Spring Bean的生命周期
一、生命周期流程图
Spring Bean的完整生命周期从创建Spring容器开始,直到最终Spring容器销毁Bean,这其中包含了一系列关键点:
二、Bean的完整生命周期经历了各种方法调用,这些方法可以划分为以下几类:
1、Bean自身的方法:这个包括了Bean本身调用的方法和通过配置文件中
2、Bean级生命周期接口方法:这个包括了BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware、InitializingBean和DiposableBean这些接口的方法
3、容器级生命周期接口方法:这个包括了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 BeanPostProcessor 这两个接口实现,一般称它们的实现类为“后处理器”。
4、工厂后处理器接口方法:这个包括了AspectJWeavingEnabler, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor, CustomAutowireConfigurer等等非常有用的工厂后处理器 接口的方法。工厂后处理器也是容器级的。在应用上下文装配配置文件之后立即调用。
三、示例代码自定义Bean实现BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,ApplicationContextAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean接口
package com.cuisea.lifecycle;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.*;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
/**
* Bean生命周期
*/
public class Person implements BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,ApplicationContextAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean {
private String name;
private String beanName;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public Person() {
System.out.println("【构造器】调用Person的构造器实例化");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("【注入属性】注入属性name");
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory=beanFactory;
System.out.println("【BeanFactoryAware接口】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
this.beanName=beanName;
System.out.println("【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext=applicationContext;
System.out.println("【ApplicationContextAware接口】调用ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext()");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("【DiposibleBean接口】调用DiposibleBean.destory()");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("【InitializingBean接口】调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()");
}
// 通过的init-method属性指定的初始化方法
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("【init-method】调用的init-method属性指定的初始化方法");
}
// 通过的destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("【destroy-method】调用的destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法");
}
} BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口实现类:
package com.cuisea.lifecycle;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("这是BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类构造器!!");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用postProcessBeanFactory方法");
BeanDefinition bd = configurableListableBeanFactory.getBeanDefinition("person");
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("name", "test");
}
}BeanPostProcessor接口实现类:
package com.cuisea.lifecycle;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public MyBeanPostProcessor() {
System.out.println("这是BeanPostProcessor实现类构造器!!");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessBeforeInitialization对属性进行更改!");
return o;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessAfterInitialization对属性进行更改!");
return o;
}
}InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口实现类:
package com.cuisea.lifecycle;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter {
public MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
super();
System.out.println("这是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter实现类构造器!!");
}
// 接口方法、实例化Bean之前调用
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class beanClass,String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法");
return null;
}
// 接口方法、实例化Bean之后调用
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法");
return bean;
}
// 接口方法、设置某个属性时调用
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues var1, PropertyDescriptor[] var2, Object var3, String var4) throws BeansException{
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessPropertyValues方法");
return var1;
}
}applicationContext.xml
测试代码:
package com.cuisea;
import com.cuisea.lifecycle.Person;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class LifeCycleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
System.out.println("Spring容器初始化成功");
Person person=(Person)context.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Spring容器开始关闭");
context.close();
}
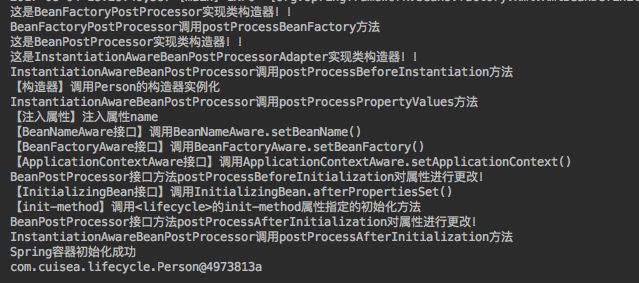
}
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/zrtqsk/p/3735273.html 流程中增加了ApplicationContextAware接口
