spring bean的init、destory的几种方法及生命周期
个人总结spring-bean的声明周期维护有三种:
- 注解:通过@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 方法 实现初始化和销毁bean之前进行的操作
- xml中配置:xml中定义init-method和destory-method方法
- 接口继承:通过bean实现InitializingBean和DisposableBean接口
任何一个事物都有自己的生命周期,生命的开始、生命中、生命结束。大家最熟悉的应该是servlet 的生命周期吧。和 servlet 一样 spring bean 也有自己的生命周期。
实现Aware接口
Spring提供了一组Aware接口是针对某个实现这些接口的Bean定制初始化的过程,为了让Bean可以获取到框架自身的一些对象。 这些接口均继承于org.springframework.beans.factory.Aware标记接口,并提供一个将由Bean实现的set*方法,Spring通过基于setter的依赖注入方式使相应的对象可以被Bean使用。
| ApplicationContextAware | 获得ApplicationContext对象 |
| BeanFactoryAware | 获得BeanFactory对象,可以用来检测Bean的作用域 |
| BeanNameAware | 获得Bean在配置文件中定义的名字 |
| ResourceLoaderAware | 获得ResourceLoader对象,可以获得classpath中某个文件 |
| ServletContextAware | 可以获取ServletContext对象,可以读取context中的参数 |
| ServletConfigAware | 可以获取ServletConfig对象,可以读取config中的参数 |
public class GiraffeService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationEventPublisherAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, EnvironmentAware, ImportAware, ResourceLoaderAware{
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
System.out.println("执行setBeanClassLoader,ClassLoader Name = " + classLoader.getClass().getName());
}
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行setBeanFactory,setBeanFactory:: giraffe bean singleton=" + beanFactory.isSingleton("giraffeService"));
}
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println("执行setBeanName:: Bean Name defined in context="
+ s);
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行setApplicationContext:: Bean Definition Names="
+ Arrays.toString(applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()));
}
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
System.out.println("执行setApplicationEventPublisher");
}
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
System.out.println("执行setEnvironment");
}
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource("classpath:spring-beans.xml");
System.out.println("执行setResourceLoader:: Resource File Name="
+ resource.getFilename());
}
public void setImportMetadata(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
System.out.println("执行setImportMetadata");
}
}BeanPostProcessor
除Aware接口之外,Spring同样可以针对容器中的所有Bean或者某些Bean定制初始化过程,只需提供一个实现BeanPostProcessor接口的类即可(下面会重点讲)。
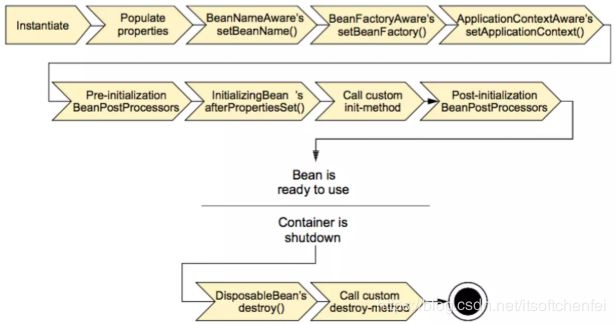
Spring Bean的生命周期
Bean生命周期是这样的:
- Bean容器找到配置文件中Spring Bean的定义。
- Bean容器利用Java Reflection API创建一个Bean的实例。
- 如果涉及到一些属性值 利用set方法设置一些属性值。
- 如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,调用setBeanName()方法,传入Bean的名字。
- 如果Bean实现了BeanClassLoaderAware接口,调用setBeanClassLoader()方法,传入ClassLoader对象的实例。
- 如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,调用setBeanClassLoader()方法,传入ClassLoader对象的实例。
- 与上面的类似,如果实现了其他*Aware接口,就调用相应的方法。
- 如果有和加载这个Bean的Spring容器相关的BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法
- 如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,执行afterPropertiesSet()方法。
- 如果Bean在配置文件中的定义包含
init-method属性,执行指定的方法。 - 如果有和加载这个Bean的Spring容器相关的BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessAfterInitialization()方法
- 当要销毁Bean的时候,如果Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,执行destroy()方法。
- 当要销毁Bean的时候,如果Bean在配置文件中的定义包含
destroy-method属性,执行指定的方法
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor
spring注释中经常提到“regular bean” 就是一个未实例化的bean,它就是BeanDefinition(bean metadata 信息),一个类被读取之后就是BeanDefinition,在被注册Ioc容器完毕以后,Spring Bean 工厂就可以随时根据需要进行实例化。对于XmlBeanFactory 来说,实例化默认是延迟进行的,也就是说在 getBean 的时候才会;而对于 ApplicationContext来说,实例化会在容器启动后通过 AbstractApplicationContext 中 reflash 方法自动进行。spring默认beanFactory为DefaultListableBeanFactory,可以从中得到证实。
BeanPostProcessor:bean级别的处理,针对某个具体的bean实例化后,初始化方法执行前(init-method或者实现了InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法)。
- ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,处理EnvironmentAware、ResourceLoaderAware、ApplicationEventPublisherAware、MessageSourceAware、ApplicationContextAware中对应的方法
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor拓展了BeanPostProcessors接口,这个接口也是非常的牛掰,可以在实例化Bean前(调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法)、后(调用postProcessAfterInstantiation)提供扩展的回调接口。
- SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,拓展了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,主要是供spring内部使用,提供有:predictBeanType(用来返回目标对象的类型)、determineCandidateConstructors(获取用来实例化的构造器)、getEarlyBeanReference(提前暴露bean引用,解决循环依赖)
- MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor,也是实例化后执行,主要缓存一些meta信息提供给后续的injectValue使用
- DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor,是对象销毁的前置回调
BeanFactoryPostProcessor:BeanFactory级别的处理,是针对整个工厂中的bean作出修改或者新注册(包括BeanDefinition)。
- ServletComponentRegisteringPostProcessor,applicationContext如果是WebApplicationContext,注入ServletRegistrationBean。
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,BeanFactory级别的处理,感觉比BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的语义环境更加强调BeanDefinition的个性化调整。
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,说实话个人感觉BeanFactoryPostProcessor更适合它的语义。
执行顺序:
1. 执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
- BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor+PriorityOrdered
- BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor+Ordered
- 剩余BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
2. 执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法(与1中排序相同)
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor执行顺序先与BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
//可以从factory中获取:BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String var1)
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory factory) throws BeansException;
}
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry var1) throws BeansException;
}
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}参阅资料
- life cycle management of a spring bean
- Spring Bean Life Cycle