人工智能:MNIST手写数字识别问题的单神经元模型实践
NIST手写数字识别问题的单神经元模型实践
按课程案例,动手完成编码实践。
在不改变模型的结构基础上,尝试采用不同的学习率、单批次样本数、训练轮数等超参数,让模型的准确率达到90%。
提交要求:
1、你认为最优的一次带运行结果的源代码文件(.ipynb 格式)
2、作为附件上传
评分标准:
1、完成案例中的代码,有完整的代码,模型能运行,准确率达87%以上;得6分;
2、准确率达89%以上;再得2分,否则得0分;
3、准确率达90%以上;再得2分,否则得0分;
代码:
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #图像的显示
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
tf.disable_eager_execution()
class Mnist:
def __init__(self,route):
self.mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(route,one_hot = True)
#定义待输入数据的占位符
self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name="X") #每张图片28*28个像素点
self.y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name="Y")
#定义模型变量
self.W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784,10]),name = "W")
self.b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]),name = "b")
#定义前向计算
self.forward = tf.matmul(self.x,self.W) + self.b #矩阵的叉乘
self.pred = tf.nn.softmax(self.forward) #Softmax 分类
def Param(self):
self.train_epochs = 300 #训练轮数
self.batch_size = 100 #单次训练样本数
self.total_batch = int(self.mnist.train.num_examples/self.batch_size) #一轮训练有多少批次
self.display_step = 1 #显示粒度
self.learning_rate = 0.01 #学习率
def Model(self):
#定义损失函数
self.loss_function = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(self.y*tf.log(self.pred),reduction_indices = 1))
#梯度下降优化器
self.optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(self.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss_function)
#定义准确率
self.correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(self.pred,1),tf.argmax(self.y,1)) #argmax将最大标签取出来
#准确率,将布尔型转换为浮点型,并计算平均值
self.accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(self.correct_prediction,tf.float32))
self.sess = tf.Session() #声明回话
self.init = tf.global_variables_initializer() #变量的初始化
self.sess.run(self.init)
class Train(Mnist): #类Train继承类Mnist
def iteration(self):
#开始训练
for epoch in range(self.train_epochs):
for batch in range(self.total_batch):
self.xs,self.ys = self.mnist.train.next_batch(self.batch_size) #读取批次数据
self.sess.run(self.optimizer,feed_dict={self.x:self.xs,self.y:self.ys}) #执行批次训练
#使用验证集计算误差和准确率
self.loss,self.acc = self.sess.run([self.loss_function,self.accuracy],
feed_dict={self.x:self.mnist.validation.images,self.y:self.mnist.validation.labels})
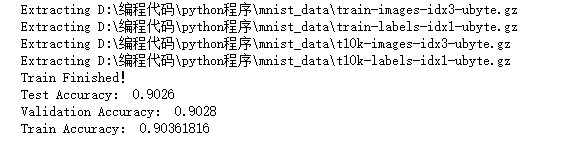
print("Train Finished!")
def Result(self):
#预测结果
self.prediction_result = self.sess.run(tf.argmax(self.pred,1),feed_dict={self.x:self.mnist.test.images})
def Print(self):
#完成训练后,在测试集上评估模型的准确率
self.accu_test = self.sess.run(self.accuracy,feed_dict={self.x:self.mnist.test.images,self.y:self.mnist.test.labels})
print("Test Accuracy:",self.accu_test)
#完成训练后,在验证集上评估模型的准确率
self.accu_validation = self.sess.run(self.accuracy,feed_dict={self.x:self.mnist.validation.images,self.y:self.mnist.validation.labels})
print("Validation Accuracy:",self.accu_validation)
#完成训练后,在测试集上评估模型的准确率
self.accu_train = self.sess.run(self.accuracy,feed_dict={self.x:self.mnist.train.images,self.y:self.mnist.train.labels})
print("Train Accuracy:",self.accu_train)
Train.Result(self) #预测结果
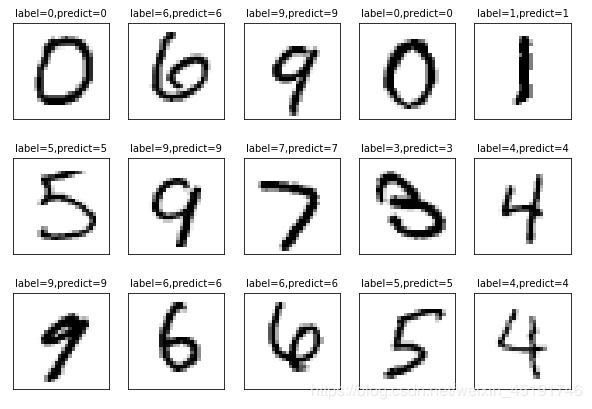
def plot_images_labels_prediction(self,images,labels,prediction,index,num=10):
#函数文档
"""
images:图像列表
labels:标签列表
prediction:预测值列表
index:从第index个开始显示
num=10:缺省依次显示10幅
"""
self.fig = plt.gcf() #获取当前图标
self.fig.set_size_inches(10,12)
if num > 25:
num = 25 #最多显示25个子图
for i in range(num):
self.ax = plt.subplot(5,5,i+1) #获取当前需要处理的子图
#显示第index个图像
self.ax.imshow(np.reshape(images[index],(28,28)),cmap="binary")
self.title = "label=" + str(np.argmax(labels[index])) #标题
if len(prediction) > 0:
self.title += (",predict=" + str(prediction[index]))
self.ax.set_title(self.title,fontsize=10) #显示标题信息字体大小10号
self.ax.set_xticks([]) #不显示坐标轴
self.ax.set_yticks([])
index += 1
plt.show()
def Plot(self):
self.plot_images_labels_prediction(self.mnist.test.images,self.mnist.test.labels,self.prediction_result,10,15)
route = r"D:\编程代码\python程序\mnist_data" #r表示原始字符串
T = Train(route) #创建类Train对象实例T
T.Param() #设置训练参数
T.Model() #模型准备工作
T.iteration() #开始迭代训练
T.Print() #打印准确率
T.Plot() #可视化结果的最终画图