法克啊,本来我的底线是要自己建网站的。。。各种原因没有成功只好在上写了。。。
这篇文章是宗旨是怎么用arduino IDE来给ESP8266写程序。ESP8266是我最近发现的很黑科技的一个东西。首先,他继承了WIFI功能,本身也有GPIO之类的,这些以前的模块都能做到到是也没有什么了,但是价格非常之便宜,淘宝只需要25块钱,比普通的Arduino还要便宜一些。而最diao的是他只要安装一个插件,就可以直接用Arduino IDE写程序,就像是给Arduino写程序一样。很多Arduino的库也可以直接使用。
首先,几乎所有的部分都是来自于Adafruit的网站,网址是https://learn.adafruit.com/add-boards-arduino-v164
恩,然后需要把Arduino升级到1.6.4以上。
这里开始可能电脑要翻墙,但是如果的电信的网络好像也可以不翻
之后对话框下面会有一个进度调,要下载大约6m的文件,但是速度很慢。
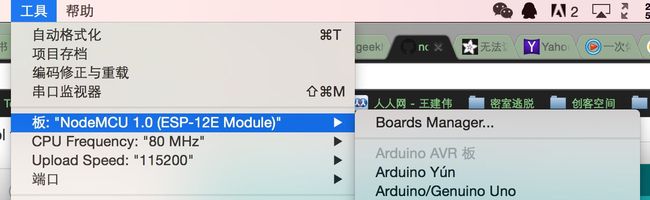
之后就可以把我的代码拷进来,整体界面和processing很像
然后就可以像给Arduino写程序一样写了。
烧写
这时候要拔掉控制板的220v插头。
烧写程序的时候要先把控制板查到usb口上,然后在插口旁边有两个按钮,先按住标有flash的按钮,然后按住标有reset的按钮,板子上的蓝灯会闪烁一下,然后点击arduino上的upload或者下载按钮。
UPDATE:
做了一个闪电云,然后拿回来以后不知道为什么就不能用了,直接接引脚是有用的,用usb供电就不行,用万用表量了一下VCC有一个限流电阻好像是断了。用杜邦线短接以后就行了。
然后不知道为什么现在烧程序不用想以前那样按按钮了。。。
然后这里是天气云(只能实现一个天气类型的展示)的代码
/*
* This sketch sends data via HTTP GET requests to data.sparkfun.com service.
*
* You need to get streamId and privateKey at data.sparkfun.com and paste them
* below. Or just customize this script to talk to other HTTP servers.
*
*/
#include
#include
#define SENSOR_PIN 15
#define PIXEL_PIN 5
#define PIXEL_COUNT 60
#define LED_IN 4
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(PIXEL_COUNT, PIXEL_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
const char* ssid = "X imlab";
const char* password = "";
const char* host = "query.yahooapis.com";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(10);
pinMode(SENSOR_PIN, INPUT);
strip.begin();
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
// We start by connecting to a WiFi network
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
pinMode(LED_IN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
if(digitalRead(SENSOR_PIN) == HIGH){
digitalWrite(LED_IN, LOW);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED_IN, HIGH);
if(WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED){
rainbowCycle(5);
colorWipe(strip.Color(0,0,0), 0);
Serial.println("connecting to WiFi");
} else {
Serial.print("connected to ");
Serial.print(ssid);
Serial.println(", and now show the weather");
digitalWrite(LED_IN, LOW);
delay(100);
digitalWrite(LED_IN, HIGH);
int code_now = getWeatherCode();
while(code_now == -1){
code_now = getWeatherCode();
}
Serial.print("weather code is");
Serial.println(code_now);
displayWeather(code_now);
}
delay(6000);
}else{
delay(200);
}
}
int getWeatherCode(){
Serial.print("connecting to ");
Serial.println(host);
// Use WiFiClient class to create TCP connections
WiFiClient client;
const int httpPort = 80;
if (!client.connect(host, httpPort)) {
Serial.println("connection failed");
return -1;
}
// We now create a URI for the request
String url = "/v1/public/yql?q=select%20*%20from%20weather.forecast%20where%20woeid%20in%20(select%20woeid%20from%20geo.placefinder%20where%20text%3D\"shenzhen\")%20and%20u%3D\"c\"%0A&format=json&diagnostics=true&env=store%3A%2F%2Fdatatables.org%2Falltableswithkeys&callback=";
Serial.print("Requesting URL: ");
Serial.println(url);
// This will send the request to the server
client.print(String("GET ") + url + " HTTP/1.1\r\n" +
"Host: " + host + "\r\n" +
"Connection: close\r\n\r\n");
delay(150);
// Read all the lines of the reply from server and print them to Serial
String str = "";
while(client.available()){
String line = client.readStringUntil('\r');
str += line;
}
//Serial.println(str);
//get the code of weather now see here: https://developer.yahoo.com/weather/documentation.html
int weather_code_begin = str.indexOf("condition\"")+20;
int weather_code_end = str.indexOf("\"", weather_code_begin);
// Serial.print("begin at ");
// Serial.println(weather_code_begin);
// Serial.print("end with");
// Serial.println(weather_code_end);
if(weather_code_end == -1){
return -1;
}
int weather_code = str.substring(weather_code_begin,weather_code_end).toInt();
Serial.print("code = ");
Serial.println(weather_code);
return weather_code;
}
void displayWeather(int code_now){
switch (code_now) {
case 25:
// code
for(int i=0; i<255; i++){
colorWipe(strip.Color(0,0,i), 0);
delay(20);
}
delay(1000);
break;
case 33:
//fair (night)
colorWipe(strip.Color(73, 147, 255),3);
break;
case 34:
//fair (day)
colorWipe(strip.Color(24,216,243),10);
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 0, 0), 0);
colorWipe(strip.Color(24,216,243),10);
break;
case 36:
// hot
for(int i=0; i<255; i++){
colorWipe(strip.Color(i,0,0), 0);
delay(20);
}
delay(1000);
break;
}
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 0, 0), 0);
}
void colorWipe_short(uint16_t be, uint16_t en, uint32_t c, uint8_t wait){
for (uint16_t i = be; i < en; i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, c);
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
// Fill the dots one after the other with a color
void colorWipe(uint32_t c, uint8_t wait) {
for (uint16_t i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, c);
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
void rainbow(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for (j = 0; j < 256; j++) {
for (i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel((i + j) & 255));
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
// Input a value 0 to 255 to get a color value.
// The colours are a transition r - g - b - back to r.
uint32_t Wheel(byte WheelPos) {
WheelPos = 255 - WheelPos;
if (WheelPos < 85) {
return strip.Color(255 - WheelPos * 3, 0, WheelPos * 3);
}
if (WheelPos < 170) {
WheelPos -= 85;
return strip.Color(0, WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3);
}
WheelPos -= 170;
return strip.Color(WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3, 0);
}
// Slightly different, this makes the rainbow equally distributed throughout
void rainbowCycle(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for(j=0; j<256*5; j++) { // 5 cycles of all colors on wheel
for(i=0; i< strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel(((i * 256 / strip.numPixels()) + j) & 255));
}
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}