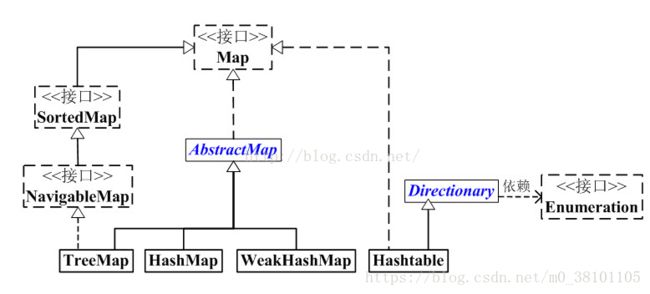
Map集合的源码解读
package java.util;
public interface Map {
boolean isEmpty();
boolean containsKey(Object key);
boolean containsValue(Object value);
V get(Object key);
V put(K key, V value);
V remove(Object key);
void putAll(Map m);
void clear();
Set keySet(); //保存key的Set
Collection values(); //保存value的Collection
Set> entrySet(); //保存Map.Entry的Set
interface Entry { //Map内部的一个接口,Entry中封装了key和value信息
K getKey();
V getValue();
V setValue(V value);
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}
AbstractMap继承了Map,但没有实现entrySet()方法(该方法还是abstract修饰),如果要继承AbstractMap,需要自己实现entrySet()方法。没有真正实现put(K key, V value)方法,这里“没有真正实现”的意思是,该方法在形式上已经实现了,即没有用abstract修饰了,但是方法内部仅仅是抛出个异常,并没有真正实现方法体内容,从下面的源码中可以看到。
package java.util;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public abstract class AbstractMap implements Map {
//空构造方法
protected AbstractMap() {
}
//返回Map中存储多少键值对
public int size() {
return entrySet().size();
}
//判断Map是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
//判断Map中是否包含值为value的键值对
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
//entrySet()返回一个装有Map.Entry的Set,然后获得Set的iterator
Iterator> i = entrySet().iterator();
if (value==null) { //从这里可以看出Map中允许value==null
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry e = i.next();
if (e.getValue()==null)
return true;
}
} else {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry e = i.next();
if (value.equals(e.getValue()))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//判断Map中是否含有键为key的键值对
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
Iterator> i = entrySet().iterator();
if (key==null) { //从这里可以看出Map中允许key==null
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry e = i.next();
if (e.getKey()==null)
return true;
}
} else {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry e = i.next();
if (key.equals(e.getKey()))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//通过key获得对应的value值
public V get(Object key) {
Iterator> i = entrySet().iterator();
if (key==null) {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry e = i.next();
if (e.getKey()==null) //从这里可以看出,key=null的必须value=null
return e.getValue();
}
} else {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry e = i.next();
if (key.equals(e.getKey()))
return e.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}
public V put(K key, V value) { //put方法体内部没有具体实现,需要继承后自己实现
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//删除指定key的Entry
public V remove(Object key) {
Iterator> i = entrySet().iterator();
Entry correctEntry = null; //用来保存待删除的Entry
if (key==null) {
while (correctEntry==null && i.hasNext()) {
Entry e = i.next();
if (e.getKey()==null)
correctEntry = e;
}
} else {
while (correctEntry==null && i.hasNext()) {
Entry e = i.next();
if (key.equals(e.getKey()))
correctEntry = e;
}
}
V oldValue = null; //用来保存待删除Entry的value值
if (correctEntry !=null) { //correctEntry不为null表示找到了待删除的Entry
oldValue = correctEntry.getValue();
i.remove();
}
return oldValue;
}
//向Map中添加新的Map m
public void putAll(Map m) {
for (Map.Entry e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue()); //调用上面未实现的put方法
}
//清空整个Map
public void clear() {
entrySet().clear();
}
//keySet用来保存key的Set,values用来保存value的Collection
transient volatile Set keySet = null;
transient volatile Collection values = null;
//获取Map中所有的key,保存到keySet成员变量中返回。keySet是个Set类型
public Set keySet() {
if (keySet == null) {
keySet = new AbstractSet() { //内部类AbstractSet
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Iterator() {//内部类Iterator
private Iterator> i = entrySet().iterator();
public boolean hasNext() {
return i.hasNext();
}
public K next() {
return i.next().getKey();
}
public void remove() {
i.remove();
}
};
}
public int size() {
return AbstractMap.this.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return AbstractMap.this.isEmpty();
}
public void clear() {
AbstractMap.this.clear();
}
public boolean contains(Object k) {
return AbstractMap.this.containsKey(k);
}
};
}
return keySet;
}
//获取Map中所有的value,保存到values成员变量中返回。values是个Collection类型
public Collection values() {
if (values == null) {
values = new AbstractCollection() {
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Iterator() {
private Iterator> i = entrySet().iterator();
public boolean hasNext() {
return i.hasNext();
}
public V next() {
return i.next().getValue();
}
public void remove() {
i.remove();
}
};
}
public int size() {
return AbstractMap.this.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return AbstractMap.this.isEmpty();
}
public void clear() {
AbstractMap.this.clear();
}
public boolean contains(Object v) {
return AbstractMap.this.containsValue(v);
}
};
}
return values;
}
public abstract Set> entrySet(); //未实现,还是抽象方法
//Map中的equals方法,从源码中可以看出,比较的是value的值,所有value值都相等才返回true
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) //如果对象都一样,必然返回true
return true;
if (!(o instanceof Map)) //传进来的对象若不是Map类型肯定false
return false;
Map m = (Map) o;
if (m.size() != size()) //两个对象的size不同肯定false
return false;
try { //好了,上面的条件都满足了,下面就挨个比较value值了
Iterator> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
if (value == null) {
if (!(m.get(key)==null && m.containsKey(key)))
return false;
} else {
if (!value.equals(m.get(key)))
return false;
}
}
} catch (ClassCastException unused) {
return false;
} catch (NullPointerException unused) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
//hashCode
public int hashCode() {
int h = 0;
Iterator> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
h += i.next().hashCode(); //调用Entry中的hashCode()方法
return h;
}
//实现toString方法:{key=value}形式输出
public String toString() {
Iterator> i = entrySet().iterator();
if (! i.hasNext())
return "{}";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); //使用StringBuilder
sb.append('{');
for (;;) {
Entry e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
sb.append(key == this ? "(this Map)" : key);
sb.append('=');
sb.append(value == this ? "(this Map)" : value);
if (! i.hasNext())
return sb.append('}').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
AbstractMap result = (AbstractMap)super.clone();
result.keySet = null;
result.values = null;
return result;
}
private static boolean eq(Object o1, Object o2) {
return o1 == null ? o2 == null : o1.equals(o2);
}
//SimpleEntry实现了Map类中的Entry接口,另外也实现了Serializable接口,可序列化
public static class SimpleEntry
implements Entry, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8499721149061103585L;
private final K key;
private V value;
public SimpleEntry(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public SimpleEntry(Entry entry) {
this.key = entry.getKey();
this.value = entry.getValue();
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public V setValue(V value) {
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
return eq(key, e.getKey()) && eq(value, e.getValue());
}
public int hashCode() {
return (key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
//SimpleImmutableEntry实现了Map类中的Entry接口,另外也实现了Serializable接口,可序列化
public static class SimpleImmutableEntry
implements Entry, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7138329143949025153L;
private final K key;
private final V value;
public SimpleImmutableEntry(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public SimpleImmutableEntry(Entry entry) {
this.key = entry.getKey();
this.value = entry.getValue();
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public V setValue(V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
return eq(key, e.getKey()) && eq(value, e.getValue());
}
public int hashCode() {
return (key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
//重写了toString方法,返回key=value形式
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
}
SortedMap也是一个接口,继承与Map接口,Sorted表示它是一个有序的键值映射。
SortedMap的排序方式有两种:自然排序和指定比较器排序。插入有序的SortedMap的所有元素都必须实现Comparable接口(或被指定的比较器所接受)。
SortedMap定义的API:
//继承与Map的API不再赘写
package java.util;
public interface SortedMap extends Map {
Comparator comparator(); //返回比较器对象
SortedMap subMap(K fromKey, K toKey); //返回指定key范围内的Map
SortedMap headMap(K toKey); //返回小于指定key的部分集合
SortedMap tailMap(K fromKey); //返回大于等于指定key的部分集合
K firstKey(); //返回第一个元素的key
K lastKey(); //返回最后一个元素的key
}
NavigableMap继承与SortedMap,先看它的API
package java.util;
public interface NavigableMap extends SortedMap {
Map.Entry lowerEntry(K key);
K lowerKey(K key);
Map.Entry floorEntry(K key);
K floorKey(K key);
Map.Entry ceilingEntry(K key);
K ceilingKey(K key);
Map.Entry higherEntry(K key);
K higherKey(K key);
Map.Entry lastEntry();
Map.Entry pollLastEntry();
NavigableMap descendingMap();
NavigableSet navigableKeySet();
NavigableSet descendingKeySet();
NavigableMap subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive,
K toKey, boolean toInclusive);
NavigableMap headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive);
NavigableMap tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive);
SortedMap subMap(K fromKey, K toKey);
SortedMap headMap(K toKey);
SortedMap tailMap(K fromKey);
}
Dictionary中也包括了操作键值对的基本方法呢,它的定义以及API如下:
package java.util;
public abstract
class Dictionary {
public Dictionary() {
}
abstract public int size();
abstract public boolean isEmpty();
abstract public Enumeration keys();
abstract public Enumeration elements();
abstract public V get(Object key);
abstract public V put(K key, V value);
abstract public V remove(Object key);
}
set的底层就是用Map来实现的,所以熟悉map的底层对我们的学习大有帮助。