RT-Thread驱动——RTC PCF8563
1 介绍
1.1 RTC选择
RTC选择不外乎就两种,独立外挂和CPU集成,精度要求不高或者联网的情况下使用集成RTC即可,可节约成本。独立RTC的选择则比较多,从低端到高精度的,各大厂商都有可选择,常用的如DS1302、PCF8563、DS3231等。对于时间要求严格,并且没有连接网络无法同步网络时间,则需要选择独立RTC,对于RT-Thread来说,本人针对PCF8563和DS3231都进行测试过,并且在产品上已经使用。所以选择一款经典的RTC芯片,以PCF8563为例,阐述RTT下的RTC驱动实现,举一反三,根据此更换其他RTC芯片则是依葫芦画瓢。
1.2 PCF8563
PCF8563是一款非常经典的实时时钟(RTC)芯片,是飞利浦(PHILIPS)司推出的一款工业级内含I2C 总线接口功能的具有极低功耗的多功能时钟/日历芯片。PCF8563的驱动源码和说明文档也是非常多,特别是可以参考Linux内核的PCF8563源码。
2 RT-Thread驱动
2.1 RTT驱动模型
RTT驱动模型和Linux比较类似,严格分为几层,而且层次分明,层与层之间都有标准的访问接口,最上层封则装成统一的接口,即是open、read、write、close。
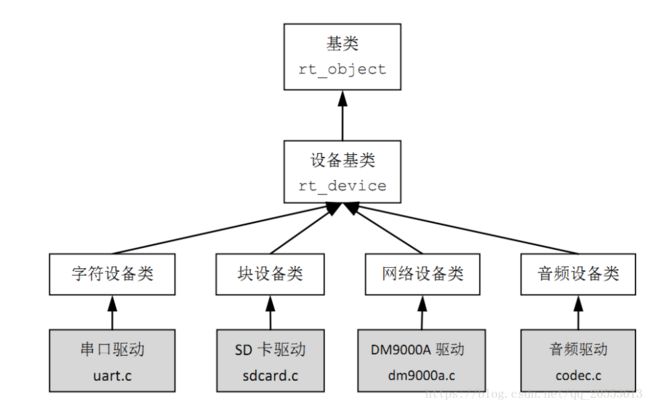
RTT 驱动类型为“struct rt_device”结构体,其原型如下:
/**
* Device structure
*/
struct rt_device
{
struct rt_object parent; /**< inherit from rt_object */
enum rt_device_class_type type; /**< device type */
rt_uint16_t flag; /**< device flag */
rt_uint16_t open_flag; /**< device open flag */
rt_uint8_t ref_count; /**< reference count */
rt_uint8_t device_id; /**< 0 - 255 */
/* device call back */
rt_err_t (*rx_indicate)(rt_device_t dev, rt_size_t size);
rt_err_t (*tx_complete)(rt_device_t dev, void *buffer);
/* common device interface */
rt_err_t (*init) (rt_device_t dev);
rt_err_t (*open) (rt_device_t dev, rt_uint16_t oflag);
rt_err_t (*close) (rt_device_t dev);
rt_size_t (*read) (rt_device_t dev, rt_off_t pos, void *buffer, rt_size_t size);
rt_size_t (*write) (rt_device_t dev, rt_off_t pos, const void *buffer, rt_size_t size);
rt_err_t (*control)(rt_device_t dev, rt_uint8_t cmd, void *args);
void *user_data; /**< device private data */
};
其中的函数指针部分就是需要我们在底层重点实现的,其他参数则为描述驱动类型或者调用驱动的方式设置。
2.2 RTT的RTC框架模型
RTT兼容C库的时间获取函数—“time”,并重写了time函数,其实现源码如下。
#if defined (__IAR_SYSTEMS_ICC__) && (__VER__) >= 6020000
#pragma module_name = "?time"
time_t (__time32)(time_t *t) /* Only supports 32-bit timestamp */
#else
time_t time(time_t *t)
#endif
{
static rt_device_t device = RT_NULL;
time_t time_now = 0;
/* optimization: find rtc device only first. */
if (device == RT_NULL)
{
device = rt_device_find("rtc");
}
/* read timestamp from RTC device. */
if (device != RT_NULL)
{
if (rt_device_open(device, 0) == RT_EOK)
{
rt_device_control(device, RT_DEVICE_CTRL_RTC_GET_TIME, &time_now);
rt_device_close(device);
}
}
/* if t is not NULL, write timestamp to *t */
if (t != RT_NULL)
{
*t = time_now;
}
return time_now;
}
设置日期和时间的函数分别为“set_date”和“set_time”,这个几个函数需要我们关注的地方是RTC驱动注册名称为“rtc”,及“control”函数。了解这几个函数,主要是熟悉访问RTC驱动的方式,以下面实现PCF8563驱动过程。
2.3 RTT驱动调用过程
3 RTT PCF8563驱动
在使用RTT驱动框架控制一个外设时,原则上最基本的需要实现的函数实体分别有“init”、“open”、“close”、“read”、“write”以及“control”函数,这样应用层就可也驱动框架接口(API)访问底层外设。
而通过上文分析RTT下的RTC设备模型可看出,访问RTC设备是循序地按照“open->read/write->close”的来处理,对于行时间的获取和设置,都是通“control”函数接口进行。因此我们在这里需要关键实现的即是“control”函数接口对应的实体函数,该函数的功能包括从PCF8563读出时间和向PCF8563写入设定的时间。而对于“open”、“close”函数,则暂保留为空,如果后期RTT框架有改动,则增加open和close的内容。
3.1 PCF8563设备接口实现——control函数实现
static rt_err_t rt_pcf8563_control(rt_device_t dev, int cmd, void *args)
{
rt_err_t ret = RT_EOK;
time_t *time;
struct tm time_temp;
rt_uint8_t buff[7];
RT_ASSERT(dev != RT_NULL);
rt_memset(&time_temp, 0, sizeof(struct tm));
switch (cmd)
{
case RT_DEVICE_CTRL_RTC_GET_TIME:
time = (time_t *)args;
ret = pcf8563_read_reg(REG_PCF8563_SEC,buff,7);
if(ret == RT_EOK)
{
time_temp.tm_year = bcd_to_hex(buff[6]&SHIELD_PCF8563_YEAR) + 2000 - 1900;
time_temp.tm_mon = bcd_to_hex(buff[5]&SHIELD_PCF8563_MON) - 1;
time_temp.tm_mday = bcd_to_hex(buff[3]&SHIELD_PCF8563_DAY);
time_temp.tm_hour = bcd_to_hex(buff[2]&SHIELD_PCF8563_HOUR);
time_temp.tm_min = bcd_to_hex(buff[1]&SHIELD_PCF8563_MIN);
time_temp.tm_sec = bcd_to_hex(buff[0]&SHIELD_PCF8563_SEC);
*time = mktime(&time_temp);
}
break;
case RT_DEVICE_CTRL_RTC_SET_TIME:
{
struct tm *time_new;
time = (time_t *)args;
time_new = localtime(time);
buff[6] = hex_to_bcd(time_new->tm_year + 1900 - 2000);
buff[5] = hex_to_bcd(time_new->tm_mon + 1);
buff[3] = hex_to_bcd(time_new->tm_mday);
buff[4] = hex_to_bcd(time_new->tm_wday+1);
buff[2] = hex_to_bcd(time_new->tm_hour);
buff[1] = hex_to_bcd(time_new->tm_min);
buff[0] = hex_to_bcd(time_new->tm_sec);
ret = pcf8563_write_reg(REG_PCF8563_SEC,buff,7);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return RT_EOK;
}
-
“RT_DEVICE_CTRL_RTC_GET_TIME”和“RT_DEVICE_CTRL_RTC_SET_TIME”分别是RTT定义的获取时间命令字和设置时间命令字。 -
RTT的RTC模型与Linux系统类似,将具体年月日换算成时间戳。
-
关于年和月的处理:
struct tm为标准C库定义的结构体,结构体中的“tm_year”(年份)是从1900年开始的,“tm_mon”(月份)范围是0—11,0表示1月;而PCF8563的年份值范围是0—99,月份值范围是1—12,因此要做相关处理。 -
“pcf8563_read_reg”和“pcf8563_write_reg”是PCF8563读写寄存器函数,通过此两函数从寄存器获取时间或者设置(写入)时间。 -
从PCF8563中获取的时间值为BCD码,故需编写
“bcd_to_hex”转换函数将BCD码转换为十进制数;同理在设置时间前,需要将十进制数转换为BCD码,即“hex_to_bcd”函数,然后再写寄存器。两者函数源码如下。
/* bcd to hex */
static unsigned char bcd_to_hex(unsigned char data)
{
unsigned char temp;
temp = ((data>>4)*10 + (data&0x0f));
return temp;
}
/* hex_to_bcd */
static unsigned char hex_to_bcd(unsigned char data)
{
unsigned char temp;
temp = (((data/10)<<4) + (data%10));
return temp;
}
3.2 PCF8563底层驱动
PCF8563底层驱动即是通过i2c总线读写其寄存器,而i2c总线RTT已经统一好框架,通过RTT的标准框架调用i2c总线进行访问PCF8563。这里i2c总线框架与底层分离,i2c总线底层的实现则与具体cpu型号相关。
第一步,定义一个注册设备用的PCF8563结构体
struct pcf8563_device
{
struct rt_device rtc_parent;
struct rt_i2c_bus_device *i2c_device;
};
rtc_parent是标准RTT驱动设备框架参数。i2c_device是i2c总线指针,通过该指针调用i2c总线,使用前必须初始化。
第二步,编写PCF8563读写函数
/* pcf8563 read register */
rt_uint8_t pcf8563_read_reg(rt_uint8_t reg,rt_uint8_t *data,rt_uint8_t data_size)
{
struct rt_i2c_msg msg[2];
msg[0].addr = PCF8563_ARRD;
msg[0].flags = RT_I2C_WR;
msg[0].len = 1;
msg[0].buf = ®
msg[1].addr = PCF8563_ARRD;
msg[1].flags = RT_I2C_RD;
msg[1].len = data_size;
msg[1].buf = data;
if(rt_i2c_transfer(pcf8563_dev.i2c_device, msg, 2) != 2)
return RT_ERROR;
return RT_EOK;
}
/* pcf8563 write register */
rt_err_t pcf8563_write_reg(rt_uint8_t reg, rt_uint8_t *data,rt_uint8_t data_size)
{
struct rt_i2c_msg msg[2];
msg[0].addr = PCF8563_ARRD;
msg[0].flags = RT_I2C_WR;
msg[0].len = 1;
msg[0].buf = ®
msg[1].addr = PCF8563_ARRD;
msg[1].flags = RT_I2C_WR | RT_I2C_NO_START;
msg[1].len = data_size;
msg[1].buf = data;
if (rt_i2c_transfer(pcf8563_dev.i2c_device, msg, 2) == 2)
{
return RT_EOK;
}
else
{
rt_kprintf("i2c bus write failed!\r\n");
return -RT_ERROR;
}
}
- 使用到RTT的i2c接口函数为
“rt_i2c_transfer”,入口参数分别为:i2c设备指针、信息帧、帧数。 “struct rt_i2c_msg”是RTT定义的i2c信息帧,原型如下。
struct rt_i2c_msg
{
rt_uint16_t addr;
rt_uint16_t flags;
rt_uint16_t len;
rt_uint8_t *buf;
};
addr,i2c器件地址,不包括读写位,如PCF8563的地址为0x51。flags,标识位,有几种类型,包括读、写、10bit i2c地址选择、应答、非应答。
#define RT_I2C_WR 0x0000
#define RT_I2C_RD (1u << 0)
#define RT_I2C_ADDR_10BIT (1u << 2) /* this is a ten bit chip address */
#define RT_I2C_NO_START (1u << 4)
#define RT_I2C_IGNORE_NACK (1u << 5)
#define RT_I2C_NO_READ_ACK (1u << 6) /* when I2C reading, we do not ACK */
len,数据长度。buf,数据缓存指针(发送或者接收)。- 对于读函数,需要两帧信息,第一帧发送读寄存器地址数据,第二帧开始接收返回数据;对于写函数,同样需要两帧,第一帧发送写寄存器地址数据,第二帧发送待写入的数据。
3.3 初始化
初始化包括两部分,一是指定i2c总线,PCF8563读写函数通过调用i2c总线进行访问;而是RTC设备初始化,上层应用从而可通过标准接口访问PCF8563。
/* pcf8563 device int */
int rt_hw_pcf8563_init(void)
{
struct rt_i2c_bus_device *i2c_device;
uint8_t data;
i2c_device = rt_i2c_bus_device_find("i2c1");
if (i2c_device == RT_NULL)
{
#ifdef RT_USE_FINSH_DEBUG
rt_kprintf("i2c bus device %s not found!\r\n", "i2c1");
#endif
return 1;
}
pcf8563_dev.i2c_device = i2c_device;
/* register rtc device */
pcf8563_dev.rtc_parent.type = RT_Device_Class_RTC;
pcf8563_dev.rtc_parent.init = RT_NULL;
pcf8563_dev.rtc_parent.open = rt_pcf8563_open;
pcf8563_dev.rtc_parent.close = RT_NULL;
pcf8563_dev.rtc_parent.read = rt_pcf8563_read;
pcf8563_dev.rtc_parent.write = RT_NULL;
pcf8563_dev.rtc_parent.control = rt_pcf8563_control;
pcf8563_dev.rtc_parent.user_data = RT_NULL; /* no private */
rt_device_register(&pcf8563_dev.rtc_parent, "rtc", RT_DEVICE_FLAG_RDWR);
/* init pcf8563 */
data = 0x7f; /* close clock out */
if (pcf8563_write_reg(REG_PCF8563_CLKOUT, &data, 1) != RT_EOK)
{
return -RT_ERROR;
}
return RT_EOK;
}
INIT_DEVICE_EXPORT(rt_hw_pcf8563_init);
- 初始化最开始定义的
“pcf8563_dev”,其中“rt_pcf8563_open”、“rt_pcf8563_read”只是空函数,没有实现内容;然后注册为“rtc”设备,RTT默认调用RTC的名称为“rtc”,采用统一命名,更换RTC芯片时保证该命名一致。 - 调用RTT宏
“INIT_DEVICE_EXPORT”完成初始化。
4 完整源码
#ifndef _DRV_PCF8563_H_
#define _DRV_PCF8563_H_
#include /*
* File : drv_pcf8563.c
* This file is part of RT-Thread RTOS
* COPYRIGHT (C) 2006 - 2018, RT-Thread Development Team
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
* with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
* 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Change Logs:
* Date Author Notes
* 2018-04-20 Acuity the first version
*/
#include 