使用dom4j支持xpath的操作( 可以直接获取到某个元素)
采用dom4j对xpath 的操作,可以直接获取到某个元素,不用像sax 一样一层一层解析
第一种形式
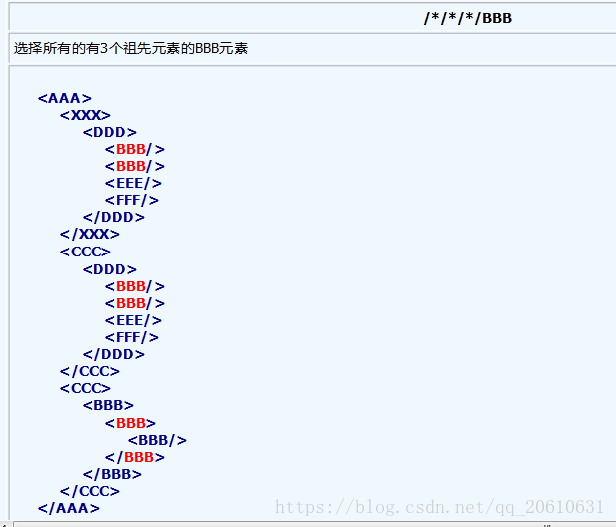
/AAA/DDD/BBB: 表示一层一层的,AAA下面 DDD下面的BBB
第二种形式
//BBB: 表示和这个名称相同,表示只要名称是BBB,都得到
第三种形式
/ *: 所有元素
第四种形式
BBB[1]: 表示第一个BBB元素
×× BBB[last()]:表示最后一个BBB元素
第五种形式
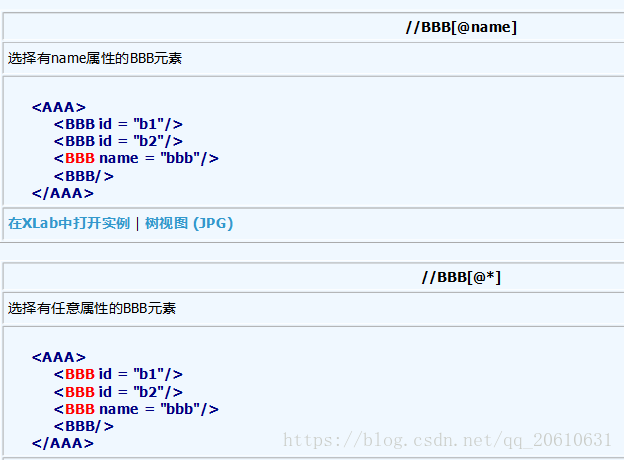
//BBB[@id]: 表示只要BBB元素上面有id属性,都得到
第六种形式
//BBB[@id='b1'] 表示元素名称是BBB,在BBB上面有id属性,并且id的属性值是b1
使用dom4j支持xpath具体操作
默认的情况下,dom4j不支持xpath
如果想要在dom4j里面是有xpath
第一步需要,引入支持xpath的jar包,使用 jaxen-1.1-beta-6.jar
需要把jar包导入到项目中
在dom4j里面提供了两个方法,用来支持xpath
selectNodes("xpath表达式")
- 获取多个节点
selectSingleNode("xpath表达式")
- 获取一个节点
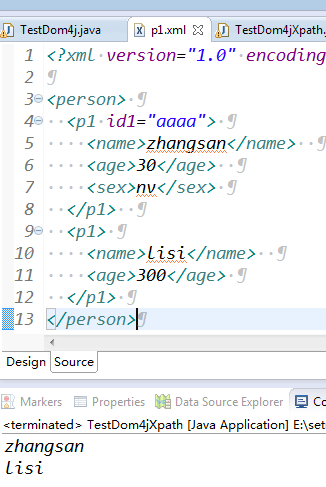
使用xpath实现:查询xml中所有name元素的值
所有name元素的xpath表示: //name
使用selectNodes("//name");
代码和步骤
/
1、得到document
2、直接使用selectNodes("//name")方法得到所有的name元素
/
//得到document
Document document = Dom4jUtils.getDocument(Dom4jUtils.PATH);
//使用selectNodes("//name")方法得到所有的name元素
List
//遍历list集合
for (Node node : list) {
//node是每一个name元素
//得到name元素里面的值
String s = node.getText();
System.out.println(s);
}
//查询xml中所有name元素的值
public static void test1() throws Exception {
/*
* 1、得到document
* 2、直接使用selectNodes("//name")方法得到所有的name元素
*
* */
//得到document
Document document = Dom4jUtils.getDocument(Dom4jUtils.PATH);
//使用selectNodes("//name")方法得到所有的name元素
List list = document.selectNodes("//name");
//遍历list集合
for (Node node : list) {
//node是每一个name元素
//得到name元素里面的值
String s = node.getText();
System.out.println(s);
}
} 
使用xpath实现:获取第一个p1下面的name的值
//p1[@id1='aaaa']/name
使用到 selectSingleNode("//p1[@id1='aaaa']/name")
步骤和代码
/
1、得到document
2、直接使用selectSingleNode方法实现
- xpath : //p1[@id1='aaaa']/name
/
//得到document
Document document = Dom4jUtils.getDocument(Dom4jUtils.PATH);
//直接使用selectSingleNode方法实现
Node name1 = document.selectSingleNode("//p1[@id1='aaaa']/name"); //name的元素
//得到name里面的值
String s1 = name1.getText();
System.out.println(s1);
//使用xpath实现:获取第一个p1下面的name的值
public static void test2() throws Exception {
/*
* 1、得到document
* 2、直接使用selectSingleNode方法实现
* - xpath : //p1[@id1='aaaa']/name
* */
//得到document
Document document = Dom4jUtils.getDocument(Dom4jUtils.PATH);
//直接使用selectSingleNode方法实现
Node name1 = document.selectSingleNode("//p1[@id1='aaaa']/name"); //name的元素
//得到name里面的值
String s1 = name1.getText();
System.out.println(s1);
}
14、实现简单的学生管理系统
使用xml当做数据,存储学生信息
创建一个xml文件,写一些学生信息
100
zhangsan
20
101
lisi
30
package cn.itcast.service;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.Node;
import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter;
import cn.itcast.vo.Student;
public class StuService {
//查询 根据id查询学生信息
public static Student getStu(String id) throws Exception {
/*
* 1、创建解析器
* 2、得到document
*
* 3、获取到所有的id
* 4、返回的是list集合,遍历list集合
* 5、得到每一个id的节点
* 6、id节点的值
* 7、判断id的值和传递的id值是否相同
* 8、如果相同,先获取到id的父节点stu
* 9、通过stu获取到name age值
*
* */
//创建解析器
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
//得到document
Document document = saxReader.read("src/student.xml");
//获取所有的id
List list = document.selectNodes("//id");
//创建student对象
Student student = new Student();
//遍历list
for (Node node : list) { //node是每一个id节点
//得到id节点的值
String idv = node.getText();
//判断id是否相同
if(idv.equals(id)) {
//得到id的父节点 stu
Element stu = node.getParent();
//通过stu获取name和age
String namev = stu.element("name").getText();
String agev = stu.element("age").getText();
student.setId(idv);
student.setName(namev);
student.setAge(agev);
}
}
return student;
}
//增加
public static void addStu(Student student) throws Exception {
/*
* 1、创建解析器
* 2、得到document
* 3、获取到根节点
* 4、在根节点上面创建stu标签
* 5、在stu标签上面依次添加id name age
* 6、在id name age上面依次添加值
*
* 7、回写xml
* */
//创建解析器
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
//得到document
Document document = saxReader.read("src/student.xml");
//得到根节点
Element root = document.getRootElement();
//在根节点上面添加stu
Element stu = root.addElement("stu");
//在stu标签上面依次添加id name age标签
Element id1 = stu.addElement("id");
Element name1 = stu.addElement("name");
Element age1 = stu.addElement("age");
//在id name age上面依次添加值
id1.setText(student.getId());
name1.setText(student.getName());
age1.setText(student.getAge());
//回写xml
OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint();
XMLWriter xmlWriter = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream("src/student.xml"), format);
xmlWriter.write(document);
xmlWriter.close();
}
//删除 根据学生的id删除
public static void delStu(String id) throws Exception {
/*
* 1、创建解析器
* 2、得到document
*
* 3、获取到所有的id
* 使用xpath //id 返回 list集合
* 4、遍历list集合
* 5、判断集合里面的id和传递的id是否相同
* 6、如果相同,把id所在的stu删除
*
* */
//创建解析器
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
//得到document
Document document = saxReader.read("src/student.xml");
//获取所有的id xpath: //id
List list = document.selectNodes("//id");
//遍历list集合
for (Node node : list) { //node是每一个id的元素
//得到id的值
String idv = node.getText();
//判断idv和传递的id是否相同
if(idv.equals(id)) { //id相同
//得到stu节点
Element stu = node.getParent();
//获取stu的父节点
Element student = stu.getParent();
//删除stu
student.remove(stu);
}
}
//回写xml
OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint();
XMLWriter xmlWriter = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream("src/student.xml"), format);
xmlWriter.write(document);
xmlWriter.close();
}
}
package cn.itcast.test;
import cn.itcast.service.StuService;
import cn.itcast.vo.Student;
public class TestStu {
/**
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// testAdd();
// testDel();
testSelect();
}
//测试查询方法
public static void testSelect() throws Exception {
Student stu = StuService.getStu("100");
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
//测试删除方法
public static void testDel() throws Exception {
StuService.delStu("103");
}
//测试添加方法
public static void testAdd() throws Exception {
//设置值
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setId("103");
stu.setName("wangwu");
stu.setAge("40");
StuService.addStu(stu);
}
}
package cn.itcast.vo;
public class Student {
private String id;
private String name;
private String age;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
增加操作
/
1、创建解析器
2、得到document
3、获取到根节点
4、在根节点上面创建stu标签
5、在stu标签上面依次添加id name age
addElement方法添加
6、在id name age上面依次添加值
setText方法
7、回写xml
/
删除操作(根据id删除)
/
1、创建解析器
2、得到document
3、获取到所有的id
使用xpath //id 返回 list集合
4、遍历list集合
5、判断集合里面的id和传递的id是否相同
6、如果相同,把id所在的stu删除
/
查询操作(根据id查询)
/
1、创建解析器
2、得到document
3、获取到所有的id
4、返回的是list集合,遍历list集合
5、得到每一个id的节点
6、id节点的值
7、判断id的值和传递的id值是否相同
8、如果相同,先获取到id的父节点stu
9、通过stu获取到name age值
把这些值封装到一个对象里面 返回对象
/