heapq 模块提供了堆算法。heapq是一种子节点和父节点排序的树形数据结构。这个模块提供heap[k] <= heap[2*k+1] and heap[k] <= heap[2*k+2]。为了比较不存在的元素被人为是无限大的。heap最小的元素总是[0]。
打印 heapq 类型
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
import
math
import
random
from
cStringIO
import
StringIO
def
show_tree(tree, total_width
=
36
, fill
=
' '
):
output
=
StringIO()
last_row
=
-
1
for
i, n
in
enumerate
(tree):
if
i:
row
=
int
(math.floor(math.log(i
+
1
,
2
)))
else
:
row
=
0
if
row !
=
last_row:
output.write(
'\n'
)
columns
=
2
*
*
row
col_width
=
int
(math.floor((total_width
*
1.0
)
/
columns))
output.write(
str
(n).center(col_width, fill))
last_row
=
row
print
output.getvalue()
print
'-'
*
total_width
print
return
data
=
random.sample(
range
(
1
,
8
),
7
)
print
'data: '
, data
show_tree(data)
|
打印结果
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
data: [3, 2, 6, 5, 4, 7, 1]
3
2 6
5 4 7 1
-------------------------
heapq.heappush(heap, item)
|
push一个元素到heap里, 修改上面的代码
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
heap
=
[]
data
=
random.sample(
range
(
1
,
8
),
7
)
print
'data: '
, data
for
i
in
data:
print
'add %3d:'
%
i
heapq.heappush(heap, i)
show_tree(heap)
|
打印结果
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
data: [6, 1, 5, 4, 3, 7, 2]
add 6:
6
------------------------------------
add 1:
1
6
------------------------------------
add 5:
1
6 5
------------------------------------
add 4:
1
4 5
6
------------------------------------
add 3:
1
3 5
6 4
------------------------------------
add 7:
1
3 5
6 4 7
------------------------------------
add 2:
1
3 2
6 4 7 5
------------------------------------
|
根据结果可以了解,子节点的元素大于父节点元素。而兄弟节点则不会排序。
heapq.heapify(list)
将list类型转化为heap, 在线性时间内, 重新排列列表。
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
print
'data: '
, data
heapq.heapify(data)
print
'data: '
, data
show_tree(data)
|
打印结果
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
data: [2, 7, 4, 3, 6, 5, 1]
data: [1, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4]
1
3 2
7 6 5 4
------------------------------------
heapq.heappop(heap)
|
删除并返回堆中最小的元素, 通过heapify() 和heappop()来排序。
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
data
=
random.sample(
range
(
1
,
8
),
7
)
print
'data: '
, data
heapq.heapify(data)
show_tree(data)
heap
=
[]
while
data:
i
=
heapq.heappop(data)
print
'pop %3d:'
%
i
show_tree(data)
heap.append(i)
print
'heap: '
, heap
|
打印结果
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
data: [4, 1, 3, 7, 5, 6, 2]
1
4 2
7 5 6 3
------------------------------------
pop 1:
2
4 3
7 5 6
------------------------------------
pop 2:
3
4 6
7 5
------------------------------------
pop 3:
4
5 6
7
------------------------------------
pop 4:
5
7 6
------------------------------------
pop 5:
6
7
------------------------------------
pop 6:
7
------------------------------------
pop 7:
------------------------------------
heap: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
|
可以看到已排好序的heap。
heapq.heapreplace(iterable, n)
删除现有元素并将其替换为一个新值。
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
data
=
random.sample(
range
(
1
,
8
),
7
)
print
'data: '
, data
heapq.heapify(data)
show_tree(data)
for
n
in
[
8
,
9
,
10
]:
smallest
=
heapq.heapreplace(data, n)
print
'replace %2d with %2d:'
%
(smallest, n)
show_tree(data)
|
打印结果
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
data: [7, 5, 4, 2, 6, 3, 1]
1
2 3
5 6 7 4
------------------------------------
replace 1 with 8:
2
5 3
8 6 7 4
------------------------------------
replace 2 with 9:
3
5 4
8 6 7 9
------------------------------------
replace 3 with 10:
4
5 7
8 6 10 9
------------------------------------
|
heapq.nlargest(n, iterable) 和 heapq.nsmallest(n, iterable)
返回列表中的n个最大值和最小值
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
data
=
range
(
1
,
6
)
l
=
heapq.nlargest(
3
, data)
print
l
# [5, 4, 3]
s
=
heapq.nsmallest(
3
, data)
print
s
# [1, 2, 3]
|
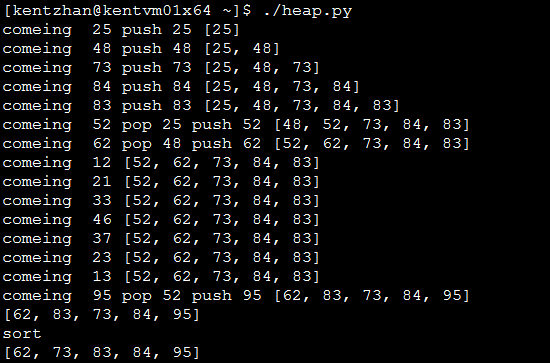
PS:一个计算题
构建元素个数为 K=5 的最小堆代码实例:
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: kentzhan
#
import
heapq
import
random
heap
=
[]
heapq.heapify(heap)
for
i
in
range
(
15
):
item
=
random.randint(
10
,
100
)
print
"comeing "
, item,
if
len
(heap) >
=
5
:
top_item
=
heap[
0
]
# smallest in heap
if
top_item < item:
# min heap
top_item
=
heapq.heappop(heap)
print
"pop"
, top_item,
heapq.heappush(heap, item)
print
"push"
, item,
else
:
heapq.heappush(heap, item)
print
"push"
, item,
pass
print
heap
pass
print
heap
print
"sort"
heap.sort()
print
heap
|
结果: