Python3爬虫从零开始:Beautiful Soup的使用
中文文档:https://beautifulsoup.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/v4.4.0/#id49
基本用法
实例1:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html ="""
The Dormouse's story
The Dormouse's story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters;and
their names were
,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
...
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.prettify())
print(type(soup))
print(soup.title.string)
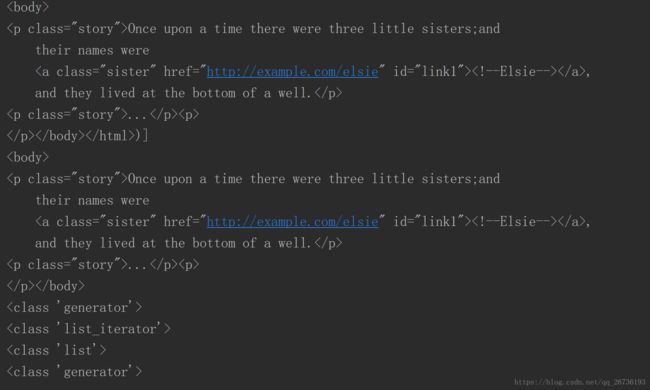
结果:
说明1:
可以看到,我们输入的并不是一个完整的HTML字符串,缺少了等标签,我们初始化BeautifulSoup时完成了自动更正格式。
说明2:
soup.prettify()方法将xml/html标签独占一行:https://beautifulsoup.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/v4.4.0/#id49
节点选择器
实例2:提取信息和嵌套选择
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html ="""
The Dormouse's story
The Dormouse's story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters;and
their names were
,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
...
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
#获取节点#
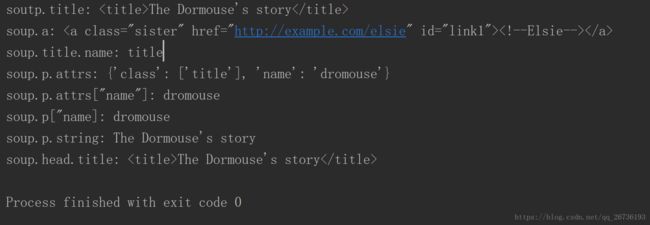
print('soutp.title:',soup.title) #选择元素
print('soup.a:',soup.a) #取得的只是第一个a节点
#获取名称#
print('soup.title.name:',soup.title.name) # .name获取名称
#获取属性#
print('soup.p.attrs:',soup.p.attrs) # .attrs获取所有属性
print('soup.p.attrs["name"]:',soup.p.attrs['name']) #获取限定属性
print('soup.p["name]:',soup.p['name']) #更简单的写法
#获取内容#
print('soup.p.string:',soup.p.string)
#嵌套选择#
print('soup.head.title:',soup.head.title)
结果
实例3:子节点
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html ="""
The Dormouse's story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters;and
their names were
,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
...
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
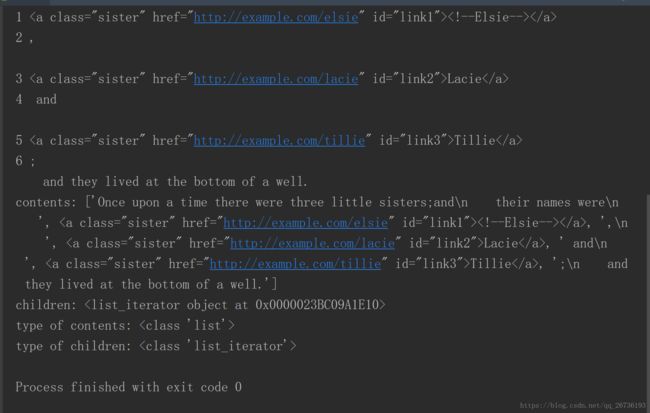
for i,content in enumerate(soup.p.contents):
print(i,content)
for i,child in enumerate(soup.p.children):
print(i,child)
#遍历输出是一致的。
print('contents:',soup.p.contents)
print('children:',soup.p.children)
print('type of contents:',type(soup.p.contents))
print('type of children:',type(soup.p.children))
结果:
说明:通过contents属性和children属性都能获取直接子节点,但注意两者区别。
实例4:子孙节点
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html ="""
The Dormouse's story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters;and
their names were
,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
...
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
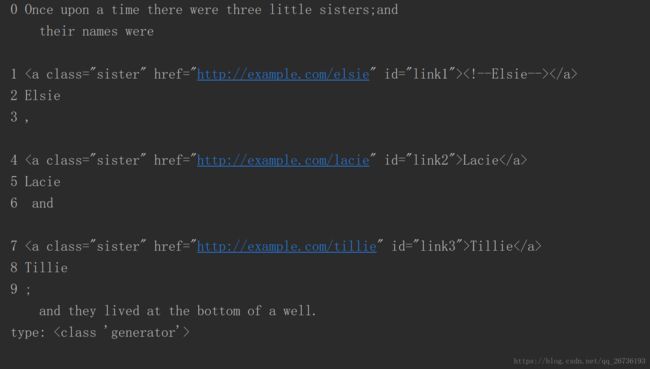
for i,content in enumerate(soup.p.descendants):
print(i,content)
print('type:',type(soup.p.descendants))
结果:
实例5:父节点和祖先节点
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html ="""
The Dormouse's story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters;and
their names were
,
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
...
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
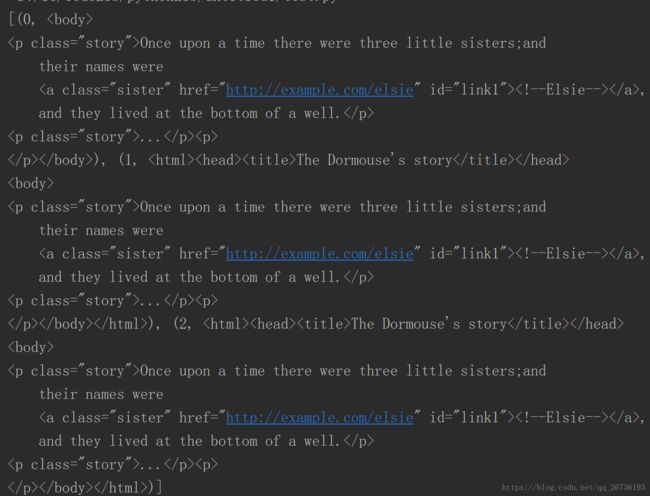
print(list(enumerate(soup.p.parents)))
print(soup.p.parent)
print(type(soup.p.parents))
print(type(soup.p.children))
print(type(soup.p.contents))
print(type(soup.p.descendants))
结果:
说明1:
parent属性获取的是父节点,parents属性获取的是所有的祖先节点。
说明2:
区分不同属性的类型。
实例6:兄弟选择器
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html ="""
The Dormouse's story
hahaha
Leraning
C++
HELLO
Java
World
Python
JS
...
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print('Next Sibling:',soup.a.next_sibling)
print('Prev Sibling:',soup.a.previous_sibling)
print('Next Siblings',list(enumerate(soup.a.next_siblings)))
print('Prev Siblings',list(enumerate(soup.a.previous_siblings)))
结果:
实例7:方法选择器
find_all() API如下:find_all(name,attrs,recursive,text,**kwargs)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html ="""
Hello
- C++
- Java
- Python>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
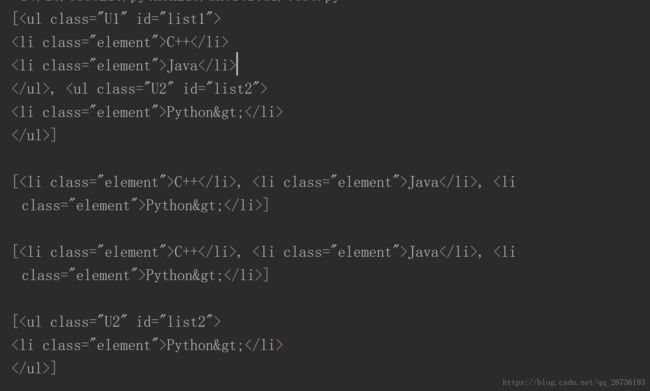
print(soup.find_all(name='ul')) #根据name查询元素
print()
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'class':'element'})) #根据attrs查询元素,参数类型是字典型
print()
print(soup.find_all(id='list2')) #另一种写法
print()
print(soup.find_all(class_='element')) #class是Python中关键字,这里记得加_结果:
补充:除了find_all()方法,还有find()方法,返回第一个匹配的元素。
实例8:CSS选择器
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html ="""
Hello
- C++
- Java
- Python
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
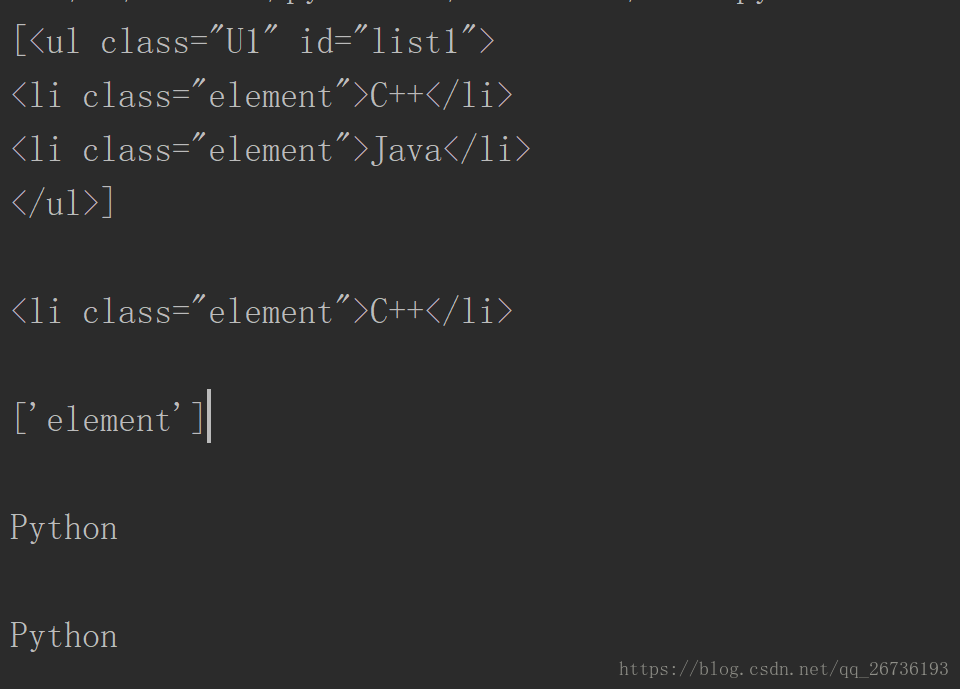
print(soup.select('.U1')) #选择器选择
print()
print(soup.select('ul li')[0]) #限定选择
print()
print(soup.select('ul li')[0].attrs['class']) #获取属性
print()
print(soup.select('li')[2].string) #获取文本
print()
print(soup.select('li')[2].get_text()) #另一个获取文本方法结果: