模型评估与调参
一、通过管道创建工作流
1.1 数据导入与预处理
# 导入相关数据集
import pandas as pd
import urllib
try:
df = pd.read_csv('https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases'
'/breast-cancer-wisconsin/wdbc.data', header=None)
except urllib.error.URLError:
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/'
'python-machine-learning-book/master/code/'
'datasets/wdbc/wdbc.data', header=None)
print('rows, columns:', df.shape)
df.head()
rows, columns: (569, 32)
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ... | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 842302 | M | 17.99 | 10.38 | 122.80 | 1001.0 | 0.11840 | 0.27760 | 0.3001 | 0.14710 | ... | 25.38 | 17.33 | 184.60 | 2019.0 | 0.1622 | 0.6656 | 0.7119 | 0.2654 | 0.4601 | 0.11890 |
| 1 | 842517 | M | 20.57 | 17.77 | 132.90 | 1326.0 | 0.08474 | 0.07864 | 0.0869 | 0.07017 | ... | 24.99 | 23.41 | 158.80 | 1956.0 | 0.1238 | 0.1866 | 0.2416 | 0.1860 | 0.2750 | 0.08902 |
| 2 | 84300903 | M | 19.69 | 21.25 | 130.00 | 1203.0 | 0.10960 | 0.15990 | 0.1974 | 0.12790 | ... | 23.57 | 25.53 | 152.50 | 1709.0 | 0.1444 | 0.4245 | 0.4504 | 0.2430 | 0.3613 | 0.08758 |
| 3 | 84348301 | M | 11.42 | 20.38 | 77.58 | 386.1 | 0.14250 | 0.28390 | 0.2414 | 0.10520 | ... | 14.91 | 26.50 | 98.87 | 567.7 | 0.2098 | 0.8663 | 0.6869 | 0.2575 | 0.6638 | 0.17300 |
| 4 | 84358402 | M | 20.29 | 14.34 | 135.10 | 1297.0 | 0.10030 | 0.13280 | 0.1980 | 0.10430 | ... | 22.54 | 16.67 | 152.20 | 1575.0 | 0.1374 | 0.2050 | 0.4000 | 0.1625 | 0.2364 | 0.07678 |
5 rows × 32 columns
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
X = df.loc[:, 2:].values
y = df.loc[:, 1].values
le = LabelEncoder()
# 将目标转为0-1变量
y = le.fit_transform(y)
le.transform(['M', 'B'])
array([1, 0])
## 创建训练集和测试集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = \
train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.20, random_state=1)
1.2 将transformer(数据转化)和Estimator(模型预测)放入同一个管道
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler # 用于进行数据标准化
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA # 用于进行特征降维
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression # 用于模型预测
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
pipe_lr = Pipeline([('scl', StandardScaler()),
('pca', PCA(n_components=2)),
('clf', LogisticRegression(random_state=1))])
pipe_lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
print('Test Accuracy: %.3f' % pipe_lr.score(X_test, y_test))
y_pred = pipe_lr.predict(X_test)
Test Accuracy: 0.947
二、K折交叉验证
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
kfold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=10,
random_state=1).split(X_train, y_train)
scores = []
for k, (train, test) in enumerate(kfold):
pipe_lr.fit(X_train[train], y_train[train])
score = pipe_lr.score(X_train[test], y_train[test])
scores.append(score)
print('Fold: %s, Class dist.: %s, Acc: %.3f' % (k+1,
np.bincount(y_train[train]), score))
print('\nCV accuracy: %.3f +/- %.3f' % (np.mean(scores), np.std(scores)))
Fold: 1, Class dist.: [256 153], Acc: 0.891
Fold: 2, Class dist.: [256 153], Acc: 0.978
Fold: 3, Class dist.: [256 153], Acc: 0.978
Fold: 4, Class dist.: [256 153], Acc: 0.913
Fold: 5, Class dist.: [256 153], Acc: 0.935
Fold: 6, Class dist.: [257 153], Acc: 0.978
Fold: 7, Class dist.: [257 153], Acc: 0.933
Fold: 8, Class dist.: [257 153], Acc: 0.956
Fold: 9, Class dist.: [257 153], Acc: 0.978
Fold: 10, Class dist.: [257 153], Acc: 0.956
CV accuracy: 0.950 +/- 0.029
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
scores = cross_val_score(estimator=pipe_lr,
X=X_train,
y=y_train,
cv=10,
n_jobs=1)
print('CV accuracy scores: %s' % scores)
print('CV accuracy: %.3f +/- %.3f' % (np.mean(scores), np.std(scores)))
CV accuracy scores: [ 0.89130435 0.97826087 0.97826087 0.91304348 0.93478261 0.97777778
0.93333333 0.95555556 0.97777778 0.95555556]
CV accuracy: 0.950 +/- 0.029
三、曲线调参
3.1 学习曲线
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import learning_curve
pipe_lr = Pipeline([('scl', StandardScaler()),
('clf', LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', random_state=0))])
train_sizes, train_scores, test_scores =\
learning_curve(estimator=pipe_lr,
X=X_train,
y=y_train,
train_sizes=np.linspace(0.1, 1.0, 10), #在0.1和1间线性的取10个值
cv=10,
n_jobs=1)
train_mean = np.mean(train_scores, axis=1)
train_std = np.std(train_scores, axis=1)
test_mean = np.mean(test_scores, axis=1)
test_std = np.std(test_scores, axis=1)
plt.plot(train_sizes, train_mean,
color='blue', marker='o',
markersize=5, label='training accuracy')
plt.fill_between(train_sizes,
train_mean + train_std,
train_mean - train_std,
alpha=0.15, color='blue')
plt.plot(train_sizes, test_mean,
color='green', linestyle='--',
marker='s', markersize=5,
label='validation accuracy')
plt.fill_between(train_sizes,
test_mean + test_std,
test_mean - test_std,
alpha=0.15, color='green')
plt.grid()
plt.xlabel('Number of training samples')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.ylim([0.8, 1.0])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
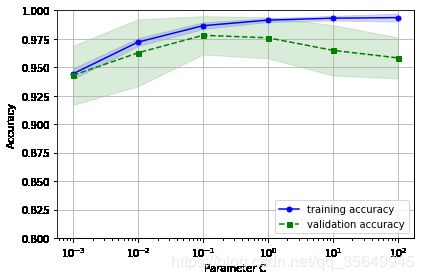
3.2 验证曲线
from sklearn.model_selection import validation_curve
param_range = [0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 10.0, 100.0]
train_scores, test_scores = validation_curve(
estimator=pipe_lr,
X=X_train,
y=y_train,
param_name='clf__C',
param_range=param_range,
cv=10)
train_mean = np.mean(train_scores, axis=1)
train_std = np.std(train_scores, axis=1)
test_mean = np.mean(test_scores, axis=1)
test_std = np.std(test_scores, axis=1)
plt.plot(param_range, train_mean,
color='blue', marker='o',
markersize=5, label='training accuracy')
plt.fill_between(param_range, train_mean + train_std,
train_mean - train_std, alpha=0.15,
color='blue')
plt.plot(param_range, test_mean,
color='green', linestyle='--',
marker='s', markersize=5,
label='validation accuracy')
plt.fill_between(param_range,
test_mean + test_std,
test_mean - test_std,
alpha=0.15, color='green')
plt.grid()
plt.xscale('log')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.xlabel('Parameter C')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.ylim([0.8, 1.0])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
3.3 网格搜索
构建字典
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
pipe_svc = Pipeline([('scl', StandardScaler()),
('clf', SVC(random_state=1))])
param_range = [0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 10.0, 100.0, 1000.0]
param_grid = [{'clf__C': param_range,
'clf__kernel': ['linear']},
{'clf__C': param_range,
'clf__gamma': param_range,
'clf__kernel': ['rbf']}]
gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=pipe_svc,
param_grid=param_grid,
scoring='accuracy',
cv=10,
n_jobs=-1)
gs = gs.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(gs.best_score_)
print(gs.best_params_)
0.978021978022
{'clf__C': 0.1, 'clf__kernel': 'linear'}
clf = gs.best_estimator_
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
print('Test accuracy: %.3f' % clf.score(X_test, y_test))
Test accuracy: 0.965
3.4 嵌套交叉验证
gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=pipe_svc,
param_grid=param_grid,
scoring='accuracy',
cv=2)
# Note: Optionally, you could use cv=2
# in the GridSearchCV above to produce
# the 5 x 2 nested CV that is shown in the figure.
scores = cross_val_score(gs, X_train, y_train, scoring='accuracy', cv=5)
print('CV accuracy: %.3f +/- %.3f' % (np.mean(scores), np.std(scores)))
CV accuracy: 0.965 +/- 0.025
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=0),
param_grid=[{'max_depth': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, None]}],
scoring='accuracy',
cv=2)
scores = cross_val_score(gs, X_train, y_train, scoring='accuracy', cv=5)
print('CV accuracy: %.3f +/- %.3f' % (np.mean(scores), np.std(scores)))
CV accuracy: 0.921 +/- 0.029
四、性能评价指标
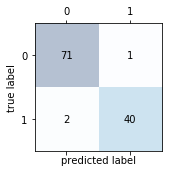
4.1 混淆矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
pipe_svc.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = pipe_svc.predict(X_test)
confmat = confusion_matrix(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_pred)
print(confmat)
[[71 1]
[ 2 40]]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(2.5, 2.5))
ax.matshow(confmat, cmap=plt.cm.Blues, alpha=0.3)
for i in range(confmat.shape[0]):
for j in range(confmat.shape[1]):
ax.text(x=j, y=i, s=confmat[i, j], va='center', ha='center')
plt.xlabel('predicted label')
plt.ylabel('true label')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
4.2 其他评价指标
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score, recall_score, f1_score
print('Precision: %.3f' % precision_score(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_pred))
print('Recall: %.3f' % recall_score(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_pred))
print('F1: %.3f' % f1_score(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_pred))
Precision: 0.976
Recall: 0.952
F1: 0.964
4.3 根据指定评价指标自动选出最优模型
from sklearn.metrics import make_scorer
scorer = make_scorer(f1_score, pos_label=0)
c_gamma_range = [0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 10.0]
param_grid = [{'clf__C': c_gamma_range,
'clf__kernel': ['linear']},
{'clf__C': c_gamma_range,
'clf__gamma': c_gamma_range,
'clf__kernel': ['rbf']}]
gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=pipe_svc,
param_grid=param_grid,
scoring=scorer,
cv=10,
n_jobs=-1)
gs = gs.fit(X_train, y_train)
print(gs.best_score_)
print(gs.best_params_)
0.982798668208
{'clf__C': 0.1, 'clf__kernel': 'linear'}
X_train
array([[ 1.79900000e+01, 2.06600000e+01, 1.17800000e+02, ...,
1.97400000e-01, 3.06000000e-01, 8.50300000e-02],
[ 2.02900000e+01, 1.43400000e+01, 1.35100000e+02, ...,
1.62500000e-01, 2.36400000e-01, 7.67800000e-02],
[ 9.00000000e+00, 1.44000000e+01, 5.63600000e+01, ...,
1.38900000e-02, 2.99100000e-01, 7.80400000e-02],
...,
[ 1.72000000e+01, 2.45200000e+01, 1.14200000e+02, ...,
1.89900000e-01, 3.31300000e-01, 1.33900000e-01],
[ 1.40300000e+01, 2.12500000e+01, 8.97900000e+01, ...,
7.96300000e-02, 2.22600000e-01, 7.61700000e-02],
[ 1.30300000e+01, 1.84200000e+01, 8.26100000e+01, ...,
5.01300000e-02, 1.98700000e-01, 6.16900000e-02]])
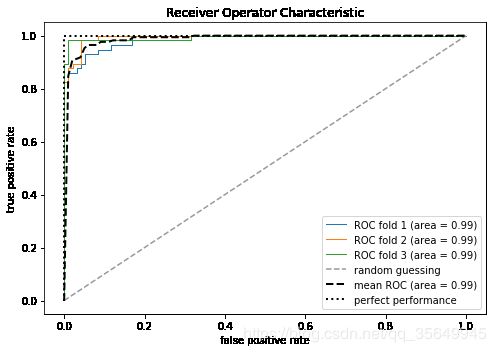
4.4 绘制ROC曲线
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
from scipy import interp
pipe_lr = Pipeline([('scl', StandardScaler()),
('pca', PCA(n_components=2)),
('clf', LogisticRegression(penalty='l2',
random_state=0,
C=100.0))])
# 因为全部特征丢进去的话,预测效果太好,画ROC曲线不好看哈哈哈,所以只是取了2个特征
X_train2 = X_train[:, [4, 14]]
cv = list(StratifiedKFold(n_splits=3,
random_state=1).split(X_train, y_train))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
mean_tpr = 0.0
mean_fpr = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
all_tpr = []
for i, (train, test) in enumerate(cv):
probas = pipe_lr.fit(X_train2[train],
y_train[train]).predict_proba(X_train2[test])
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_train[test],
probas[:, 1],
pos_label=1)
mean_tpr += interp(mean_fpr, fpr, tpr)
mean_tpr[0] = 0.0
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
plt.plot(fpr,
tpr,
lw=1,
label='ROC fold %d (area = %0.2f)'
% (i+1, roc_auc))
plt.plot([0, 1],
[0, 1],
linestyle='--',
color=(0.6, 0.6, 0.6),
label='random guessing')
mean_tpr /= len(cv)
mean_tpr[-1] = 1.0
mean_auc = auc(mean_fpr, mean_tpr)
plt.plot(mean_fpr, mean_tpr, 'k--',
label='mean ROC (area = %0.2f)' % mean_auc, lw=2)
plt.plot([0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1],
lw=2,
linestyle=':',
color='black',
label='perfect performance')
plt.xlim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('false positive rate')
plt.ylabel('true positive rate')
plt.title('Receiver Operator Characteristic')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
X_test
array([[ 1.46900000e+01, 1.39800000e+01, 9.82200000e+01, ...,
1.10800000e-01, 2.82700000e-01, 9.20800000e-02],
[ 1.31700000e+01, 1.86600000e+01, 8.59800000e+01, ...,
2.08800000e-01, 3.90000000e-01, 1.17900000e-01],
[ 1.29500000e+01, 1.60200000e+01, 8.31400000e+01, ...,
1.05600000e-01, 3.38000000e-01, 9.58400000e-02],
...,
[ 9.02900000e+00, 1.73300000e+01, 5.87900000e+01, ...,
1.75000000e-01, 4.22800000e-01, 1.17500000e-01],
[ 1.45300000e+01, 1.93400000e+01, 9.42500000e+01, ...,
9.59400000e-02, 2.47100000e-01, 7.46300000e-02],
[ 1.37800000e+01, 1.57900000e+01, 8.83700000e+01, ...,
3.31200000e-02, 1.85900000e-01, 6.81000000e-02]])
pipe_lr = pipe_lr.fit(X_train2, y_train)
y_labels = pipe_lr.predict(X_test[:, [4, 14]])
y_probas = pipe_lr.predict_proba(X_test[:, [4, 14]])[:, 1]
# note that we use probabilities for roc_auc
# the `[:, 1]` selects the positive class label only
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, accuracy_score
print('ROC AUC: %.3f' % roc_auc_score(y_true=y_test, y_score=y_probas))
print('Accuracy: %.3f' % accuracy_score(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_labels))
ROC AUC: 0.752
Accuracy: 0.711