Mybatis中@Param注解详细使用和原理分析
对于目前市场上火爆的持久层框架MyBatis相信大家在工作中肯定是用得很多,但是你对其mapper接口代理对象和其方法上的@Param注解又了解多少呢?
废话不多说,接来下就给大家来分析下
MapperRegistry
MapperRegistry是用于注册和缓存当前框架中所有的mapper接口
public class MapperRegistry {
//框架的配置对象
private final Configuration config;
//存放已经注册的mapper接口和其代码对象的工厂
private final Map, MapperProxyFactory> knownMappers = new HashMap, MapperProxyFactory>();;
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//从map中取出已经注册的mapper接口代理对象的工厂
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
//创建并返回mapper接口的代码对象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
}
...其他方法省略...
}
上述代码是SqlSession中调用getMapper(mapper接口)方法的底层,也就是说我们调用getMapper方法其底层是调用了MapperRegistry对象的getMapper方法,那么我们继续往下研究那就要去看MapperProxyFactory中的newInstance方法啦
MapperProxyFactory
MapperProxyFactory是mapper的代理工厂专门用于创建mapper接口的代理对象
public class MapperProxyFactory {
//代理的接口
private final Class mapperInterface;
//缓存代理的方法
private final Map methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap();
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
//创建一个MapperProxy对象,其内部封装了方法拿到接口的代码对象
final MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy); //调用方法返回接口的代理对象
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
//底层使用JDK动态创建接口的代理对象
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
...其他方法省略...
}
通过上述代码我们最终看到了mapper接口的代理对象其底层使用的是JDK的动态代理技术创建并返回代理对象,最终接口中所有的方法都会由mapperProxy对象中的invoke方法来实现,当前类的字段MapperMethod对象至关总要,后期代理对象的invoke所执行的方法,最终是会调用到其对象的execute方法
MapperProxy
MapperProxy类实现了JDK动态代理的InvocationHandler接口,最后将由该对象的invoke方法来完成真正的方法执行
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache;
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//判断是否是Object类中的方法,如equals/hashCode/toString等方法
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try { //原封不动调用Object类中方法作为代理对象方法的默认实现
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
//接口中其他的方法则调用之前方法缓冲器的处理策略
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
...其他方法省略...
}
MapperMethod
MapperMethod类是处理mapper接口中方法的真正处理器,该类内部的execute明确了代理的方法参数要怎么处理,查询得到的结果怎么封装然后返回
public class MapperMethod {
//对执行的SQL标签的封装,包含SQL类型和任务的完整ID等信息
private final SqlCommand command;
//代理方法的签名,其内部封装了一系列操作,如方法多参数时对@Param注解的处理
private final MethodSignature method;
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) { //针对DML/DQL操作执行
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
}
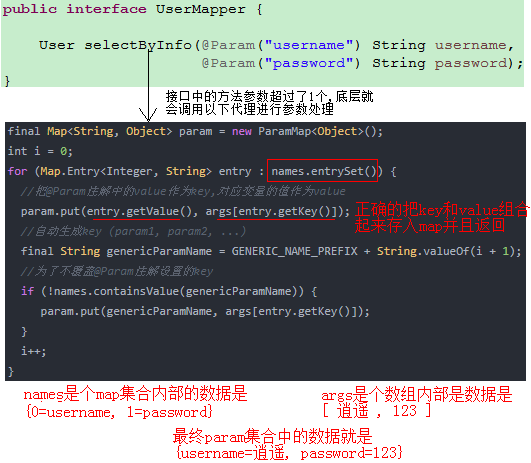
MethodSignature类中的convertArgsToSqlCommandParam方法处理接口中的参数怎么转换成能用于执行SQL任务的参数,以下是底层执行的getNamedParams方法
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
//接口方法没有参数,返回null
return null;
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
//接口方法上只有1个参数则返回唯一的那个对象
return args[names.firstKey()];
} else {
//接口方法上不止一个参数,就会把所有的参数封装到Map中然后返回
final Map param = new ParamMap 结合一个实际的例子来说明下:

假如调用方法时传入的实际参数是username=逍遥,password=123,那么在调用时我们可以发现接口中的方法超过1个的所以方法会执行最后的else代码
作者:梁开权,叩丁狼教育讲师。