数据结构精录&总结Episode.8 数据结构入门之查找(基于Visual C++)
最近两天魅族17手机发布,罗永浩老师又要开始直播带货了。但是一改往日的自信,罗永浩老师对于本次魅族17发布会的态度不甚悲观。其中他在微博上的回复提到,魅族17发布会看不看都无所谓,因为首先是可以看回放,其次是大家口头支持一波实际上还是都买Iphone去了。
有点酸,但是支持国货当然更不应该停留在言论上。2020Q1季度的财报显示,手机成交额/成交量仍然是Iphone11占领头衔,除次以外小米Redmi系列勉强上榜,诸如华为等国内一众呼声很高的企业连影子都没有。
再过两天博主也决定要将自己的Iphone更换成华为P40 Pro了,不管曾经这些公司怎么样,做了什么,支持国货总是有利无弊的。尤其是在当前疫情期间国际经济等等形势都不景气的情况下。
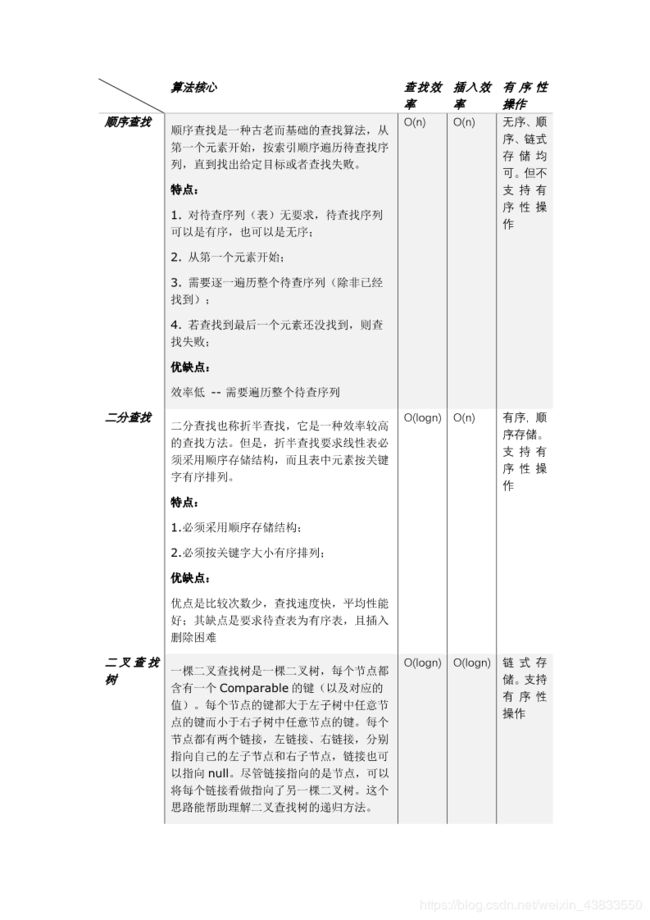
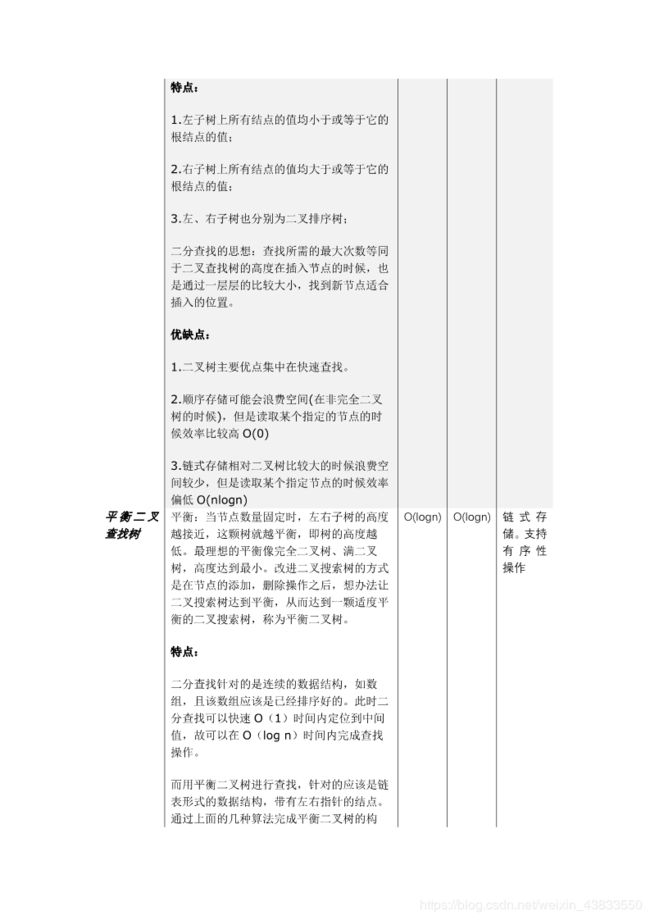
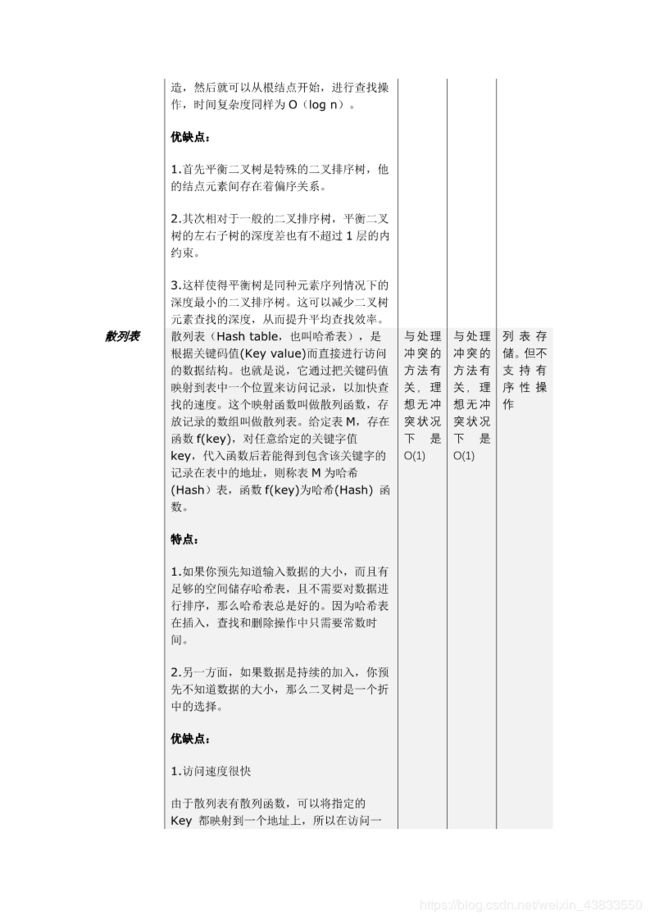
查找算法,总结起来分为线性表查找、树表查找和散列表查找三大类,其中线性表查找分为顺序查找和折半查找,树表查找分为二叉查找树与平衡二叉查找树。实际上树表查找中还有许许多多的子分支如红黑树,这些对于非计算机专业的同学来说仅需了解,故次从略。以下是博主自行编写的的查找算法总结表。
上述总结对应的代码如下,具体解释等已嵌入注释中。
// 第八章 查找.cpp : 此文件不包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将分别在下述的各个cpp中。编写—JoeyBG,算法尚有不足之处,敬请谅解。
//
/*
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
*/
// 运行程序: Ctrl + F5 或调试 >“开始执行(不调试)”菜单
// 调试程序: F5 或调试 >“开始调试”菜单
// 入门使用技巧:
// 1. 使用解决方案资源管理器窗口添加/管理文件
// 2. 使用团队资源管理器窗口连接到源代码管理
// 3. 使用输出窗口查看生成输出和其他消息
// 4. 使用错误列表窗口查看错误
// 5. 转到“项目”>“添加新项”以创建新的代码文件,或转到“项目”>“添加现有项”以将现有代码文件添加到项目
// 6. 将来,若要再次打开此项目,请转到“文件”>“打开”>“项目”并选择 .sln 文件 //顺序查找
#include
using namespace std;
#define Maxsize 100
int SqSearch(int r[],int n,int x)//顺序查找
{
for(int i=0;i>n;
cout<<"请依次n个元素:"<>r[i];
r2[i+1]=r[i];//r2[]数组0空间未用,做监视哨
}
cout<>x;
//i=SqSearch(r,n,x);
// if(i==-1)
// cout<<"该数列中没有要查找的元素"< //折半查找
#include
#include //排序sort函数需要该头文件
#include
using namespace std;
const int M=100;
int x,n,i;
int s[M];
int BinarySearch(int s[],int n,int x)//二分查找非递归算法
{
int low=0,high=n-1; //low指向有序数组的第一个元素,high指向有序数组的最后一个元素
while(low<=high)
{
int middle=(low+high)/2; //middle为查找范围的中间值
if(x==s[middle]) //x等于查找范围的中间值,算法结束
return middle;
else if(x>s[middle]) //x大于查找范围的中间元素,则从左半部分查找
low=middle+1;
else //x小于查找范围的中间元素,则从右半部分查找
high=middle-1;
}
return -1;
}
int recursionBS (int s[],int x,int low,int high) //二分查找递归算法
{
//low指向数组的第一个元素,high指向数组的最后一个元素
if(low>high) //递归结束条件
return -1;
int middle=(low+high)/2; //计算middle值(查找范围的中间值)
if(x==s[middle]) //x等于s[middle],查找成功,算法结束
return middle;
else if(x>n;
cout<<"请依次输入数列中的元素:";
for(i=0;i>s[i];
sort(s,s+n); //二分查找的序列必须是有序的,如果无序需要先排序
cout<<"排序后的数组为:";
for(i=0;i>x;
//i=BinarySearch(s,n,x);
i=recursionBS(s,x,0,n-1);
if(i==-1)
cout<<"该数列中没有要查找的元素"< //二叉查找树
#include
using namespace std;
#define ENDFLAG -1
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct BSTNode{
ElemType data; //结点数据域
BSTNode *lchild,*rchild; //左右孩子指针
}BSTNode,*BSTree;
BSTree SearchBST(BSTree T,ElemType key)//二叉排序树的递归查找
{
//若查找成功,则返回指向该数据元素结点的指针,否则返回空指针
if((!T)|| key==T->data)
return T;
else if (keydata)
return SearchBST(T->lchild,key);//在左子树中继续查找
else
return SearchBST(T->rchild,key); //在右子树中继续查找
}
void InsertBST(BSTree &T,ElemType e)//二叉排序树的插入
{
//当二叉排序树T中不存在关键字等于e的数据元素时,则插入该元素
if(!T)
{
BSTree S=new BSTNode; //生成新结点
S->data=e; //新结点S的数据域置为e
S->lchild=S->rchild=NULL;//新结点S作为叶子结点
T=S; //把新结点S链接到已找到的插入位置
}
else if(edata)
InsertBST(T->lchild,e );//插入左子树
else if(e>T->data)
InsertBST(T->rchild,e);//插入右子树
}
void CreateBST(BSTree &T )//二叉排序树的创建
{
//依次读入一个关键字为key的结点,将此结点插入二叉排序树T中
T=NULL;
ElemType e;
cin>>e;
while(e!=ENDFLAG)//ENDFLAG为自定义常量,作为输入结束标志
{
InsertBST(T,e); //插入二叉排序树T中
cin>>e;
}
}
void DeleteBST(BSTree &T,char key)
{
//从二叉排序树T中删除关键字等于key的结点
BSTree p=T;BSTree f=NULL;
BSTree q;
BSTree s;
if(!T) return; //树为空则返回
while(p)//查找
{
if(p->data==key) break; //找到关键字等于key的结点p,结束循环
f=p; //f为p的双亲
if (p->data>key)
p=p->lchild; //在p的左子树中继续查找
else
p=p->rchild; //在p的右子树中继续查找
}
if(!p) return; //找不到被删结点则返回
//三种情况:p左右子树均不空、无右子树、无左子树
if((p->lchild)&&(p->rchild))//被删结点p左右子树均不空
{
q=p;
s=p->lchild;
while(s->rchild)//在p的左子树中继续查找其前驱结点,即最右下结点
{
q=s;
s=s->rchild;
}
p->data=s->data; //s的值赋值给被删结点p,然后删除s结点
if(q!=p)
q->rchild=s->lchild; //重接q的右子树
else
q->lchild=s->lchild; //重接q的左子树
delete s;
}
else
{
if(!p->rchild)//被删结点p无右子树,只需重接其左子树
{
q=p;
p=p->lchild;
}
else if(!p->lchild)//被删结点p无左子树,只需重接其右子树
{
q=p;
p=p->rchild;
}
/*――――――――――将p所指的子树挂接到其双亲结点f相应的位置――――――――*/
if(!f)
T=p; //被删结点为根结点
else if(q==f->lchild)
f->lchild=p; //挂接到f的左子树位置
else
f->rchild=p;//挂接到f的右子树位置
delete q;
}
}
void InOrderTraverse(BSTree &T)//中序遍历
{
if(T)
{
InOrderTraverse(T->lchild);
cout<data<<"\t";
InOrderTraverse(T->rchild);
}
}
int main()
{
BSTree T;
cout<<"请输入一些整型数,-1结束"<>key;
BSTree result=SearchBST(T,key);
if(result)
cout<<"找到"<>key;
DeleteBST(T,key);
cout<<"当前有序二叉树中序遍历结果为"< //平衡二叉查找树
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef struct AVLNode{
int data;
int height;
struct AVLNode *lchild;
struct AVLNode *rchild;
}*AVLTree;
AVLTree Empty(AVLTree &T)//删除树
{
if(T==NULL) return NULL;
Empty(T->lchild);
Empty(T->rchild);
delete T;
return NULL;
}
inline int Height(AVLTree T)//计算高度
{
if(T==NULL) return 0;
return T->height;
}
void updateHeight(AVLTree &T)
{
T->height=max(Height(T->lchild),Height(T->rchild))+1;
}
AVLTree LL_Rotation(AVLTree &T)//LL旋转
{
AVLTree temp=T->lchild;
T->lchild=temp->rchild;
temp->rchild=T;
updateHeight(T);//更新高度
updateHeight(temp);
return temp;
}
AVLTree RR_Rotation(AVLTree &T)//RR旋转
{
AVLTree temp=T->rchild;
T->rchild=temp->lchild;
temp->lchild=T;
updateHeight(T);//更新高度
updateHeight(temp);
return temp;
}
AVLTree LR_Rotation(AVLTree &T)//LR旋转
{
T->lchild=RR_Rotation(T->lchild);
return LL_Rotation(T);
}
AVLTree RL_Rotation(AVLTree &T)//RL旋转
{
T->rchild=LL_Rotation(T->rchild);
return RR_Rotation(T);
}
AVLTree Insert(AVLTree &T,int x)
{
if(T==NULL) //如果为空,创建新结点
{
T=new AVLNode;
T->lchild=T->rchild=NULL;
T->data=x;
T->height=1;
return T;
}
if(T->data==x) return T;//查找成功,什么也不做,查找失败时才插入
if(xdata)//插入到左子树
{
T->lchild=Insert(T->lchild,x);//注意插入后饭后结果挂接到T->lchild
if(Height(T->lchild)-Height(T->rchild)==2)//插入后看是否平衡,如果不平衡显然是插入的那一边高度大
{ //沿着高度大的那条路径判断
if(xlchild->data)//判断是LL还是LR,即插入的是lchild节点的lchild 还是rchild
T=LL_Rotation(T);
else
T=LR_Rotation(T);
}
}
else//插入到右子树
{
T->rchild=Insert(T->rchild,x);
if(Height(T->rchild)-Height(T->lchild)==2)
{
if(x>T->rchild->data)
T=RR_Rotation(T);
else
T=RL_Rotation(T);
}
}
updateHeight(T);
return T;
}
AVLTree adjust(AVLTree &T)//删除结点后,需要判断是否还是平衡,如果不平衡,就要调整
{
if(T==NULL) return NULL;
if(Height(T->lchild)-Height(T->rchild)==2)//沿着高度大的那条路径判断
{
if(Height(T->lchild->lchild)>=Height(T->lchild->rchild))
T=LL_Rotation(T);
else
T=LR_Rotation(T);
}
if(Height(T->rchild)-Height(T->lchild)==2)//沿着高度大的那条路径判断
{
if(Height(T->rchild->rchild)>=Height(T->rchild->lchild))
T=RR_Rotation(T);
else
T=RL_Rotation(T);
}
updateHeight(T);
return T;
}
AVLTree Delete(AVLTree &T,int x)
{
if(T==NULL) return NULL;
if(T->data==x)//如果找到删除节点
{
if(T->rchild==NULL)//如果该节点的右孩子为NULL,那么直接删除
{
AVLTree temp=T;
T=T->lchild;
delete temp;
}
else//否则,将其右子树的最左孩子作为这个节点,并且递归删除这个节点的值
{
AVLTree temp;
temp=T->rchild;
while(temp->lchild)
temp=temp->lchild;
T->data=temp->data;
T->rchild=Delete(T->rchild,T->data);
updateHeight(T);
}
return T;
}
if(T->data>x)//调节删除节点后可能涉及的节点
T->lchild=Delete(T->lchild,x);
if(T->datarchild=Delete(T->rchild,x);
updateHeight(T);
T=adjust(T);
return T;
}
void Preorder(AVLTree T)//前序遍历方便看树的结果
{
if(T==NULL) return ;
cout<data<<"\t"<height<lchild);
Preorder(T->rchild);
}
void Inorder(AVLTree T)//中序遍历方便看树的结果
{
if(T==NULL) return ;
Inorder(T->lchild);
cout<data<<"\t"<height<rchild);
}
void Posorder(AVLTree T)//后序遍历方便看树的结果
{
if(T==NULL) return ;
Posorder(T->lchild);
Posorder(T->rchild);
cout<data<<"\t"<height<>n;
for(int i=0;i>x;
T=Insert(T,x);
}
return T;
}
int main()
{
int x;
AVLTree root=NULL;
root=Empty(root);
CreateAVL(root);
show(root);
cin>>x;
root=Delete(root,x);
show(root);
return 0;
}
//散列表
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define m 15//哈希表的表长
#define NULLKEY 0//单元为空的标记
int HT[m],HC[m];
int H(int key)//哈希函数
{
return key%13;
}
int Linedetect(int HT[],int H0,int key,int &cnt)
{
int Hi;
for(int i=1;i>x;//14 36 42 38 40 15 19 12 51 65 34 25
if(!InsertHash(HT,x))
{
cout<<"创建哈希表失败!"<>x;
int result=SearchHash(HT,x);
if(result!=-1)
cout<<"在第"< /*
参考资料:
1、陈小玉:趣学数据结构,人民邮电出版社,2019.09
*/
由于查找章节北理乐学平台是没有给出具体的代码练习题的,仅有知识点考核的选择题,在仔细阅读了上述总结的概念和代码后,正确回答它们不难,此略。