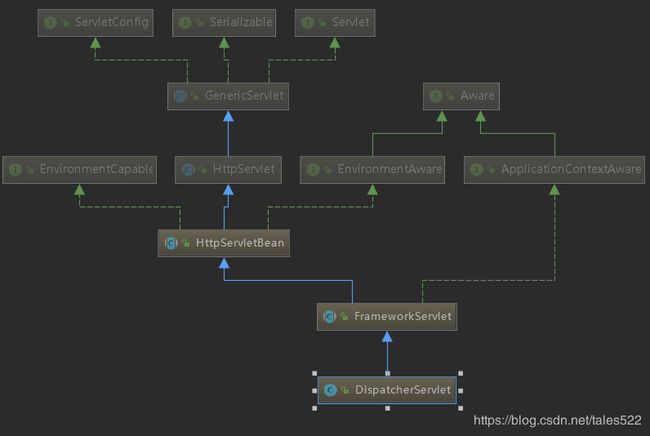
SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet初始化流程
对于SpringMVC启动流程,我们首先要从大方向上把握,那就是他也是处在Java EE容器中的组件,所以必须会和Java EE的规范流程有一定关系,具体说来就是容器会先后初始化Listener,Filter,Servlet,所以我们可以看到web.xml中配置了Spring的启动入口ContextLoaderListener,
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
具体的工作就是父类ContextLoader#contextInitialized()来实现的,我们就不看细节了,这个方法的主要工作就是创建root ioc,root ioc将作为全局变量存放到ApplicationContext中,创建过程中会调用AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()方法,这个里面就就是具体的ioc初始化等工作了。Listener中完成后就是Filter初始化了,这里就略过了,Filter初始化完成后就是Servlet初始化了,在SpringMVC中就是DispatcherServlet了,DispatcherServlet最终继承于Servlet,所以本质上和我们认知的Servlet没有区别,上面的IOC容器是Spring的,下面DispatcherServlet也会创建一个IOC容器,这两个IOC容器是父子关系,下面我们来看看具体流程:
Servlet这里就不做解释了,我们直接看HttpServletBean的init()方法,这个就是入口:
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}看到下面的initServletBean()方法了没,看看吧:
protected void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
}没错,留给子类实现了,下面是FrameworkServlet中的实现:
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}然后这里又有个initWebApplicationContext()方法,是我们需要看的:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}然后里面有个onRefresh()方法,一样的套路又是,留给子类来实现:
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}我们来看看子类DispatcherServlet的实现:
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}