spring源码分析 一
核心类介绍
1.DefaultListableBeanFactory
源码:
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
-- XmlBeanFactory 自定义的 XML 读取器
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
}
XmlBeanFactory继承DefaultListableBeanFactory,而DefaultListableBeanFactory是整个bean加载的核心部分,是spring注册及加载bean的默认实现,而对于XmlBeanFactory和DefaultListableBeanFactory不同的地方其实在XmlBeanFactory中使用了自定义的XML读取器。
DefaultListableBeanFactory的类图和层次结构图如下:
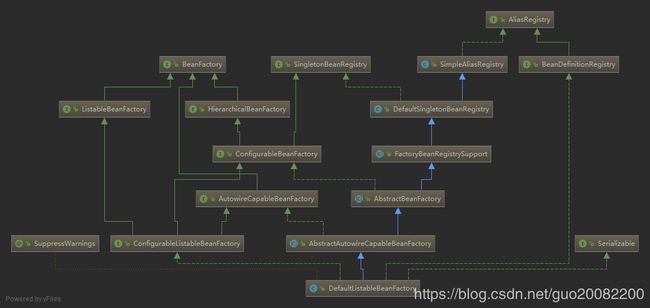
其中:
org.springframework.core.AliasRegistry 源码如下:
package org.springframework.core;
-- 映射别名(managing aliases)的公共接口
-- org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry的父接口
public interface AliasRegistry {
-- 给定一个名字name,注册为别名 alias
-- 如果别名已经使用 抛异常 IllegalStateException
void registerAlias(String name, String alias);
-- 移除别名
-- 如果别名不存在 抛异常 IllegalStateException
void removeAlias(String alias);
-- 给定个字符串判断是否是别名
boolean isAlias(String name);
-- 获取name对应的所有的别名
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
org.springframework.core.SimpleAliasRegistry源码如下:
package org.springframework.core;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringValueResolver;
// AliasRegistry 的简单实现
// BeanDefinitionRegistry 的 base class
public class SimpleAliasRegistry implements AliasRegistry {
/** Logger available to subclasses */
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
/** Map from alias to canonical name
* 这里创建的是 ConcurrentHashMap
*/
private final Map<String, String> aliasMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
@Override
public void registerAlias(String name, String alias) {
Assert.hasText(name, "'name' must not be empty");
Assert.hasText(alias, "'alias' must not be empty");
//同步锁
synchronized (this.aliasMap) {
//如果 alias 和 name 一样
if (alias.equals(name)) {
// 将别名移除
this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Alias definition '" + alias + "' ignored since it points to same name");
}
}
else {
-- 获取别名对应的name
String registeredName = this.aliasMap.get(alias);
-- 如果不是null
if (registeredName != null) {
if (registeredName.equals(name)) {
// An existing alias - no need to re-register
return;
}
if (!allowAliasOverriding()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot define alias '" + alias + "' for name '" +
name + "': It is already registered for name '" + registeredName + "'.");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding alias '" + alias + "' definition for registered name '" +
registeredName + "' with new target name '" + name + "'");
}
}
checkForAliasCircle(name, alias);
-- 像map里面添加别名映射
this.aliasMap.put(alias, name);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Alias definition '" + alias + "' registered for name '" + name + "'");
}
}
}
}
/**
* 别名是否允许覆盖
* 默认是 true
*/
protected boolean allowAliasOverriding() {
return true;
}
// 判断给定的名字是否有给定的别名注册
public boolean hasAlias(String name, String alias) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : this.aliasMap.entrySet()) {
String registeredName = entry.getValue();
if (registeredName.equals(name)) {
String registeredAlias = entry.getKey();
if (registeredAlias.equals(alias) || hasAlias(registeredAlias, alias)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void removeAlias(String alias) {
synchronized (this.aliasMap) {
String name = this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
if (name == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No alias '" + alias + "' registered");
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean isAlias(String name) {
return this.aliasMap.containsKey(name);
}
@Override
public String[] getAliases(String name) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
synchronized (this.aliasMap) {
retrieveAliases(name, result);
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
/**
* Transitively retrieve all aliases for the given name.
* @param name the target name to find aliases for
* @param result the resulting aliases list
*/
private void retrieveAliases(String name, List<String> result) {
this.aliasMap.forEach((alias, registeredName) -> {
if (registeredName.equals(name)) {
result.add(alias);
retrieveAliases(alias, result);
}
});
}
/**
* Resolve all alias target names and aliases registered in this
* factory, applying the given StringValueResolver to them.
* The value resolver may for example resolve placeholders
* in target bean names and even in alias names.
* @param valueResolver the StringValueResolver to apply
*/
public void resolveAliases(StringValueResolver valueResolver) {
Assert.notNull(valueResolver, "StringValueResolver must not be null");
synchronized (this.aliasMap) {
Map<String, String> aliasCopy = new HashMap<>(this.aliasMap);
aliasCopy.forEach((alias, registeredName) -> {
String resolvedAlias = valueResolver.resolveStringValue(alias);
String resolvedName = valueResolver.resolveStringValue(registeredName);
if (resolvedAlias == null || resolvedName == null || resolvedAlias.equals(resolvedName)) {
this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
}
else if (!resolvedAlias.equals(alias)) {
String existingName = this.aliasMap.get(resolvedAlias);
if (existingName != null) {
if (existingName.equals(resolvedName)) {
// Pointing to existing alias - just remove placeholder
this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot register resolved alias '" + resolvedAlias + "' (original: '" + alias +
"') for name '" + resolvedName + "': It is already registered for name '" +
registeredName + "'.");
}
checkForAliasCircle(resolvedName, resolvedAlias);
this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
this.aliasMap.put(resolvedAlias, resolvedName);
}
else if (!registeredName.equals(resolvedName)) {
this.aliasMap.put(alias, resolvedName);
}
});
}
}
/**
* Check whether the given name points back to the given alias as an alias
* in the other direction already, catching a circular reference upfront
* and throwing a corresponding IllegalStateException.
* @param name the candidate name
* @param alias the candidate alias
* @see #registerAlias
* @see #hasAlias
*/
protected void checkForAliasCircle(String name, String alias) {
if (hasAlias(alias, name)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot register alias '" + alias +
"' for name '" + name + "': Circular reference - '" +
name + "' is a direct or indirect alias for '" + alias + "' already");
}
}
/**
* Determine the raw name, resolving aliases to canonical names.
* @param name the user-specified name
* @return the transformed name
*/
public String canonicalName(String name) {
String canonicalName = name;
// Handle aliasing...
String resolvedName;
do {
resolvedName = this.aliasMap.get(canonicalName);
if (resolvedName != null) {
canonicalName = resolvedName;
}
}
while (resolvedName != null);
return canonicalName;
}
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry
BeanDefinitionRegistry 源码不在写了,主要是对BeanDefinition的CRUD操作
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.SingletonBeanRegistry
定义对单例的注册及获取,源码略去
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory
定义获取bean,以及bean的各种属性
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
是SingletonBeanRegistry实现
public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry {...}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.FactoryBeanRegistrySupport
在DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry基础上增加对FactoryBean的特殊处理功能
public abstract class FactoryBeanRegistrySupport
extends DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry {}
org.springframework.beans.factory.HierarchicalBeanFactory
源码如下:
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* Sub-interface implemented by bean factories that can be part
* of a hierarchy.
*
* The corresponding {@code setParentBeanFactory} method for bean
* factories that allow setting the parent in a configurable
* fashion can be found in the ConfigurableBeanFactory interface.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 07.07.2003
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory#setParentBeanFactory
*/
public interface HierarchicalBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
/**
* Return the parent bean factory, or {@code null} if there is none.
*/
@Nullable
BeanFactory getParentBeanFactory();
/**
* Return whether the local bean factory contains a bean of the given name,
* ignoring beans defined in ancestor contexts.
* This is an alternative to {@code containsBean}, ignoring a bean
* of the given name from an ancestor bean factory.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return whether a bean with the given name is defined in the local factory
* @see BeanFactory#containsBean
*/
boolean containsLocalBean(String name);
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory
源码如下:
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import java.beans.PropertyEditor;
import java.security.AccessControlContext;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyEditorRegistrar;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyEditorRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.TypeConverter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.HierarchicalBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.StringValueResolver;
/**
* 提供了一些工具配置一个bean工厂,该类不是让客户端使用的,是让spring框架内部使用
*/
public interface ConfigurableBeanFactory extends HierarchicalBeanFactory, SingletonBeanRegistry {
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = "singleton";
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = "prototype";
void setParentBeanFactory(BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws IllegalStateException;
void setBeanClassLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader beanClassLoader);
@Nullable
ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader();
/**
* Specify a temporary ClassLoader to use for type matching purposes.
* Default is none, simply using the standard bean ClassLoader.
* A temporary ClassLoader is usually just specified if
* load-time weaving is involved, to make sure that actual bean
* classes are loaded as lazily as possible. The temporary loader is
* then removed once the BeanFactory completes its bootstrap phase.
* @since 2.5
*/
void setTempClassLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader tempClassLoader);
@Nullable
ClassLoader getTempClassLoader();
void setCacheBeanMetadata(boolean cacheBeanMetadata);
boolean isCacheBeanMetadata();
/**
* Specify the resolution strategy for expressions in bean definition values.
* There is no expression support active in a BeanFactory by default.
* An ApplicationContext will typically set a standard expression strategy
* here, supporting "#{...}" expressions in a Unified EL compatible style.
* @since 3.0
*/
void setBeanExpressionResolver(@Nullable BeanExpressionResolver resolver);
/**
* Return the resolution strategy for expressions in bean definition values.
* @since 3.0
*/
@Nullable
BeanExpressionResolver getBeanExpressionResolver();
/**
* Specify a Spring 3.0 ConversionService to use for converting
* property values, as an alternative to JavaBeans PropertyEditors.
* @since 3.0
*/
void setConversionService(@Nullable ConversionService conversionService);
/**
* Return the associated ConversionService, if any.
* @since 3.0
*/
@Nullable
ConversionService getConversionService();
/**
* Add a PropertyEditorRegistrar to be applied to all bean creation processes.
* Such a registrar creates new PropertyEditor instances and registers them
* on the given registry, fresh for each bean creation attempt. This avoids
* the need for synchronization on custom editors; hence, it is generally
* preferable to use this method instead of {@link #registerCustomEditor}.
* @param registrar the PropertyEditorRegistrar to register
*/
void addPropertyEditorRegistrar(PropertyEditorRegistrar registrar);
/**
* Register the given custom property editor for all properties of the
* given type. To be invoked during factory configuration.
* Note that this method will register a shared custom editor instance;
* access to that instance will be synchronized for thread-safety. It is
* generally preferable to use {@link #addPropertyEditorRegistrar} instead
* of this method, to avoid for the need for synchronization on custom editors.
* @param requiredType type of the property
* @param propertyEditorClass the {@link PropertyEditor} class to register
*/
void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, Class<? extends PropertyEditor> propertyEditorClass);
/**
* Initialize the given PropertyEditorRegistry with the custom editors
* that have been registered with this BeanFactory.
* @param registry the PropertyEditorRegistry to initialize
*/
void copyRegisteredEditorsTo(PropertyEditorRegistry registry);
/**
* Set a custom type converter that this BeanFactory should use for converting
* bean property values, constructor argument values, etc.
* This will override the default PropertyEditor mechanism and hence make
* any custom editors or custom editor registrars irrelevant.
* @see #addPropertyEditorRegistrar
* @see #registerCustomEditor
* @since 2.5
*/
void setTypeConverter(TypeConverter typeConverter);
/**
* Obtain a type converter as used by this BeanFactory. This may be a fresh
* instance for each call, since TypeConverters are usually not thread-safe.
* If the default PropertyEditor mechanism is active, the returned
* TypeConverter will be aware of all custom editors that have been registered.
* @since 2.5
*/
TypeConverter getTypeConverter();
/**
* Add a String resolver for embedded values such as annotation attributes.
* @param valueResolver the String resolver to apply to embedded values
* @since 3.0
*/
void addEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver valueResolver);
/**
* Determine whether an embedded value resolver has been registered with this
* bean factory, to be applied through {@link #resolveEmbeddedValue(String)}.
* @since 4.3
*/
boolean hasEmbeddedValueResolver();
/**
* Resolve the given embedded value, e.g. an annotation attribute.
* @param value the value to resolve
* @return the resolved value (may be the original value as-is)
* @since 3.0
*/
@Nullable
String resolveEmbeddedValue(String value);
/**
* Add a new BeanPostProcessor that will get applied to beans created
* by this factory. To be invoked during factory configuration.
* Note: Post-processors submitted here will be applied in the order of
* registration; any ordering semantics expressed through implementing the
* {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered} interface will be ignored. Note
* that autodetected post-processors (e.g. as beans in an ApplicationContext)
* will always be applied after programmatically registered ones.
* @param beanPostProcessor the post-processor to register
*/
void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor);
/**
* Return the current number of registered BeanPostProcessors, if any.
*/
int getBeanPostProcessorCount();
/**
* Register the given scope, backed by the given Scope implementation.
* @param scopeName the scope identifier
* @param scope the backing Scope implementation
*/
void registerScope(String scopeName, Scope scope);
/**
* Return the names of all currently registered scopes.
* This will only return the names of explicitly registered scopes.
* Built-in scopes such as "singleton" and "prototype" won't be exposed.
* @return the array of scope names, or an empty array if none
* @see #registerScope
*/
String[] getRegisteredScopeNames();
/**
* Return the Scope implementation for the given scope name, if any.
* This will only return explicitly registered scopes.
* Built-in scopes such as "singleton" and "prototype" won't be exposed.
* @param scopeName the name of the scope
* @return the registered Scope implementation, or {@code null} if none
* @see #registerScope
*/
@Nullable
Scope getRegisteredScope(String scopeName);
/**
* Provides a security access control context relevant to this factory.
* @return the applicable AccessControlContext (never {@code null})
* @since 3.0
*/
AccessControlContext getAccessControlContext();
/**
* Copy all relevant configuration from the given other factory.
* Should include all standard configuration settings as well as
* BeanPostProcessors, Scopes, and factory-specific internal settings.
* Should not include any metadata of actual bean definitions,
* such as BeanDefinition objects and bean name aliases.
* @param otherFactory the other BeanFactory to copy from
*/
void copyConfigurationFrom(ConfigurableBeanFactory otherFactory);
/**
* Given a bean name, create an alias. We typically use this method to
* support names that are illegal within XML ids (used for bean names).
* Typically invoked during factory configuration, but can also be
* used for runtime registration of aliases. Therefore, a factory
* implementation should synchronize alias access.
* @param beanName the canonical name of the target bean
* @param alias the alias to be registered for the bean
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if the alias is already in use
*/
void registerAlias(String beanName, String alias) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
/**
* Resolve all alias target names and aliases registered in this
* factory, applying the given StringValueResolver to them.
* The value resolver may for example resolve placeholders
* in target bean names and even in alias names.
* @param valueResolver the StringValueResolver to apply
* @since 2.5
*/
void resolveAliases(StringValueResolver valueResolver);
/**
* Return a merged BeanDefinition for the given bean name,
* merging a child bean definition with its parent if necessary.
* Considers bean definitions in ancestor factories as well.
* @param beanName the name of the bean to retrieve the merged definition for
* @return a (potentially merged) BeanDefinition for the given bean
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean definition with the given name
* @since 2.5
*/
BeanDefinition getMergedBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Determine whether the bean with the given name is a FactoryBean.
* @param name the name of the bean to check
* @return whether the bean is a FactoryBean
* ({@code false} means the bean exists but is not a FactoryBean)
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @since 2.5
*/
boolean isFactoryBean(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Explicitly control the current in-creation status of the specified bean.
* For container-internal use only.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param inCreation whether the bean is currently in creation
* @since 3.1
*/
void setCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName, boolean inCreation);
/**
* Determine whether the specified bean is currently in creation.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return whether the bean is currently in creation
* @since 2.5
*/
boolean isCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName);
/**
* Register a dependent bean for the given bean,
* to be destroyed before the given bean is destroyed.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param dependentBeanName the name of the dependent bean
* @since 2.5
*/
void registerDependentBean(String beanName, String dependentBeanName);
/**
* Return the names of all beans which depend on the specified bean, if any.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the array of dependent bean names, or an empty array if none
* @since 2.5
*/
String[] getDependentBeans(String beanName);
/**
* Return the names of all beans that the specified bean depends on, if any.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the array of names of beans which the bean depends on,
* or an empty array if none
* @since 2.5
*/
String[] getDependenciesForBean(String beanName);
/**
* Destroy the given bean instance (usually a prototype instance
* obtained from this factory) according to its bean definition.
* Any exception that arises during destruction should be caught
* and logged instead of propagated to the caller of this method.
* @param beanName the name of the bean definition
* @param beanInstance the bean instance to destroy
*/
void destroyBean(String beanName, Object beanInstance);
/**
* Destroy the specified scoped bean in the current target scope, if any.
* Any exception that arises during destruction should be caught
* and logged instead of propagated to the caller of this method.
* @param beanName the name of the scoped bean
*/
void destroyScopedBean(String beanName);
/**
* Destroy all singleton beans in this factory, including inner beans that have
* been registered as disposable. To be called on shutdown of a factory.
* Any exception that arises during destruction should be caught
* and logged instead of propagated to the caller of this method.
*/
void destroySingletons();
}
