Shiro框架:认证和授权原理
前言
Shiro作为解决权限问题的常用框架,常用于解决认证、授权、加密、会话管理等场景。本文将对Shiro的认证和授权原理进行介绍:
- Shiro可以做什么?
- Shiro是由什么组成的?
- 举个Shiro的例子呗?
- Shiro认证的原理是咋样的?
- Shiro授权的原理是咋样的?
1. Shiro可以做什么?
在构建一个网络应用的时候,权限检验管理作为非常重要的安全措施,需要包含以下几点:
- 用户认证 — 用户身份识别。得知道来的人是谁;
- 用户授权 — 用户权限访问控制。得知道来的人有没有资格进来,又不是“我家大门常打开”;
- 密码加密 — 加密敏感数据,防止被偷窥。就像是家里上锁,上几把锁,原子锁还是电子锁?
- 会话管理 — 与用户相关的时间敏感的状态信息。类似于阅后即焚的信件。
Shiro支持以上的功能,而且它提供的API可以帮助我们很容易就开发出足够好的应用。Shiro具备认证、授权、加密、会话管理、集成Web、缓存等功能,相当好用。
2. Shiro是由什么组成的?
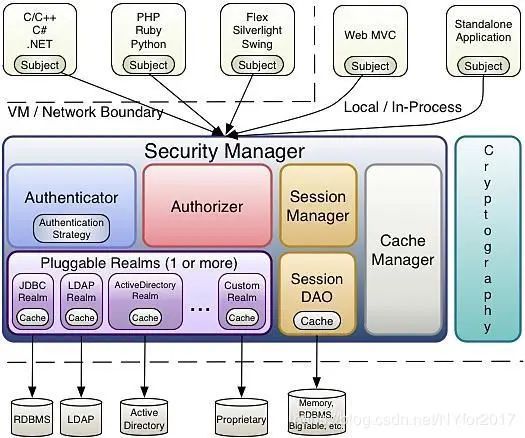
下图是Shiro的架构图:
可以看出来,Security Manager是Shiro的核心,连认证、授权、会话管理等都是在这里面执行的。接下来我们来看看这些组件分别是做什么用的:
- Subject:主体,可以是用户或程序,主体可以访问Security Manager以获得认证、授权、会话等服务;
- Security Manager:安全管理器,主体所需的认证、授权功能都是在这里进行的,是Shiro的核心;
- § Authenticator:认证器,主体的认证过程通过Authenticator进行;
- § Authorizer:授权器,主体的授权过程通过Authorizer进行;
- § Session Manager:shiro的会话管理器,与web应用提供的Session管理分隔开;
- § Session DAO:通过Session DAO管理Session数据,针对个性化的Session数据存储,需要使用到Session DAO;
- § Cache Manager:缓存管理器,主要对Session和授权数据进行缓存。因为这些数据不怎么改变,为了提高访问速度选择将其缓存起来;
- § Realm:域,可以有一个或多个域,可通过Realm存储授权和认证的逻辑;
- Cryptography:密码管理,Shiro提供了一套加密/解密的组件,如MD5散列算法等。
3. 举个Shiro的例子呗?
笔者采用Shiro官网给的例子,来梳理Shiro认证、授权的过程:
shiro.ini
创建一个文件shiro.ini,其功用相当于Realm。shiro默认使用的也是IniRealm:
# =============================================================================
# Tutorial INI configuration
#
# Usernames/passwords are based on the classic Mel Brooks' film "Spaceballs" :)
# =============================================================================
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Users and their (optional) assigned roles
# username = password, role1, role2, ..., roleN
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[users]
root = secret, admin
guest = guest, guest
presidentskroob = 12345, president
darkhelmet = ludicrousspeed, darklord, schwartz
lonestarr = vespa, goodguy, schwartz
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Roles with assigned permissions
# roleName = perm1, perm2, ..., permN
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[roles]
admin = *
schwartz = lightsaber:*
goodguy = winnebago:drive:eagle5
在上面这串代码中,已经给出了用户和角色信息。root = secret, admin表示,用户名为root,密码是secret,角色是admin;**schwartz = lightsaber:**表示角色schwartz拥有权限lightsaber:。
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.session.Session;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Tutorial {
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Tutorial.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("My First Apache Shiro Application");
//引用shiro.ini的配置信息
Factory factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
//获取SecurityManager安全管理器
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// get the currently executing user:
//获取单签主体(用户)
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!)
//获取当前主体的会话
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");
if (value.equals("aValue")) {
log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
}
// let's login the current user so we can check against roles and permissions:
//判断当前用户是否认证
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
//将账号和密码封装为UsernamePasswordToken中
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
//记住我
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
//进行登录操作
currentUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " +
"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//unexpected condition? error?
}
}
//say who they are:
//print their identifying principal (in this case, a username):
log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully.");
//test a role:
//检查是否有相应角色权限
if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) {
log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!");
} else {
log.info("Hello, mere mortal.");
}
//test a typed permission (not instance-level)
//判断是否有资源操作权限
if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")) {
log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only.");
}
//a (very powerful) Instance Level permission:
if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) {
log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. " +
"Here are the keys - have fun!");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!");
}
//all done - log out!
//退出
currentUser.logout();
System.exit(0);
}
}
我们可以从示例代码中提取出认证、授权过程中比较常用的API:
认证
//获取当前主体(用户)
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//判断当前用户是否认证
currentUser.isAuthenticated()
//将账号和密码封装为UsernamePasswordToken中
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
//记住我
token.setRememberMe(true);
//进行登录操作
currentUser.login(token);
判断权限
//检查是否有相应角色权限
currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")
//判断是否有资源操作权限
currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")
从上面代码我们可以看出,Shiro中认证过程大概是:
- 先获取当前用户信息,判断当前用户是否认证
- 如果没认证,就将账号和密码封装成UserPasswordToken,进行登录操作
接下来,我们通过读源码,来看看Shiro的认证和授权原理是怎么样的。
4. Shiro认证的原理是咋样的?
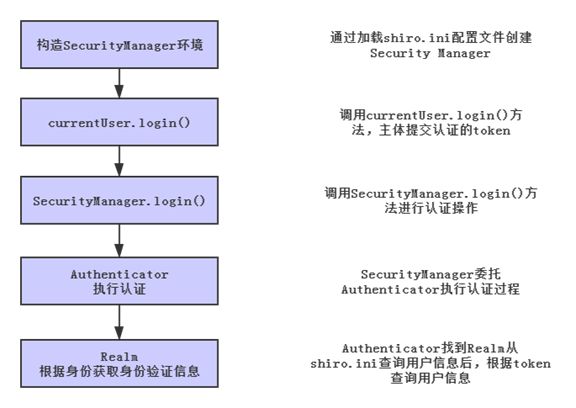
通过从login()方法使用Debug追踪Shiro的认证逻辑,可以得到以下代码执行顺序:
//在构造了Security Manager之后,提交认证,参数是封装了用户信息的token
currentUser.login(token);
//Security Manager执行认证
Subject subject = this.securityManager.login(this, token);
AuthenticationInfo info = this.authenticate(token);
//Security Manager委托给Authenticator执行认证逻辑
this.authenticator.authenticate(token);
AuthenticationInfo info = this.doAuthenticate(token);
//获取多Realm进行身份认证
Collection realms = this.getRealms();
doSingleRealmAuthentication(realm, token);
AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token);
//调用对应的Realm进行校验,认证成功则返回用户属性
AuthenticationInfo info = realm.doGetAuthenticationInfo(token);
简单说,认证过程的流程是这样的:
5. Shiro授权的原理是咋样的?
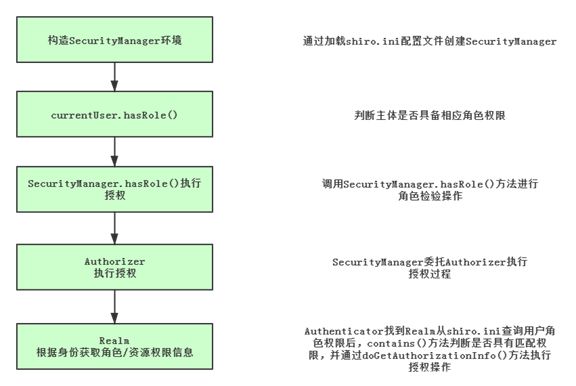
我们还是追踪一下源码,可以知道以下执行顺序:
//判断当前主体是否有角色限制
currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")
//判断当前主体是否具备资源操作权限
currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")
//委托给securityManager判断角色是否与既定的角色匹配
this.securityManager.hasRole(this.getPrincipals(), roleIdentifier)
//securityManager委托Authorizer进行角色检验
this.authorizer.hasRole(principals, roleIdentifier)
//Authorizer判断Realm的角色/权限是否和传入的匹配
AuthorizationInfo info = this.getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
return info.getRoles().contains(roleIdentifier)
//执行Realm进行授权操作
info = this.doGetAuthorizationInfo(principals);
简单点看,Shiro的授权过程是这样的:
综上,我们可以知道,无论是认证还是授权操作,都需要SecurityManager中的Realm来定义用户认证时需要的账户信息,以及授权时所需的权限信息。而Realm一般不会采用Shiro官网介绍的“ini配置文件”方式,而是通过自定义Realm组件来实现:
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
/**
* 执行授权逻辑
*
* @param principalCollection
* @return
*/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
User user = (User) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
SecurityUtils.getSubject().getSession().setAttribute(String.valueOf(user), SecurityUtils.getSubject().getPrincipals());
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
info.addRole(...);
return info;
}
/**
* 执行认证逻辑
*
* @param authenticationToken
* @return
* @throws AuthenticationException
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken;
User user = userService.findByName(token.getUsername());
if (user == null || !token.getUsername().equals(user.getUsername())) {
throw new UnknownAccountException("此账号不存在");
}
...
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user);
}
}如果采用上述方式来定义Realm,那么还需要自定义ShiroConfig作为组件。
参考资料:
shiro原理及其运行流程介绍
极简入门,Shiro的认证与授权流程解析
关注微信公众号"木不是丁";获取更多学习资源
![]()