Python中,添加写入数据到已经存在的Excel的xls文件,即打开excel文件,写入新数据
背景
Python中,xlrd主要用来读取excel文件, xlwt主要用来写文件,本文主要介绍打开已经存在的excel的xls文件,然后在最后新的一行的数据。要用到xlutils包,它依赖于前两个包。
折腾过程
1.找到了参考资料:
writing to existing workbook using xlwt
其实是没有直接实现:
打开已有的excel文件,然后在文件最后写入,添加新数据
的函数的。
只不过,可以利用:
Working with Excel Files in Python
中的库,组合实现。
2. writing to existing workbook using xlwt
给出了示例代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
rom xlutils.copy
import
copy
# http://pypi.python.org/pypi/xlutils
from
xlrd
import
open_workbook
# http://pypi.python.org/pypi/xlrd
from
xlwt
import
easyxf
# http://pypi.python.org/pypi/xlwt
START_ROW
=
297
# 0 based (subtract 1 from excel row number)
col_age_november
=
1
col_summer1
=
2
col_fall1
=
3
rb
=
open_workbook(file_path,formatting_info
=
True
)
r_sheet
=
rb.sheet_by_index(
0
)
# read only copy to introspect the file
wb
=
copy(rb)
# a writable copy (I can't read values out of this, only write to it)
w_sheet
=
wb.get_sheet(
0
)
# the sheet to write to within the writable copy
for
row_index
in
range
(START_ROW, r_sheet.nrows):
age_nov
=
r_sheet.cell(row_index, col_age_november).value
if
age_nov
=
=
3
:
#If 3, then Combo I 3-4 year old for both summer1 and fall1
w_sheet.write(row_index, col_summer1,
'Combo I 3-4 year old'
)
w_sheet.write(row_index, col_fall1,
'Combo I 3-4 year old'
)
wb.save(file_path
+
'.out'
+
os.path.splitext(file_path)[
-
1
])
|
3. 刚又看到,有更简洁的代码:
|
1
2
3
4
|
from
xlutils.copy
import
copy
w
=
copy(
'book1.xls'
)
w.get_sheet(
0
).write(
0
,
0
,
"foo"
)
w.save(
'book2.xls'
)
|
4.现在打算去试试。
先去安装xlrd:
【记录】Python中安装xlrd模块
6.再去安装xlutils:
【记录】Python中安装可以读写excel的xls文件的xlutils模块(需依赖于xlrd和xlwt)
7.接着可以去写代码了。
8.先是:
【已解决】Python中使用xlutils.copy出错:AttributeError: ‘module’ object has no attribute ‘copy’
9.后是:
【已解决】Python中使用xlutils的copy出错:AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘datemode’
10.后来是用如下代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
import
xlwt;
import
xlrd;
#import xlutils;
from
xlutils.copy
import
copy;
#init xls file
#styleBlueBkg= xlwt.easyxf('pattern: pattern solid, fore_colour sky_blue;');
#styleBold = xlwt.easyxf('font: bold on');
styleBoldRed
=
xlwt.easyxf(
'font: color-index red, bold on'
);
headerStyle
=
styleBoldRed;
wb
=
xlwt.Workbook();
ws
=
wb.add_sheet(gConst[
'xls'
][
'sheetName'
]);
ws.write(
0
,
0
,
"Header"
, headerStyle);
ws.write(
0
,
1
,
"CatalogNumber"
, headerStyle);
ws.write(
0
,
2
,
"PartNumber"
, headerStyle);
wb.save(gConst[
'xls'
][
'fileName'
]);
#open existed xls file
#newWb = xlutils.copy(gConst['xls']['fileName']);
#newWb = copy(gConst['xls']['fileName']);
oldWb
=
xlrd.open_workbook(gConst[
'xls'
][
'fileName'
]);
print
oldWb;
#
newWb
=
copy(oldWb);
print
newWb;
#
newWs
=
newWb.get_sheet(
0
);
newWs.write(
1
,
0
,
"value1"
);
newWs.write(
1
,
1
,
"value2"
);
newWs.write(
1
,
2
,
"value3"
);
print
"write new values ok"
;
newWb.save(gConst[
'xls'
][
'fileName'
]);
print
"save with same name ok"
;
|
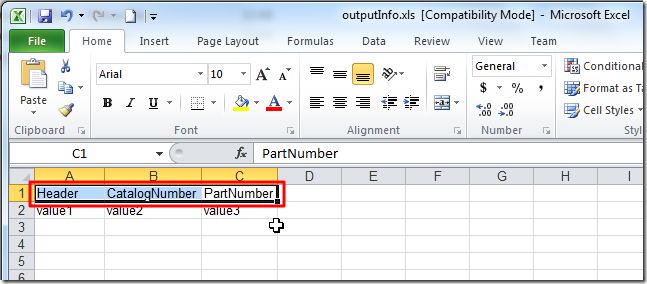
实现了,打开,刚刚保存的,已经存在的xls文件,
然后写入新数据的目的。
但是有个缺点,
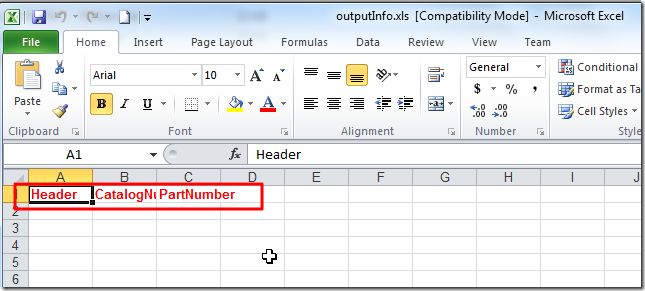
第一次保存时的,带格式(标题内容为红色粗体)的内容:
重新写入新数据,再保存时,却丢失了之前的格式(标题没了红色粗体了):
11.后来还是参考:
writing to existing workbook using xlwt
中的那个标准答案,在用xlrd.open_workbook时,添加对应的参数formatting_info=True,就可以保留原有格式了。
完整代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
import
xlwt;
import
xlrd;
#import xlutils;
from
xlutils.copy
import
copy;
#init xls file
#styleBlueBkg= xlwt.easyxf('pattern: pattern solid, fore_colour sky_blue;');
#styleBold = xlwt.easyxf('font: bold on');
styleBoldRed
=
xlwt.easyxf(
'font: color-index red, bold on'
);
headerStyle
=
styleBoldRed;
wb
=
xlwt.Workbook();
ws
=
wb.add_sheet(gConst[
'xls'
][
'sheetName'
]);
ws.write(
0
,
0
,
"Header"
, headerStyle);
ws.write(
0
,
1
,
"CatalogNumber"
, headerStyle);
ws.write(
0
,
2
,
"PartNumber"
, headerStyle);
wb.save(gConst[
'xls'
][
'fileName'
]);
#open existed xls file
#newWb = xlutils.copy(gConst['xls']['fileName']);
#newWb = copy(gConst['xls']['fileName']);
oldWb
=
xlrd.open_workbook(gConst[
'xls'
][
'fileName'
], formatting_info
=
True
);
print
oldWb;
#
newWb
=
copy(oldWb);
print
newWb;
#
newWs
=
newWb.get_sheet(
0
);
newWs.write(
1
,
0
,
"value1"
);
newWs.write(
1
,
1
,
"value2"
);
newWs.write(
1
,
2
,
"value3"
);
print
"write new values ok"
;
newWb.save(gConst[
'xls'
][
'fileName'
]);
print
"save with same name ok"
;
|
|
1
|
|
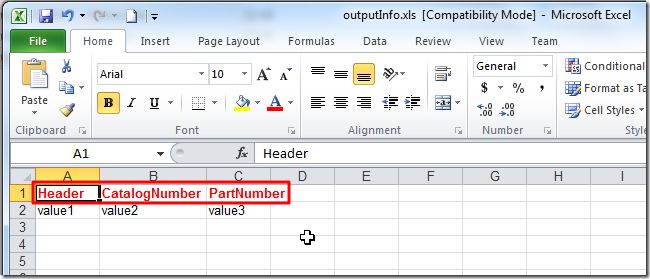
最后重新写入的数据,就可以保留之前的格式了(标题为红色粗体):
总结
python中操作,本身就复杂的xls文件,还是有点小麻烦的。
想要,往已经存在的xls文件中,写入新的行,新的数据,对应的逻辑为:
- 用xlrd.open_workbook打开已有的xsl文件
- 注意添加参数formatting_info=True,得以保存之前数据的格式
- 然后用,from xlutils.copy import copy;,之后的copy去从打开的xlrd的Book变量中,拷贝出一份,成为新的xlwt的Workbook变量
- 然后对于xlwt的Workbook变量,就是正常的:
- 通过get_sheet去获得对应的sheet
- 拿到sheet变量后,就可以往sheet中,写入新的数据
- 写完新数据后,最终save保存
相关完整代码为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
import
xlwt;
import
xlrd;
#import xlutils;
from
xlutils.copy
import
copy;
styleBoldRed
=
xlwt.easyxf(
'font: color-index red, bold on'
);
headerStyle
=
styleBoldRed;
wb
=
xlwt.Workbook();
ws
=
wb.add_sheet(gConst[
'xls'
][
'sheetName'
]);
ws.write(
0
,
0
,
"Header"
, headerStyle);
ws.write(
0
,
1
,
"CatalogNumber"
, headerStyle);
ws.write(
0
,
2
,
"PartNumber"
, headerStyle);
wb.save(gConst[
'xls'
][
'fileName'
]);
#open existed xls file
#newWb = xlutils.copy(gConst['xls']['fileName']);
#newWb = copy(gConst['xls']['fileName']);
oldWb
=
xlrd.open_workbook(gConst[
'xls'
][
'fileName'
], formatting_info
=
True
);
print
oldWb;
#
newWb
=
copy(oldWb);
print
newWb;
#
newWs
=
newWb.get_sheet(
0
);
newWs.write(
1
,
0
,
"value1"
);
newWs.write(
1
,
1
,
"value2"
);
newWs.write(
1
,
2
,
"value3"
);
print
"write new values ok"
;
newWb.save(gConst[
'xls'
][
'fileName'
]);
print
"save with same name ok"
;
|
其中,关于如何下载和安装对应的库,可参考:
【记录】Python中生成(写入数据到)Excel文件中
【记录】Python中安装xlrd模块
【记录】Python中安装可以读写excel的xls文件的xlutils模块(需依赖于xlrd和xlwt)