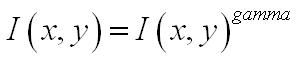HOG特征检测---简述
HOG特征检测---简述
1、HOG介绍
HOG:方向梯度直方图(histogram of oriented gradient),用于目标检测的特征描述子。一种解决人体目标检测的图像描述子,是一种用于表征图像局部梯度方向和梯度强度分布特性的描述符。
HOG特征原理:
HOG的核心思想是所检测的局部物体外形能够被光强梯度或边缘方向的分布所描述。通过将整幅图像分割成小的连接区域(称为cells),每个cell生成一个方向梯度直方图或者cell中pixel的边缘方向,这些直方图的组合可表示出(所检测目标的目标)描述子。为改善准确率,局部直方图可以通过计算图像中一个较大区域(称为block)的光强作为measure被对比标准化,然后用这个值(measure)归一化这个block中的所有cells.这个归一化过程完成了更好的照射/阴影不变性。
与其他描述子相比,HOG得到的描述子保持了几何和光学转化不变性(除非物体方向改变)。因此HOG描述子尤其适合人的检测。
HOG特征提取方法就是将一个image:
- 1. 灰度化(将图像看做一个x,y,z(灰度)的三维图像)
- 2. 划分成小cells(2*2)
- 3. 计算每个cell中每个pixel的gradient(即orientation)
- 4. 统计每个cell的梯度直方图(不同梯度的个数),即可形成每个cell的descriptor
2、HOG特征检测步骤:
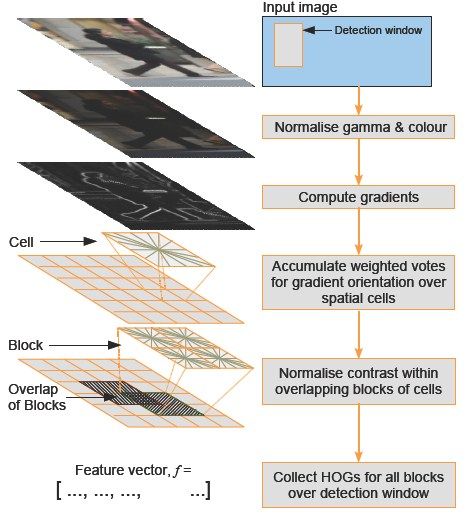
颜色空间归一化-------->梯度计算------------->梯度方向直方图---------->重叠块直方图归一化----------->HOG特征
(1)颜色空间归一化
①图像灰度化:对于彩色图像,将RGB分量转化成灰度图像。
②Gamma校正
在图像照度不均匀的情况下,可以通过Gamma校正,将图像整体亮度提高或降低。在实际中可以采用两种不同的方式进行Gamma标准化,平方根、对数法。这里我们采用平方根的办法,公式如下(其中Gamma=1/2):
(2)计算图像每个像素的梯度(包括大小和方向)
计算图像横坐标和纵坐标方向的梯度,并据此计算每个像素位置的梯度方向值;求导操作不仅能够捕获轮廓,人影和一些纹理信息,还能进一步弱化光照的影响。
梯度算子:水平边缘算子: [-1, 0, 1] ;垂直边缘算子: [-1, 0, 1]T
图像中像素点(x,y)的梯度为:
如3×3 Sobel 模板,或对角线模板(diagonal masks),在这个行人检测的实验中,这些复杂模板的表现都较差,所以作者的结论是:模板越简单,效果反而越好。
(3)将图像分割为小的Cell单元格
由于Cell单元格是HOG特征最小的结构单位,而且其块Block和检测窗口Win的滑动步长就是一个Cell的宽度或高度,所以,先把整个图像分割为一个个的Cell单元格(8*8像素)。
(4)为每个单元格构建梯度方向直方图【重点】
这步的目的是:统计局部图像梯度信息并进行量化(或称为编码),得到局部图像区域的特征描述向量。同时能够保持对图像中人体对象的姿势和外观的弱敏感性。
我们将图像分成若干个“单元格cell”,例如每个cell为8*8个像素(可以是矩形的(rectangular),也可以是星形的(radial))。假设我们采用9个bin的直方图来统计这8*8个像素的梯度信息。也就是将cell的梯度方向360度分成9个方向块,如图所示:例如:如果这个像素的梯度方向是20-40度,直方图第2个bin的计数就加一,这样,对cell内每个像素用梯度方向在直方图中进行加权投影(映射到固定的角度范围),就可以得到这个cell的梯度方向直方图了,就是该cell对应的9维特征向量(因为有9个bin)。
像素梯度方向用到了,那么梯度大小呢?梯度大小就是作为投影的权值的。例如说:这个像素的梯度方向是20-40度,然后它的梯度大小是2(假设啊),那么直方图第2个bin的计数就不是加一了,而是加二(假设啊)。
单元格Cell中的每一个像素点都为某个基于方向的直方图通道(orientation-based histogram channel)投票。投票是采取加权投票(weighted voting)的方式,即每一票都是带权值的,这个权值是根据该像素点的梯度幅度计算出来。可以采用幅值本身或者它的函数来表示这个权值,实际测试表明: 使用幅值来表示权值能获得最佳的效果,当然,也可以选择幅值的函数来表示,比如幅值的平方根(square root)、幅值的平方(square of the gradient magnitude)、幅值的截断形式(clipped version of the magnitude)等。根据Dalal等人论文的测试结果,采用梯度幅值量级本身得到的检测效果最佳,使用量级的平方根会轻微降低检测结果,而使用二值的边缘权值表示会严重降低效果。
其中,加权采用三线性插值(链接为详细说明的博文)方法,即将当前像素的梯度方向大小、像素在cell中的x坐标与y坐标这三个值来作为插值权重,而被用来插入的值为像素的梯度幅值。采用三线性插值的好处在于:避免了梯度方向直方图在cell边界和梯度方向量化的bin边界处的突然变化。

(5)把单元格组合成大的块(block),块内归一化梯度直方图【重点】
(6)生成HOG特征描述向量
(7)生成HOG特征描述向量
3、OpenCV2.4.11中HOG的介绍
注:HOG在OpenCV中的几个模块中都有,略有差别,OpenCV的官方文档中只有对GPU模块的HOG。
(1)GPU模块中的HOG
gpu::HOGDescriptor
struct gpu::HOGDescriptor
//The class implements Histogram of Oriented Gradients ([Dalal2005]) object detector.
结构体定义如下:
struct CV_EXPORTS HOGDescriptor
{
enum { DEFAULT_WIN_SIGMA = -1 };
enum { DEFAULT_NLEVELS = 64 };
enum { DESCR_FORMAT_ROW_BY_ROW, DESCR_FORMAT_COL_BY_COL };
HOGDescriptor(Size win_size=Size(64, 128), Size block_size=Size(16, 16),
Size block_stride=Size(8, 8), Size cell_size=Size(8, 8),
int nbins=9, double win_sigma=DEFAULT_WIN_SIGMA,
double threshold_L2hys=0.2, bool gamma_correction=true,
int nlevels=DEFAULT_NLEVELS);
size_t getDescriptorSize() const;
size_t getBlockHistogramSize() const;
void setSVMDetector(const vector& detector);
static vector getDefaultPeopleDetector();
static vector getPeopleDetector48x96();
static vector getPeopleDetector64x128();
void detect(const GpuMat& img, vector& found_locations,
double hit_threshold=0, Size win_stride=Size(),
Size padding=Size());
void detectMultiScale(const GpuMat& img, vector& found_locations,
double hit_threshold=0, Size win_stride=Size(),
Size padding=Size(), double scale0=1.05,
int group_threshold=2);
void getDescriptors(const GpuMat& img, Size win_stride,
GpuMat& descriptors,
int descr_format=DESCR_FORMAT_COL_BY_COL);
Size win_size;
Size block_size;
Size block_stride;
Size cell_size;
int nbins;
double win_sigma;
double threshold_L2hys;
bool gamma_correction;
int nlevels;
private:
// Hidden
}
常用函数介绍:
(1)C++: gpu::HOGDescriptor::HOGDescriptorSize win_size=Size(64, 128), Size block_size=Size(16, 16), Size block_stride=Size(8, 8), Size cell_size=Size(8, 8), int nbins=9, double win_sigma=DEFAULT_WIN_SIGMA, double threshold_L2hys=0.2, bool gamma_correction=true, int nlevels=DEFAULT_NLEVELS
创建HOG描述子和检测子
(2)C++: void gpu::HOGDescriptor::setSVMDetector(const vector
设置线性SVM分类器的系数
(3)C++: static vector
返回用于训练人检测的分类器系数
(4)C++: void gpu::HOGDescriptor::detectMultiScale(const GpuMat& img, vector
执行多尺度窗口对象检测
(2)objdetect/objdetect.hpp中HOG
结构体定义如下:
struct CV_EXPORTS_W HOGDescriptor
{
public:
enum { L2Hys=0 };
enum { DEFAULT_NLEVELS=64 };
CV_WRAP HOGDescriptor() : winSize(64,128), blockSize(16,16), blockStride(8,8),
cellSize(8,8), nbins(9), derivAperture(1), winSigma(-1),
histogramNormType(HOGDescriptor::L2Hys), L2HysThreshold(0.2), gammaCorrection(true),
nlevels(HOGDescriptor::DEFAULT_NLEVELS)
{}
CV_WRAP HOGDescriptor(Size _winSize, Size _blockSize, Size _blockStride,
Size _cellSize, int _nbins, int _derivAperture=1, double _winSigma=-1,
int _histogramNormType=HOGDescriptor::L2Hys,
double _L2HysThreshold=0.2, bool _gammaCorrection=false,
int _nlevels=HOGDescriptor::DEFAULT_NLEVELS)
: winSize(_winSize), blockSize(_blockSize), blockStride(_blockStride), cellSize(_cellSize),
nbins(_nbins), derivAperture(_derivAperture), winSigma(_winSigma),
histogramNormType(_histogramNormType), L2HysThreshold(_L2HysThreshold),
gammaCorrection(_gammaCorrection), nlevels(_nlevels)
{}
CV_WRAP HOGDescriptor(const String& filename)
{
load(filename);
}
HOGDescriptor(const HOGDescriptor& d)
{
d.copyTo(*this);
}
virtual ~HOGDescriptor() {}
CV_WRAP size_t getDescriptorSize() const;
CV_WRAP bool checkDetectorSize() const;
CV_WRAP double getWinSigma() const;
CV_WRAP virtual void setSVMDetector(InputArray _svmdetector);
virtual bool read(FileNode& fn);
virtual void write(FileStorage& fs, const String& objname) const;
CV_WRAP virtual bool load(const String& filename, const String& objname=String());
CV_WRAP virtual void save(const String& filename, const String& objname=String()) const;
virtual void copyTo(HOGDescriptor& c) const;
CV_WRAP virtual void compute(const Mat& img,
CV_OUT vector& descriptors,
Size winStride=Size(), Size padding=Size(),
const vector& locations=vector()) const;
//with found weights output
CV_WRAP virtual void detect(const Mat& img, CV_OUT vector& foundLocations,
CV_OUT vector& weights,
double hitThreshold=0, Size winStride=Size(),
Size padding=Size(),
const vector& searchLocations=vector()) const;
//without found weights output
virtual void detect(const Mat& img, CV_OUT vector& foundLocations,
double hitThreshold=0, Size winStride=Size(),
Size padding=Size(),
const vector& searchLocations=vector()) const;
//with result weights output
CV_WRAP virtual void detectMultiScale(const Mat& img, CV_OUT vector& foundLocations,
CV_OUT vector& foundWeights, double hitThreshold=0,
Size winStride=Size(), Size padding=Size(), double scale=1.05,
double finalThreshold=2.0,bool useMeanshiftGrouping = false) const;
//without found weights output
virtual void detectMultiScale(const Mat& img, CV_OUT vector& foundLocations,
double hitThreshold=0, Size winStride=Size(),
Size padding=Size(), double scale=1.05,
double finalThreshold=2.0, bool useMeanshiftGrouping = false) const;
CV_WRAP virtual void computeGradient(const Mat& img, CV_OUT Mat& grad, CV_OUT Mat& angleOfs,
Size paddingTL=Size(), Size paddingBR=Size()) const;
CV_WRAP static vector getDefaultPeopleDetector();
CV_WRAP static vector getDaimlerPeopleDetector();
CV_PROP Size winSize;
CV_PROP Size blockSize;
CV_PROP Size blockStride;
CV_PROP Size cellSize;
CV_PROP int nbins;
CV_PROP int derivAperture;
CV_PROP double winSigma;
CV_PROP int histogramNormType;
CV_PROP double L2HysThreshold;
CV_PROP bool gammaCorrection;
CV_PROP vector svmDetector;
CV_PROP int nlevels;
// evaluate specified ROI and return confidence value for each location
void detectROI(const cv::Mat& img, const vector &locations,
CV_OUT std::vector& foundLocations, CV_OUT std::vector& confidences,
double hitThreshold = 0, cv::Size winStride = Size(),
cv::Size padding = Size()) const;
// evaluate specified ROI and return confidence value for each location in multiple scales
void detectMultiScaleROI(const cv::Mat& img,
CV_OUT std::vector& foundLocations,
std::vector& locations,
double hitThreshold = 0,
int groupThreshold = 0) const;
// read/parse Dalal's alt model file
void readALTModel(std::string modelfile);
void groupRectangles(vector& rectList, vector& weights, int groupThreshold, double eps) const;
};
行人检测-----opencv2.4.11官方实例
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/objdetect/objdetect.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
// static void help()
// {
// printf(
// "\nDemonstrate the use of the HoG descriptor using\n"
// " HOGDescriptor::hog.setSVMDetector(HOGDescriptor::getDefaultPeopleDetector());\n"
// "Usage:\n"
// "./peopledetect ( | .txt)\n\n");
// }
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat img;
FILE* f = 0;
char _filename[1024];
if( argc == 1 )
{
printf("Usage: peopledetect ( | .txt)\n");
return 0;
}
img = imread(argv[1]);
if( img.data )
{
strcpy(_filename, argv[1]);
}
else
{
f = fopen(argv[1], "rt");
if(!f)
{
fprintf( stderr, "ERROR: the specified file could not be loaded\n");
return -1;
}
}
HOGDescriptor hog;
hog.setSVMDetector(HOGDescriptor::getDefaultPeopleDetector());
namedWindow("people detector", 1);
for(;;)
{
char* filename = _filename;
if(f)
{
if(!fgets(filename, (int)sizeof(_filename)-2, f))
break;
//while(*filename && isspace(*filename))
// ++filename;
if(filename[0] == '#')
continue;
int l = (int)strlen(filename);
while(l > 0 && isspace(filename[l-1]))
--l;
filename[l] = '\0';
img = imread(filename);
}
printf("%s:\n", filename);
if(!img.data)
continue;
fflush(stdout);
vector found, found_filtered;
double t = (double)getTickCount();
// run the detector with default parameters. to get a higher hit-rate
// (and more false alarms, respectively), decrease the hitThreshold and
// groupThreshold (set groupThreshold to 0 to turn off the grouping completely).
hog.detectMultiScale(img, found, 0, Size(8,8), Size(32,32), 1.05, 2);
t = (double)getTickCount() - t;
printf("tdetection time = %gms\n", t*1000./cv::getTickFrequency());
size_t i, j;
for( i = 0; i < found.size(); i++ )
{
Rect r = found[i];
for( j = 0; j < found.size(); j++ )
if( j != i && (r & found[j]) == r)
break;
if( j == found.size() )
found_filtered.push_back(r);
}
for( i = 0; i < found_filtered.size(); i++ )
{
Rect r = found_filtered[i];
// the HOG detector returns slightly larger rectangles than the real objects.
// so we slightly shrink the rectangles to get a nicer output.
r.x += cvRound(r.width*0.1);
r.width = cvRound(r.width*0.8);
r.y += cvRound(r.height*0.07);
r.height = cvRound(r.height*0.8);
rectangle(img, r.tl(), r.br(), cv::Scalar(0,255,0), 3);
}
imshow("people detector", img);
int c = waitKey(0) & 255;
if( c == 'q' || c == 'Q' || !f)
break;
}
if(f)
fclose(f);
return 0;
}
为了在Windows下运行,对官方代码进行修改:
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/objdetect/objdetect.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
static void help()
{
printf(
"\nDemonstrate the use of the HoG descriptor using\n"
" HOGDescriptor::hog.setSVMDetector(HOGDescriptor::getDefaultPeopleDetector());\n"
"Usage:\n"
"./peopledetect ( | .txt)\n\n");
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat img;
FILE* f = 0;
char _filename[1024];
help();
argv[1]="E:\\b.jpg"; //待检测的图像路径
img = imread(argv[1]); //读入图像
if( img.data )
{
strcpy(_filename, argv[1]); //将待检测图像路径传给_filename
}
else
{
f = fopen(argv[1], "rt"); //用于图像列表的处理
if(!f)
{
fprintf( stderr, "ERROR: the specified file could not be loaded\n");
return -1;
}
}
HOGDescriptor hog; //定义HOG描述子对象hog
hog.setSVMDetector(HOGDescriptor::getDefaultPeopleDetector()); //设置线性SVM分类器的系数;返回用于训练人检测的分类器系数
namedWindow("people detector", 1);
for(;;)
{
char* filename = _filename;
if(f) //用于图像列表的处理
{
if(!fgets(filename, (int)sizeof(_filename)-2, f))
break;
//while(*filename && isspace(*filename))
// ++filename;
if(filename[0] == '#')
continue;
int l = (int)strlen(filename);
while(l > 0 && isspace(filename[l-1]))
--l;
filename[l] = '\0';
img = imread(filename);
}
printf("%s:\n", filename);
if(!img.data)
continue;
fflush(stdout); //清除读写缓冲区,需要立即把输出缓冲区的数据进行物理写入时
vector found, found_filtered;
double t = (double)getTickCount(); //计时开始
// run the detector with default parameters. to get a higher hit-rate
// (and more false alarms, respectively), decrease the hitThreshold and
// groupThreshold (set groupThreshold to 0 to turn off the grouping completely).
hog.detectMultiScale(img, found, 0, Size(8,8), Size(32,32), 1.05, 2); //执行多尺度窗口对象检测
t = (double)getTickCount() - t; //计时结束
printf("tdetection time = %gms\n", t*1000./cv::getTickFrequency());
size_t i, j;
for( i = 0; i < found.size(); i++ ) //进行画矩形
{
Rect r = found[i];
for( j = 0; j < found.size(); j++ )
if( j != i && (r & found[j]) == r)
break;
if( j == found.size() )
found_filtered.push_back(r);
}
for( i = 0; i < found_filtered.size(); i++ )
{
Rect r = found_filtered[i];
// the HOG detector returns slightly larger rectangles than the real objects.
// so we slightly shrink the rectangles to get a nicer output.
r.x += cvRound(r.width*0.1);
r.width = cvRound(r.width*0.8);
r.y += cvRound(r.height*0.07);
r.height = cvRound(r.height*0.8);
rectangle(img, r.tl(), r.br(), cv::Scalar(0,255,0), 3);
}
imshow("people detector", img);
int c = waitKey(0) & 255;
if( c == 'q' || c == 'Q' || !f)
break;
}
if(f)
fclose(f);
return 0;
}
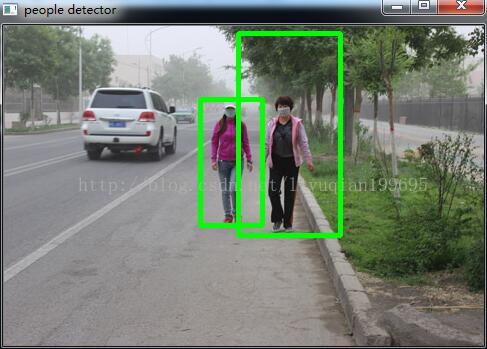
运行结果:
参考博客:
http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7365651
http://blog.csdn.net/zhazhiqiang/article/details/21047207
http://blog.csdn.net/hujingshuang/article/details/47337707/