Netty4.0学习笔记系列之五:自定义通讯协议
Netty中,通讯的双方建立连接后,会把数据按照ByteBuf的方式进行传输,例如http协议中,就是通过HttpRequestDecoder对ByteBuf数据流进行处理,转换成http的对象。基于这个思路,我自定义一种通讯协议:Server和客户端直接传输java对象。
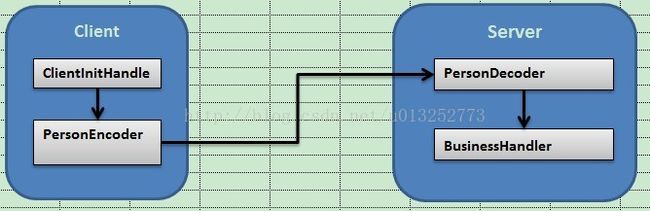
实现的原理是通过Encoder把java对象转换成ByteBuf流进行传输,通过Decoder把ByteBuf转换成java对象进行处理,处理逻辑如下图所示:
传输的java bean为Person:
package com.guowl.testobjcoder;
import java.io.Serializable;
// 必须实现Serializable接口
public class Person implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
public String toString() {
return "name:" + name + " sex:" + sex + " age:" + age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
Server端类:Server PersonDecoder BusinessHandler
1、Server:启动netty服务
package com.guowl.testobjcoder;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class Server {
public void start(int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new PersonDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new BusinessHandler());
}
}).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Server server = new Server();
server.start(8000);
}
}
package com.guowl.testobjcoder;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder;
import java.util.List;
import com.guowl.utils.ByteBufToBytes;
import com.guowl.utils.ByteObjConverter;
public class PersonDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, Listpackage com.guowl.testobjcoder;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class BusinessHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BusinessHandler.class);
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
Person person = (Person) msg;
logger.info("BusinessHandler read msg from client :" + person);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
}
}
Client端的类:Client ClientInitHandler PersonEncoder
1、Client 建立与Server的连接
package com.guowl.testobjcoder;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class Client {
public void connect(String host, int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(workerGroup);
b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
b.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
b.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new PersonEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientInitHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Client client = new Client();
client.connect("127.0.0.1", 8000);
}
}
package com.guowl.testobjcoder;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class ClientInitHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ClientInitHandler.class);
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
logger.info("HelloClientIntHandler.channelActive");
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("guowl");
person.setSex("man");
person.setAge(30);
ctx.write(person);
ctx.flush();
}
}
package com.guowl.testobjcoder;
import com.guowl.utils.ByteObjConverter;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder;
public class PersonEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Person msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
byte[] datas = ByteObjConverter.ObjectToByte(msg);
out.writeBytes(datas);
ctx.flush();
}
} package com.guowl.utils;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ByteObjConverter {
public static Object ByteToObject(byte[] bytes) {
Object obj = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bi = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream oi = null;
try {
oi = new ObjectInputStream(bi);
obj = oi.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
bi.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
oi.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return obj;
}
public static byte[] ObjectToByte(Object obj) {
byte[] bytes = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oo = null;
try {
oo = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oo.writeObject(obj);
bytes = bo.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
bo.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
oo.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return (bytes);
}
}
通过上述代码,实现了Server端与Client端直接使用person对象进行通信的目的。基于此,可以构建更为复杂的场景:Server端同时支撑多种协议,不同的协议采用不同的Decoder进行解析,解析结果保持统一,这样业务处理类可以保持接口一致。下一节将编写这样一个案例。
本例中需要注意的事项是:
1、Person对象必须实现Serializable接口,否则不能进行序列化。
2、PersonDecoder读取ByteBuf数据的时候,并没有对多次流式数据进行处理,而是简单的一次性接收,如果数据量大的情况下,可能会出现数据不完整,这个问题会在后续的学习中解决。