将任意文件写入以太坊区块的方法
以太坊除数字货币方面的应用外,还可以存储无法被篡改/删除的数据(51%双花攻击或者区块回滚除外)。
一段文字,一张照片,或者一首歌曲,只需写入以太坊区块中,即可真正做到 “恒久远 永流传” ,不会出现网盘、邮箱、网站上存储的数据丢失的情况。
以下介绍将数据写入以太坊区块的方法。
由于以太坊转账的gas存在上限,所以可发送的数据也存在限制,大约只能发送不超过44KB的数据。参考:https://blog.csdn.net/shebao3333/article/details/80112436
过大的文件,可以采取分块写入的方式。需注意,转账的gas手续费与写入的数据大小存在正比关系,即写入的越多,手续费越高,区块确认速度相对也比较慢。
前置步骤:安装chrome钱包插件METAMASK,导入钱包,试用主网购入ETH或者使用测试网络获取免费ETH,参考:https://blog.csdn.net/kaitiren/article/details/79299394
一. 将文字写入以太坊区块
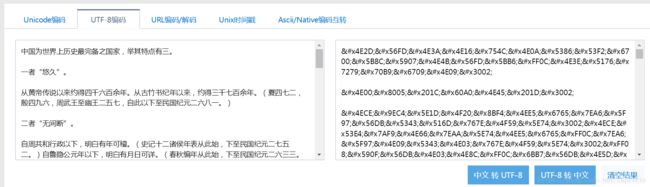
步骤:1.将文字转为UTF-8格式,可使用在线工具转换http://tool.chinaz.com/Tools/UTF-8.aspx
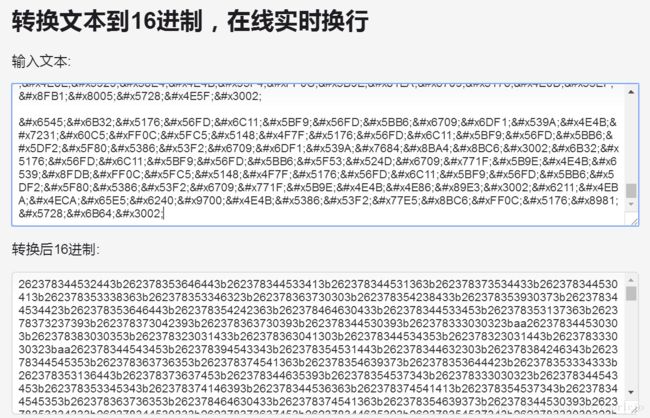
2.将utf-8编码转为16进制编码,可使用在线转换http://www.5ixuexiwang.com/str/hex.php
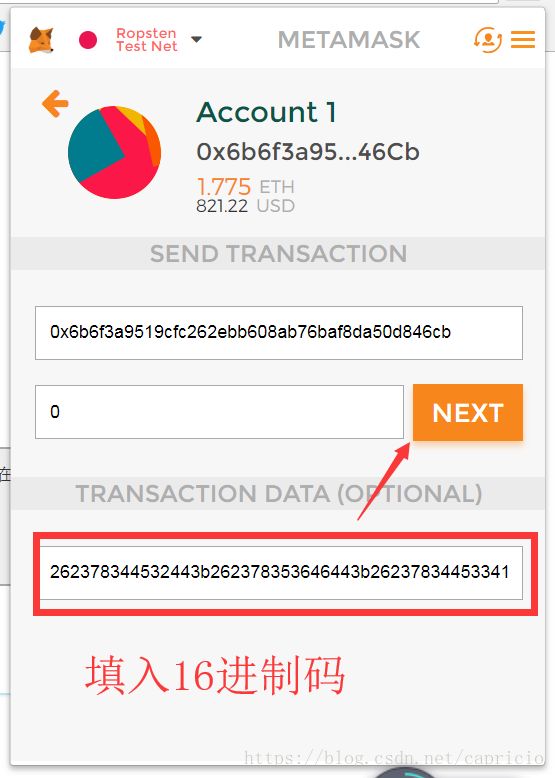
3.打开METAMASK钱包,使用send选项,发送的钱包地址可随意,发送数量为0即可
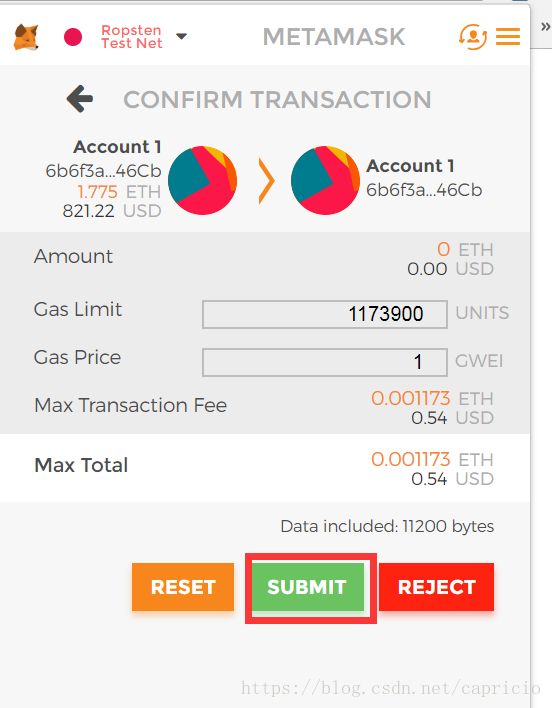
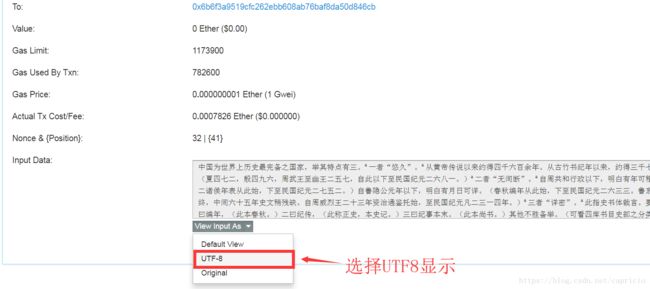
完成发送ETH后,在交易记录里查看区块信息即可:
等待交易确认完毕后,在区块交易页面下方,可以查询到刚才写入区块的文字:
这时候,这篇文章就写入了以太坊区块中,任何人无法修改与删除
区块查看:https://ropsten.etherscan.io/tx/0x5af3ba0973b6c4663730be8ef701accadea12fc6e9b0485f8974c139d4d8fe3c
二.将文件写入以太坊区块
1.将文件转为byte数组:(java实现)
public static byte[] getBytes(String filePath){
byte[] buffer = null;
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(1000);
byte[] b = new byte[1000];
int n;
while ((n = fis.read(b)) != -1) {
bos.write(b, 0, n);
}
fis.close();
bos.close();
buffer = bos.toByteArray();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return buffer;
}
2.将byte数组转为16进制字符串:(java实现)
public static String bytesToHexFun1(byte[] bytes) {
// 一个byte为8位,可用两个十六进制位标识
char[] HEX_CHAR = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5',
'6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
char[] buf = new char[bytes.length * 2];
int a = 0;
int index = 0;
for(byte b : bytes) { // 使用除与取余进行转换
if(b < 0) {
a = 256 + b;
} else {
a = b;
}
buf[index++] = HEX_CHAR[a / 16];
buf[index++] = HEX_CHAR[a % 16];
}
return new String(buf);
}
发送到以太坊区块的方法,与发送文字相同,只需将16进制编码填入交易信息即可。
从区块中还原出文件的方法,将16进制编码还原为byte数组:
public static byte[] toBytes(String str) {
if(str == null || str.trim().equals("")) {
return new byte[0];
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[str.length() / 2];
for(int i = 0; i < str.length() / 2; i++) {
String subStr = str.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 2);
bytes[i] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(subStr, 16);
}
return bytes;
}
byte数组转为文件输出到本地:
public static void writeFile(byte[] bfile, String filePath) {
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
File file = null;
try {
File dir = new File(filePath);
if(!dir.exists()&&dir.isDirectory()){//判断文件目录是否存在
dir.mkdirs();
}
file = new File(filePath);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
bos.write(bfile);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (bos != null) {
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}