Seq2Seq文本生成与tensorflow实现
1. 引言
近年来,深度神经网络在很多任务上都取得了不错的成绩,比如文本分类、图像识别等等,但是我们知道,像DNN神经网络结构只能解决一些分类或回归问题,而很多日常的任务却是一个序列到一个序列的映射问题,比如语音识别、机器翻译、对话系统等等,他们的输入和输出都是边长,而DNN要求输入和输出都是固定维度的,因此,这时需要引入新的结构,才能解决这种序列到序列的生成问题。2014年,谷歌提出了一种新的神经网络结构——Seq2Seq,就是用来专门解决这种序列的生成问题,并且在机器翻译等任务上都取得了出色的表现,本文将对该模型进行展开介绍,并用tensorflow来实现它。原论文的下载地址如下:
- 论文地址:《Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks》
2. Seq2Seq模型介绍
2.1 Seq2Seq模型结构
Seq2Seq模型主要包含两个部分,即一个编码器(encoder)和一个解码器(decoder),编码器和解码器分别采用LSTM神经元,因为LSTM神经元相比RNN更能提取长句子中的依赖信息。Seq2Seq的基本原理就是在编码器时,通过LSTM把输入转化为一个固定维度的向量作为输入句子的向量表示,然后将这个向量作为解码器中LSTM层隐藏层的初始化向量,接着逐步进行解码,将其转化为目标输出序列。
Seq2Seq模型的目标其实就是计算这样一个条件概率![]() ,其中
,其中![]() 表示输入序列,其序列长度为
表示输入序列,其序列长度为![]() ,
,![]() 表示输出序列,其序列长度为
表示输出序列,其序列长度为![]() ,
,![]() 和
和![]() 的大小可以不相同。在编码器(encoder)时,LSTM将输入序列
的大小可以不相同。在编码器(encoder)时,LSTM将输入序列![]() 转化为一个固定维度的向量
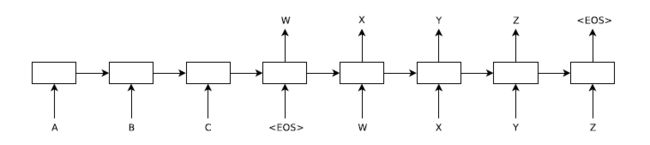
转化为一个固定维度的向量![]() ,这个向量其实就是取输入序列最后一个时间步的隐藏层状态,如图1中,输入序列“ABC”,
,这个向量其实就是取输入序列最后一个时间步的隐藏层状态,如图1中,输入序列“ABC”,![]() 即为“C”对应的隐藏层状态。接着,在解码器(decoder)时,将
即为“C”对应的隐藏层状态。接着,在解码器(decoder)时,将![]() 作为解码器的LSTM隐藏层的初始化状态,逐步地计算每个时间步的输出概率,最后将每个时间步的概率乘积作为输出序列的条件概率,其计算公式如下:
作为解码器的LSTM隐藏层的初始化状态,逐步地计算每个时间步的输出概率,最后将每个时间步的概率乘积作为输出序列的条件概率,其计算公式如下:
其中,每个时间步的条件概率![]() 都是在所有的词汇上经过softmax计算得到。
都是在所有的词汇上经过softmax计算得到。
那么,Seq2Seq是怎么确保输出序列的长度是可变的呢?其实是这样的,在输出序列时,会在每个输出序列的末尾加上一个结束标记符“![]() 预测出来的词汇刚好是“
预测出来的词汇刚好是“
另外,作者在实验中发现,有两个技巧可以很好地提高模型的效果:①适当增加encoder的LSTM层数,要比使用浅层的LSTM效果要更好;②对于输入序列,在训练时将其进行逆排序,比如图1中的“ABC”,在训练时变成“CBA”,之所以这样操作,是因为输入序列和输出序列的词汇顺序往往是有语义上的对应关系的,特别是在翻译任务中,因此,通过拟排序,可以使得两两对应的词汇更加接近,比如“A”与“W”最接近,从而使得在解码“W”时,可以更关注到“A”的信息,其他的词汇也类似。
2.2 模型的损失函数
Seq2Seq模型在训练时采用对数损失函数,即最大化真实目标序列的预测概率,其计算公式如下:
其中,![]() 表示训练集。
表示训练集。
3. Seq2Seq的tensorflow实现
下面用tensorflow对Seq2Seq模型进行复现,该版本代码加入了attention机制,有关attention机制的原理可以参见我另一篇文章《常见注意力机制原理介绍与对比》。代码实现如下:
import os
import config
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from config import seq2seq_config
from tensorflow.contrib import slim
from data_loader import gen_batch_data, encode_data, encode_data_for_predict
class Seq2Seq(object):
def __init__(self,
from_word_num=config.from_word_num + 2,
to_word_num=config.to_word_num + 2,
from_max_len=config.from_max_len,
to_max_len=config.to_max_len,
embedding_size=seq2seq_config.embedding_size,
hidden_dim=seq2seq_config.hidden_dim,
rnn_layers=seq2seq_config.rnn_layers,
batch_size=seq2seq_config.batch_size,
epoch=seq2seq_config.epoch,
learning_rate=seq2seq_config.learning_rate,
learning_decay_steps=seq2seq_config.learning_decay_steps,
learning_decay_rate=seq2seq_config.learning_decay_rate,
mode='train'
):
self.from_word_num = from_word_num
self.to_word_num = to_word_num
self.from_max_len = from_max_len
self.to_max_len = to_max_len
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.rnn_layers = rnn_layers
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.epoch = epoch
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.learning_decay_steps = learning_decay_steps
self.learning_decay_rate = learning_decay_rate
self.mode = mode
tf.reset_default_graph()
self.model()
def model(self):
# 初始化变量
self.encoder_input_data = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=[None, None], name="encoder_input_data")
self.decoder_input_data = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=[None, None], name="decoder_input_data")
self.decoder_output_data = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=[None, None], name="decoder_output_data")
self.keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='keep_prob')
# embedding层
with tf.variable_scope("embedding"):
encoder_embedding = tf.get_variable("encoder_embedding", shape=[self.from_word_num, self.embedding_size])
encoder_input_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(encoder_embedding, self.encoder_input_data)
decoder_embedding = tf.get_variable("decoder_embedding", shape=[self.to_word_num, self.embedding_size])
# encoder层
with tf.variable_scope("encoder"):
encoder_lstm_cell = self.build_rnn_cell()
encoder_outputs, encoder_states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(encoder_lstm_cell, encoder_input_emb, dtype=tf.float32)
# decoder层
with tf.variable_scope("decoder"):
with tf.variable_scope("attention"):
decoder_lstm_cell = self.build_rnn_cell()
attention_mechanism = tf.contrib.seq2seq.LuongAttention(self.hidden_dim, encoder_outputs)
decoder_cell = tf.contrib.seq2seq.AttentionWrapper(decoder_lstm_cell, attention_mechanism,
self.hidden_dim)
decoder_initial_state = decoder_cell.zero_state(tf.shape(self.encoder_input_data)[0], dtype=tf.float32)
decoder_initial_state = decoder_initial_state.clone(cell_state=encoder_states)
# 输出层
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
weights = tf.get_variable("weights", shape=[self.hidden_dim, self.to_word_num],
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.1))
biases = tf.get_variable("baises", shape=[self.to_word_num],
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
# 训练模式
if self.mode == 'train':
def cond(time, state, max_len, logits_list_pre):
return time < max_len
def body(time, state, max_len, logits_list_pre):
decoder_in = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(decoder_embedding, self.decoder_input_data[:, time])
output, state = decoder_cell(decoder_in, state)
logits = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(output, weights), biases)
logits_list_pre = logits_list_pre.write(time, logits)
return time + 1, state, max_len, logits_list_pre
logits_list_pre = tf.TensorArray(dtype=tf.float32, size=self.to_max_len, name="logits_list_pre")
loop_vars = [0, decoder_initial_state, self.to_max_len, logits_list_pre]
_, _, _, self.logits_list_pre = tf.while_loop(cond=cond, body=body, loop_vars=loop_vars)
# 预测时推理模式
elif self.mode == 'predict':
def cond(time, state, max_len, logits_list_pre, last_output):
return time < max_len
def body(time, state, max_len, logits_list_pre, last_output):
decoder_in = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(decoder_embedding, last_output)
output, state = decoder_cell(decoder_in, state)
logits = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(output, weights), biases)
logits_list_pre = logits_list_pre.write(time, logits)
last_output = tf.argmax(logits, axis=-1, output_type=tf.int32)
return time + 1, state, max_len, logits_list_pre, last_output
logits_list_pre = tf.TensorArray(dtype=tf.float32, size=self.to_max_len, name="logits_list_pre")
loop_vars = [0, decoder_initial_state, self.to_max_len, logits_list_pre, self.decoder_input_data[:, 0]]
_, _, _, self.logits_list_pre, _ = tf.while_loop(cond=cond, body=body, loop_vars=loop_vars)
# 计算损失函数
self.logits_list_pre = self.logits_list_pre.stack()
self.logits_list_pre = tf.transpose(self.logits_list_pre, perm=[1, 0, 2])
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=tf.reshape(self.decoder_output_data, [-1]),
logits=tf.reshape(self.logits_list_pre, [-1, self.to_word_num]))
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
# 优化函数
self.global_step = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(self.learning_rate, self.global_step,
self.learning_decay_steps, self.learning_decay_rate,
staircase=True)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate)
update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
self.optim = slim.learning.create_train_op(total_loss=self.loss, optimizer=optimizer, update_ops=update_ops)
def build_rnn_cell(self):
def single_rnn_cell():
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(self.hidden_dim)
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(cell, output_keep_prob=self.keep_prob)
return cell
rnn_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([single_rnn_cell() for _ in range(self.rnn_layers)])
return rnn_cell
def fit(self, from_train, to_train, from_val, to_val, from_words_index,
to_words_index, keep_prob=seq2seq_config.keep_prob,
save_path='./saves/' + config.model_select + '/',
summary_path=os.path.join('./summary', config.model_select)):
# 创建模型保存路径
if not os.path.exists(save_path):
os.makedirs(save_path)
if not os.path.exists(summary_path):
os.makedirs(summary_path)
# 将验证集转化为整数序列格式
encoder_input_data_val, decoder_input_data_val, decoder_output_data_val,_,_ = encode_data(
from_val, to_val, from_words_index, to_words_index
)
# 开始训练
tf.summary.scalar('val_loss', self.loss)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
sess = tf.Session()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(summary_path, sess.graph)
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=10)
# 加载现有的模型
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(save_path)
if ckpt:
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
train_steps = int(ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].replace('-',''))
else:
train_steps = 0
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(self.epoch):
batch_index_list = gen_batch_data(from_train, self.batch_size)
for batch_index in batch_index_list:
train_steps += 1
# 生成batch数据
from_batch = []
to_batch = []
for index in batch_index.tolist():
from_batch.append(from_train[index])
to_batch.append(to_train[index])
# 计算训练集的损失
encoder_input_data, decoder_input_data, decoder_output_data,_,_ = encode_data(
from_batch, to_batch, from_words_index, to_words_index
)
feed_dict = {self.encoder_input_data: encoder_input_data,
self.decoder_input_data: decoder_input_data,
self.decoder_output_data: decoder_output_data,
self.keep_prob: keep_prob}
_, train_loss = sess.run([self.optim, self.loss], feed_dict=feed_dict)
# 计算验证集的损失
if train_steps % 1000 == 0:
feed_dict = {self.encoder_input_data: encoder_input_data_val,
self.decoder_input_data: decoder_input_data_val,
self.decoder_output_data: decoder_output_data_val,
self.keep_prob: 1.0}
val_loss = sess.run(self.loss, feed_dict=feed_dict)
summary = sess.run(merged, feed_dict=feed_dict)
writer.add_summary(summary, global_step=train_steps)
saver.save(sess, save_path, global_step=train_steps)
msg = 'epoch:%d/%d,train_steps:%d,train_loss:%.4f,val_loss:%.4f'
print(msg % (i, self.epoch, train_steps, train_loss, val_loss))
sess.close()
def predict(self, from_test, to_test=None, from_words_index=None,
to_words_index=None, reverse_to_words_index=None,
save_path='./saves/' + config.model_select + '/',
result_path=os.path.join('./results', config.model_select)):
# 加载训练好的模型
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables())
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(save_path)
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
# 进行推理预测
predict_texts = []
batch_index_list = gen_batch_data(
from_test, batch_size=self.batch_size, shuffle=False
)
for batch_index in batch_index_list:
# 生成batch数据
from_batch = []
for index in batch_index.tolist():
from_batch.append(from_test[index])
# 计算训练集的损失
encoder_input_data = encode_data_for_predict(from_batch, from_words_index)
decoder_input_data = np.ones((self.batch_size, self.to_max_len), dtype='int32') * to_words_index['']
feed_dict = {self.encoder_input_data: encoder_input_data,
self.decoder_input_data: decoder_input_data,
self.keep_prob: 1.0}
logits = sess.run(self.logits_list_pre, feed_dict=feed_dict)
logits = np.argmax(logits, axis=2)
for j in range(self.batch_size):
predict_text = []
for k in range(self.to_max_len):
predict_word = reverse_to_words_index[logits[j, k]]
if predict_word != '':
predict_text.append(predict_word)
else:
break
predict_text = ' '.join(predict_text)
predict_texts.append(predict_text)
return predict_texts[0]
4. 总结
Seq2Seq的优缺点总结:
- 与RNN相比,Seq2Seq的优点主要是无需要求输入序列和输出序列必须完全对齐。
- 对于较长序列的生成效果也比较好。
- 模型的通用性强,适用于各种序列到序列的生成任务。