
}