linux Coherent dma 实现
linux 4.9 armv8
void *dma_alloc_coherent(struct device *dev, size_t size,dma_addr_t *dma_handle, gfp_t flag)参数:dev device 结构体中有dma相关的控制比如dma_mask,dma_handle 作实参传递返回的pa,flag分配memory时的控制选项比如GFP_KERNEL(允许睡眠) GFP_ATOMIC(原子分配)
返回值:cpu看到的va
dma_alloc_coherent(struct device *dev, size_t size,dma_addr_t *dma_handle, gfp_t flag)
--> dma_alloc_attrs(struct device *dev, size_t size, dma_addr_t *dma_handle, gfp_t flag, unsigned long attrs) unsigned long attrs)
{
struct dma_map_ops *ops = get_dma_ops(dev);
//get swiotlb_dma_ops
void *cpu_addr;
if (dma_alloc_from_coherent(dev, size, dma_handle, &cpu_addr))
return cpu_addr;
//dma_alloc_from_coherent() - try to allocate memory from the per-device coherent area 目前还没遇到perdevice的dma are
cpu_addr = ops->alloc(dev, size, dma_handle, flag, attrs);
//主要操作调用swiotlb_dam_ops的alloc callback
debug_dma_alloc_coherent(dev, size, *dma_handle, cpu_addr);
return cpu_addr;
}
--->static struct dma_map_ops swiotlb_dma_ops = {
.alloc = __dma_alloc,
.free = __dma_free,
.mmap = __swiotlb_mmap,
.get_sgtable = __swiotlb_get_sgtable,
.map_page = __swiotlb_map_page,
.unmap_page = __swiotlb_unmap_page,
.map_sg = __swiotlb_map_sg_attrs,
.unmap_sg = __swiotlb_unmap_sg_attrs,
};
---->static void *__dma_alloc(struct device *dev, size_t size,
dma_addr_t *dma_handle, gfp_t flags,
unsigned long attrs)
{
struct page *page;
void *ptr, *coherent_ptr;
bool coherent = is_device_dma_coherent(dev);
//device 的archdata里面有个dam_coherent属性,没关注这个目的是什么,常见的device这个属性是false
pgprot_t prot = __get_dma_pgprot(attrs, PAGE_KERNEL, false);
//dma memory cache 属性,会写到页表项中这是none cache 的关键
size = PAGE_ALIGN(size);
//申请的memory是page align
ptr = __dma_alloc_coherent(dev, size, dma_handle, flags, attrs);
//调用get_free_pages申请空间建立页表
if (!ptr)
goto no_mem;
/* no need for non-cacheable mapping if coherent */
if (coherent)
return ptr;
/* remove any dirty cache lines on the kernel alias */
__dma_flush_area(ptr, size);
/* create a coherent mapping */
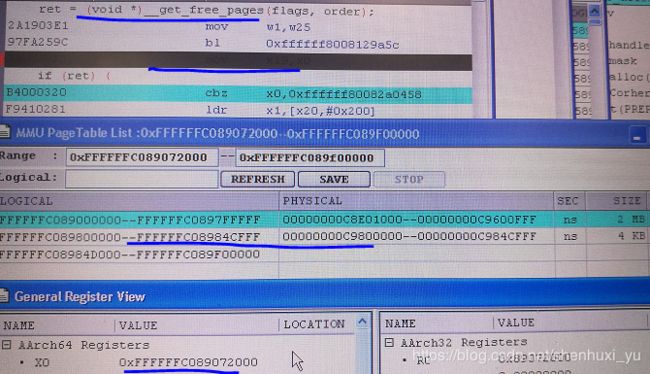
page = virt_to_page(ptr);
coherent_ptr = dma_common_contiguous_remap(page, size, VM_USERMAP,
prot, NULL);
//coherent_ptr 最终得到的coherent buf 的va
return NULL;
}
----->static void *__dma_alloc_coherent(struct device *dev, size_t size,
dma_addr_t *dma_handle, gfp_t flags,
unsigned long attrs)
{
//不考虑cma 直接调用swiotlb的接口
return swiotlb_alloc_coherent(dev, size, dma_handle, flags);
}
------>void *
swiotlb_alloc_coherent(struct device *hwdev, size_t size,
dma_addr_t *dma_handle, gfp_t flags)
{
dma_addr_t dev_addr;
void *ret;
int order = get_order(size);
u64 dma_mask = DMA_BIT_MASK(32);
if (hwdev && hwdev->coherent_dma_mask)
dma_mask = hwdev->coherent_dma_mask;
ret = (void *)__get_free_pages(flags, order);
//从buddy系统中获取order大小page,返回虚拟地址,最大限制是4M
if (ret) {
dev_addr = swiotlb_virt_to_bus(hwdev, ret);
//虚拟地址 ret转成物理地址,这里是最终得到的PA,后面会配置这个地址给具体的dma hw使用
if (dev_addr + size - 1 > dma_mask) {
//dma_mask hw决定的dma的寻址范围,目前手边的平台都可以达到32bit,高端soc有可能会超过4G空间,dram 这边可以配置对地址补位
/*
* The allocated memory isn't reachable by the device.
*/
free_pages((unsigned long) ret, order);
ret = NULL;
}
}
if (!ret) {
//获取物理内存失败
/*
* We are either out of memory or the device can't DMA to
* GFP_DMA memory; fall back on map_single(), which
* will grab memory from the lowest available address range.
*/
}
}
*dma_handle = dev_addr;
memset(ret, 0, size);
return ret;
}
------>/*
* remaps an allocated contiguous region into another vm_area.
* Cannot be used in non-sleeping contexts
*/
//在__dma_alloc 函数调用到该函数时已经通过get_free_pages拿到了vm
void *dma_common_contiguous_remap(struct page *page, size_t size,
unsigned long vm_flags,
pgprot_t prot, const void *caller)
{
int i;
struct page **pages;
void *ptr;
unsigned long pfn;
//申请页表空间,用来构建多级页表
pages = kmalloc(sizeof(struct page *) << get_order(size), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pages)
return NULL;
//构建一级页表
for (i = 0, pfn = page_to_pfn(page); i < (size >> PAGE_SHIFT); i++)
pages[i] = pfn_to_page(pfn + i);
ptr = dma_common_pages_remap(pages, size, vm_flags, prot, caller);
kfree(pages);
return ptr;
}
------>/*
* remaps an array of PAGE_SIZE pages into another vm_area
* Cannot be used in non-sleeping contexts
*/
void *dma_common_pages_remap(struct page **pages, size_t size,
unsigned long vm_flags, pgprot_t prot,
const void *caller)
{
struct vm_struct *area;
area = get_vm_area_caller(size, vm_flags, caller);
if (!area)
return NULL;
area->pages = pages;
//vm描述符与page描述符绑定,map_vm_are
if (map_vm_area(area, prot, pages)) {
vunmap(area->addr);
return NULL;
}
return area->addr;
}
------>struct vm_struct *get_vm_area_caller(unsigned long size, unsigned long flags,
const void *caller)
{
return __get_vm_area_node(size, 1, flags, VMALLOC_START, VMALLOC_END,
NUMA_NO_NODE, GFP_KERNEL, caller);
}
------>static struct vm_struct *__get_vm_area_node(unsigned long size,
unsigned long align, unsigned long flags, unsigned long start,
unsigned long end, int node, gfp_t gfp_mask, const void *caller)
{
struct vmap_area *va;
struct vm_struct *area;
BUG_ON(in_interrupt());
size = PAGE_ALIGN(size);
area = kzalloc_node(sizeof(*area), gfp_mask & GFP_RECLAIM_MASK, node);
if (unlikely(!area))
return NULL;
/*
* Allocate a region of KVA of the specified size and alignment, within the
* vstart and vend.
*/
//从VMALLOC区拿到一块vm出来
va = alloc_vmap_area(size, align, start, end, node, gfp_mask);
if (IS_ERR(va)) {
kfree(area);
return NULL;
}
setup_vmalloc_vm(area, va, flags, caller);
//vmap_area vm_struct 建立之前申请到的这段vm的描述
return area;
}
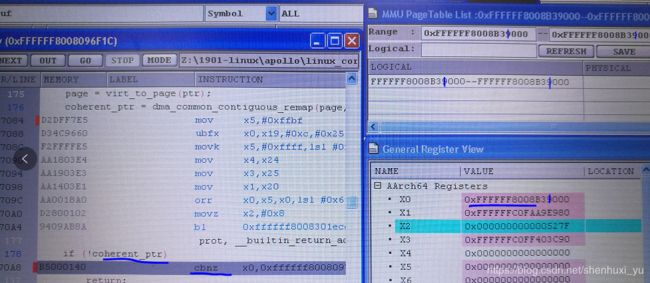
------>int map_vm_area(struct vm_struct *area, pgprot_t prot, struct page **pages)
{
unsigned long addr = (unsigned long)area->addr;
unsigned long end = addr + get_vm_area_size(area);
int err;
err = vmap_page_range(addr, end, prot, pages);
return err > 0 ? 0 : err;
}
------>static int vmap_page_range(unsigned long start, unsigned long end,
pgprot_t prot, struct page **pages)
{
int ret;
ret = vmap_page_range_noflush(start, end, prot, pages);
flush_cache_vmap(start, end);
return ret;
}
------>/*
* Set up page tables in kva (addr, end). The ptes shall have prot "prot", and
* will have pfns corresponding to the "pages" array.
*
* Ie. pte at addr+N*PAGE_SIZE shall point to pfn corresponding to pages[N]
*/
//用申请到的va区域构建page table
static int vmap_page_range_noflush(unsigned long start, unsigned long end,
pgprot_t prot, struct page **pages)
{
pgd_t *pgd;
unsigned long next;
unsigned long addr = start;
int err = 0;
int nr = 0;
BUG_ON(addr >= end);
pgd = pgd_offset_k(addr);
do {
next = pgd_addr_end(addr, end);
err = vmap_pud_range(pgd, addr, next, prot, pages, &nr);
if (err)
return err;
} while (pgd++, addr = next, addr != end);
//从pgd 到 pud 到pmd 最后到pte 填充多级页表项,以两级为例
return nr;
}
------->static int vmap_pte_range(pmd_t *pmd, unsigned long addr,
unsigned long end, pgprot_t prot, struct page **pages, int *nr)
{
pte_t *pte;
/*
* nr is a running index into the array which helps higher level
* callers keep track of where we're up to.
*/
pte = pte_alloc_kernel(pmd, addr);
if (!pte)
return -ENOMEM;
do {
struct page *page = pages[*nr];
if (WARN_ON(!pte_none(*pte)))
return -EBUSY;
if (WARN_ON(!page))
return -ENOMEM;
set_pte_at(&init_mm, addr, pte, mk_pte(page, prot));
(*nr)++;
} while (pte++, addr += PAGE_SIZE, addr != end);
//填充pte 的property字段为none cache none buf, cache miss 的情况下,直接从主存读取数据,如果是可cache able属性的页表项,发生cached miss 后会先把主存的内容放到cache 成为cache linefill 操作
return 0;
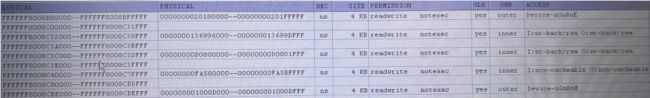
}利用debug工具看到的页表内容如下页表项属性 I:non-cacheable O:non-cacheable
dma coherent buf 的建立过程有多次memeory的申请
1. __get_free_pages: 直接从buddy系统里获取2order的连续物理页,也是最终传给dma hw 的pa,返回获取到的第一个物理页的起始va
2.alloc_vmap_area:从VMALLOC区拿出一块VM,是最终申请到的coherent buf 的va
struct vm_struct {
struct vm_struct *next;
void *addr;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long flags;
struct page **pages;
unsigned int nr_pages;
phys_addr_t phys_addr;
const void *caller;
};
3. dma_common_contiguous_remap 调用kmalloc 申请页描述符空间,用alloc_vmap_area 拿到的va构造page table
mem_map 管理node内所有物理page的全局数组
__get_free_pages 后就拿到物理连续的va 与pa而且low mem区kernel init的时候就已经建立内核页表, 为什么还要用alloc_vmap_area在去申请va 建立页表?
用debug工具看到的信息如下
第一次的建立的地址映射虚拟地址是0xffffffc08907200 该页表项映射的size 是2M
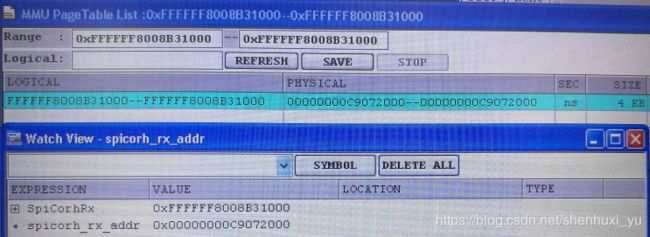
第二次建立的页表映射虚拟地址0xffffff800831000 页表项映射的size是4k,debug 工具看一直到真正使用过后才从dump到映射关系