Alpha_Beta博弈树搜索__五子棋
一、课程设计目的
- 掌握Alpha_Beta搜索法
- 用程序设计语言编制博弈游戏
二、软件与编程语言
软件:Pychram
语言:Python3.6
三、程序运行说明
电脑需安装python3.6,将Ai_Gobang.py,Ai_Gobang_Main.py和graphics.py(需自行下载源码)放置在同一项目包导入Pycharm编译软件运行控制台程序
五子棋游戏基本规则:
- 黑先、白后,从天元开始相互顺序落子
- 白棋第一手应在天元为界自己一侧布子,之后双方可任意行子。
- 最先在棋盘横向、竖向、斜向形成连续的相同色五个棋子的一方为胜。
- 黑棋禁手判负、白棋无禁手。黑棋禁手包括“三、三” “四、四” “长连”。黑方只能“四、三”胜。
- 如分不出胜负,则定为平局。
- 对局中中途退场均判为负。
- 五连与禁手同时形成,先五为胜。
四、程序设计方案
1.根据最常见的基本棋形设计评估分数
最常见的基本棋型大体有以下几种:连五,活四,冲四,活三,眠三,活二,眠二。
① 连五:顾名思义,五颗同色棋子连在一起,不需要多讲。

② 活四:有两个连五点(即有两个点可以形成五),图中白点即为连五点。
稍微思考一下就能发现活四出现的时候,如果对方单纯过来防守的话,是已经无法阻止自己连五了。

③ 冲四:有一个连五点,如下面三图,均为冲四棋型。图中白点为连五点。
相对比活四来说,冲四的威胁性就小了很多,因为这个时候,对方只要跟着防守在那个唯一的连五点上,冲四就没法形成连五。



④活三:可以形成活四的三,如下图,代表两种最基本的活三棋型。图中白点为活四点。
活三棋型是我们进攻中最常见的一种,因为活三之后,如果对方不以理会,将可以下一手将活三变成活四,而我们知道活四是已经无法单纯防守住了。所以,当我们面对活三的时候,需要非常谨慎对待。在自己没有更好的进攻手段的情况下,需要对其进行防守,以防止其形成可怕的活四棋型。
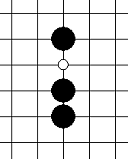

⑤眠三:只能够形成冲四的三,如下各图,分别代表最基础的六种眠三形状。图中白点代表冲四点。眠三的棋型与活三的棋型相比,危险系数下降不少,因为眠三棋型即使不去防守,下一手它也只能形成冲四,而对于单纯的冲四棋型,我们知道,是可以防守住的。



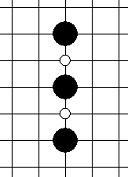


2.设计五子棋评估分数和评估函数



3.极大极小值搜索和Alpha_Beta减枝算法原理图:



Alpha_Beta搜索的过程如上:
~~~~ Alpha_Beta剪枝技术的基本思想或算法是,边生成博弈树边计算评估各节点的倒推值,并且根据评估出的倒推值范围,及时停止扩展那些已无必要再扩展的子节点,即相当于剪去了博弈树上的一些分枝,从而节约了机器开销,提高了搜索效率。
具体的剪枝方法如下:
(1) 对于一个与节点 MIN,若能估计出其倒推值的上确界 Beta,并且这个 Beta 值不大于 MIN 的父节点(一定是或节点)的估计倒推值的下确界 Alpha,即 Alpha>=Beta,则就不必再扩展该MIN 节点的其余子节点了(因为这些节点的估值对 MIN 父节点的倒推值已无任何影响了)。这一过程称为 Alpha剪枝。
(2) 对于一个或节点 MAX,若能估计出其倒推值的下确界 Alpha,并且这个Alpha值不小于 MAX 的父节点(一定是与节点)的估计倒推值的上确界Beta,即Alpha>=Beta,则就不必再扩展该 MAX 节点的其余子节点了(因为这些节点的估值对 MAX 父节点的倒推值已无任何影响了)。这一过程称为Beta剪枝。
从算法中看到:
- MAX 节点(包括起始节点)的 Alpha值永不减少;
- MIN 节点(包括起始节点)的Beta值永不增加。
在搜索期间,Alpha和 Beta值的计算如下:
- 一个 MAX 节点的Alpha值等于其后继节点当前最大的最终倒推值。
- 一个 MIN 节点的 Beta值等于其后继节点当前最小的最终倒推值。
五、程序运行结果实例图:
六、程序源代码附录:
#主程序
Ai_Gobang_Main.py
import Ai_Gobang
Ai_Gobang.Ai_Gobang_Main()
#子程序
Ai_Gobang.py
from graphics import *
from math import *
import numpy as np
#定义五子棋棋盘的行数,列数和窗口尺寸
Column = 7
Row = 7
Width = 80
#定义AI,Human和ALL五子棋布点
Ai = []
Human = []
Ai_Human = []
# 全体棋盘的点
All = []
# AI下步最佳的位置
Best_Point = [0, 0]
# 判断大于0则进攻否则防守
Ratio = 1
# 搜索深度(需要思考的步数)
Depth = 2
#定义统计函数
def Count():
global cut_count # 统计剪枝次数
cut_count = 0
global search_count # 统计搜索次数
search_count = 0
Alpha_Beta(True, Depth, -10000, 10000)
print("本次共剪枝次数:" + str(cut_count))
print("本次共搜索次数:" + str(search_count))
return Best_Point[0], Best_Point[1]
# alpha_beta剪枝
def Alpha_Beta(is_ai, Depth, alpha, beta):
# 游戏是否结束 | | 探索的递归深度是否到边界
if game_win(Ai) or game_win(Human) or Depth == 0:
return evaluation(is_ai)
blank_list = list(set(All).difference(set(Ai_Human)))
Check_point(blank_list) # 搜索顺序排序 提高剪枝效率
# 遍历每一个候选步
for next_step in blank_list:
global search_count
search_count += 1
# 如果要评估的位置没有相邻的子, 则不去评估 减少计算
if not has_neightnor(next_step):
continue
if is_ai:
Ai.append(next_step)
else:
Human.append(next_step)
Ai_Human.append(next_step)
value = -Alpha_Beta(not is_ai, Depth - 1, -beta, -alpha)
if is_ai:
Ai.remove(next_step)
else:
Human.remove(next_step)
Ai_Human.remove(next_step)
if value > alpha:
print(str(value) + "alpha:" + str(alpha) + "beta:" + str(beta))
print(Ai_Human)
if Depth == Depth:
Best_Point[0] = next_step[0]
Best_Point[1] = next_step[1]
# alpha + beta剪枝点
if value >= beta:
global cut_count
cut_count += 1
return beta
alpha = value
return alpha
#判断落子最优点
def Check_point(blank_list):
last_pt = Ai_Human[-1]
for item in blank_list:
for i in range(-1, 2):
for j in range(-1, 2):
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
if (last_pt[0] + i, last_pt[1] + j) in blank_list:
blank_list.remove((last_pt[0] + i, last_pt[1] + j))
blank_list.insert(0, (last_pt[0] + i, last_pt[1] + j))
def has_neightnor(pt):
for i in range(-1, 2):
for j in range(-1, 2):
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
if (pt[0] + i, pt[1]+j) in Ai_Human:
return True
return False
# 棋型的评估分数
Score = [(1, (0, 1, 1, 0, 0)),
(1, (0, 0, 1, 1, 0)),
(4, (1, 1, 0, 1, 0)),
(10, (0, 0, 1, 1, 1)),
(10, (1, 1, 1, 0, 0)),
(100, (0, 1, 1, 1, 0)),
(100, (0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0)),
(100, (0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0)),
(100, (1, 1, 1, 0, 1)),
(100, (1, 1, 0, 1, 1)),
(100, (1, 0, 1, 1, 1)),
(100, (1, 1, 1, 1, 0)),
(100, (0, 1, 1, 1, 1)),
(1000, (0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0)),
(10000, (1, 1, 1, 1, 1))]
# 评估函数
def evaluation(is_ai):
total_score = 0
if is_ai:
my_list = Ai
enemy_list = Human
else:
my_list = Human
enemy_list = Ai
# 算Human的得分
score_all_arr = []
my_score = 0
for pt in my_list:
m = pt[0]
n = pt[1]
my_score += cal_score(m, n, 0, 1, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr)
my_score += cal_score(m, n, 1, 0, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr)
my_score += cal_score(m, n, 1, 1, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr)
my_score += cal_score(m, n, -1, 1, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr)
#计算的得分
score_all_arr_enemy = []
enemy_score = 0
for pt in enemy_list:
m = pt[0]
n = pt[1]
enemy_score += cal_score(m, n, 0, 1, my_list, enemy_list, score_all_arr_enemy)
enemy_score += cal_score(m, n, 1, 0, my_list, enemy_list, score_all_arr_enemy)
enemy_score += cal_score(m, n, 1, 1, my_list, enemy_list, score_all_arr_enemy)
enemy_score += cal_score(m, n, -1, 1, my_list, enemy_list, score_all_arr_enemy)
total_score = my_score - enemy_score*Ratio*0.1
return total_score
# 每个方向上的分值计算
def cal_score(m, n, x_decrict, y_derice, enemy_list, my_list, score_all_arr):
add_score = 0 # 加分项
# 在一个方向上, 只取最大的得分项
max_score_shape = (0, None)
# 如果此方向上,该点已经有得分形状,不重复计算
for item in score_all_arr:
for pt in item[1]:
if m == pt[0] and n == pt[1] and x_decrict == item[2][0] and y_derice == item[2][1]:
return 0
# 在落子点 左右方向上循环查找得分形状
for offset in range(-5, 1):
# offset = -2
pos = []
for i in range(0, 6):
if (m + (i + offset) * x_decrict, n + (i + offset) * y_derice) in enemy_list:
pos.append(2)
elif (m + (i + offset) * x_decrict, n + (i + offset) * y_derice) in my_list:
pos.append(1)
else:
pos.append(0)
tmp_shap5 = (pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], pos[3], pos[4])
tmp_shap6 = (pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], pos[3], pos[4], pos[5])
for (score, shape) in Score:
if tmp_shap5 == shape or tmp_shap6 == shape:
if score > max_score_shape[0]:
max_score_shape = (score, ((m + (0+offset) * x_decrict, n + (0+offset) * y_derice),
(m + (1+offset) * x_decrict, n + (1+offset) * y_derice),
(m + (2+offset) * x_decrict, n + (2+offset) * y_derice),
(m + (3+offset) * x_decrict, n + (3+offset) * y_derice),
(m + (4+offset) * x_decrict, n + (4+offset) * y_derice)), (x_decrict, y_derice))
# 计算两个形状相交, 如两个3活 相交, 得分增加 一个子的除外
if max_score_shape[1] is not None:
for item in score_all_arr:
for pt1 in item[1]:
for pt2 in max_score_shape[1]:
if pt1 == pt2 and max_score_shape[0] > 10 and item[0] > 10:
add_score += item[0] + max_score_shape[0]
score_all_arr.append(max_score_shape)
return add_score + max_score_shape[0]
def game_win(list):
for m in range(Column):
for n in range(Row):
if n < Row - 4 and (m, n) in list and (m, n + 1) in list and (m, n + 2) in list and (
m, n + 3) in list and (m, n + 4) in list:
return True
elif m < Row - 4 and (m, n) in list and (m + 1, n) in list and (m + 2, n) in list and (
m + 3, n) in list and (m + 4, n) in list:
return True
elif m < Row - 4 and n < Row - 4 and (m, n) in list and (m + 1, n + 1) in list and (
m + 2, n + 2) in list and (m + 3, n + 3) in list and (m + 4, n + 4) in list:
return True
elif m < Row - 4 and n > 3 and (m, n) in list and (m + 1, n - 1) in list and (
m + 2, n - 2) in list and (m + 3, n - 3) in list and (m + 4, n - 4) in list:
return True
return False
def gobangwin():
win = GraphWin("Gobang game", Width * Column, Width * Row)
win.setBackground("White")
i1 = 0
while i1 <= Width * Column:
l = Line(Point(i1, 0), Point(i1, Width * Column))
l.draw(win)
i1 = i1 + Width
i2 = 0
while i2 <= Width * Row:
l = Line(Point(0, i2), Point(Width * Row, i2))
l.draw(win)
i2 = i2 + Width
return win
def Ai_Gobang_Main():
win = gobangwin()
for i in range(Column+1):
for j in range(Row+1):
All.append((i, j))
change = 0
g = 0
m = 0
n = 0
while g == 0:
if change % 2 == 1:
pos = Count()
if pos in Ai_Human:
message = Text(Point(200, 200), "不可用的位置" + str(pos[0]) + "," + str(pos[1]))
message.draw(win)
g = 1
Ai.append(pos)
Ai_Human.append(pos)
piece = Circle(Point(Width * pos[0], Width * pos[1]), 16)
piece.setFill('white')
piece.draw(win)
if game_win(Ai):
message = Text(Point(100, 100), "White win,game over")
message.draw(win)
g = 1
change = change + 1
else:
p2 = win.getMouse()
if not ((round((p2.getX()) / Width), round((p2.getY()) / Width)) in Ai_Human):
a2 = round((p2.getX()) / Width)
b2 = round((p2.getY()) / Width)
Human.append((a2, b2))
Ai_Human.append((a2, b2))
piece = Circle(Point(Width * a2, Width * b2), 16)
piece.setFill('black')
piece.draw(win)
if game_win(Human):
message = Text(Point(300, 300), "Black win,game over")
message.draw(win)
g = 1
change = change + 1
win.getMouse()
win.close()


