mybatis整合spring后一级缓存真的会失效吗?
mybatis整合spring后一级缓存真的会失效吗?
- 前言
- 1.代码案例
- 2.源码分析
- 总结
前言
在网上看了很多的文章都表示mybaits和spring整合后一级缓存会“失效”,或者说是达到了失效的效果,也就是多次查询不会命中一级缓存,大致原因如下:

那么真的如上图说的一样吗,每一次查询都会开启一个sqlsession,所以导致了一级缓存“失效”的效果吗?我们一起来探究下
1.代码案例
首先如果我们想要验证别人的结论对不对的情况,我们做的第一件事应该是自己去尝试一下,博主贴上代码以及给出测试的结果。
1.service不加上@Transactional注解时

结果:输出对象不一样没走缓存。
2.service加上@Transactional注解时
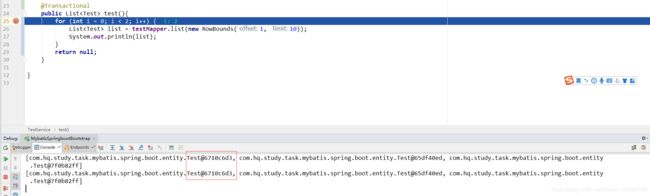
结果:两次输出的为同一对象,那这是不是就走缓存了呢?源码分析一波~~~
2.源码分析
- mybaits前面的代码我就不分析了,直接分析SqlSessionInterceptor的invoke方法。
分析思路:
1.mybatis的一级缓存是基于sqlsession的
2.如果同一个线程多次相同查询获取懂得sqlsession相同那么他就会走缓存
3.反之每次都会获取一个不同的sqlsession则会永远也不可能走缓存(sqlsession独立)
4.这里重点关注getSqlSession方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(
SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
// release the connection to avoid a deadlock if the translator is no loaded. See issue #22
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
- getSqlSession分析
代码:
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Creating a new SqlSession");
}
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
分析:
1.从上面的代码可以看出主要在于SqlSessionHolder的获取。SqlSessionHolder又来源于下面代码,ok继续往下分析。
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
- getResource分析
public static Object getResource(Object key) {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Object value = doGetResource(actualKey);
if (value != null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Retrieved value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] bound to thread [" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
return value;
}
我们的重点再一次落到了doGetResource上,进去看看
private static Object doGetResource(Object actualKey) {
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
Object value = map.get(actualKey);
// Transparently remove ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {
map.remove(actualKey);
// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...
if (map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
value = null;
}
return value;
}
可以看到 获取sqlsessionHolder主要在于resources这个成员变量里面的map,actualKey为DefaultSqlSessionFactory,如果map中存在这个key,则可能返回相同的sqlsessionHolder,那么我们看看这个resources是什么呢?
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transactional resources");
可以看到他是一个ThreadLocal,并且在当前类还提供了一个set方法(org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager#bindResource),ok先记住这个方法
public static void bindResource(Object key, Object value) throws IllegalStateException {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Assert.notNull(value, "Value must not be null");
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
// set ThreadLocal Map if none found
if (map == null) {
map = new HashMap<>();
resources.set(map);
}
Object oldValue = map.put(actualKey, value);
// Transparently suppress a ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (oldValue instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) oldValue).isVoid()) {
oldValue = null;
}
if (oldValue != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already value [" + oldValue + "] for key [" +
actualKey + "] bound to thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Bound value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] to thread [" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");
}
}
- 继续分析getSqlsession
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
//这个已经分析完了
//1.如果threadlocal的map中含有当前的sessionfactory则返回holder
//2.若无则返回null
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
//此方法自己可以看看
//当holder为null时 session也会为null
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Creating a new SqlSession");
}
//创建一个DefualtSqlSessionFacotry
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
//重点在这
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
上面的方法分析几乎都在注释里,我们这里重点分析一下registerSessionHolder这个方法。
private static void registerSessionHolder(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator, SqlSession session) {
SqlSessionHolder holder;
//重点在这,这个判断简单理解,会根据你是否开启了事务,若开启了事务则返回true否则返回false
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
Environment environment = sessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment();
if (environment.getTransactionFactory() instanceof SpringManagedTransactionFactory) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for SqlSession [" + session + "]");
}
holder = new SqlSessionHolder(session, executorType, exceptionTranslator);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new SqlSessionSynchronization(holder, sessionFactory));
holder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
holder.requested();
} else {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(environment.getDataSource()) == null) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because DataSource is not transactional");
}
} else {
throw new TransientDataAccessResourceException(
"SqlSessionFactory must be using a SpringManagedTransactionFactory in order to use Spring transaction synchronization");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active");
}
}
}
- registerSessionHolder分析
1.TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive():重点在这,这个判断简单理解,会根据你是否开启了事务,若开启了事务则返回true否则返回false
2.这时候已经接近真相了,若此时开了事务则会调用
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
此方法前面已经看过,为threadlocal的set方法,将sessionFactory和,holder放入threadlocal的map当中。
3.若未开启事务则会打印log
4.所以当同一个线程开启事务时同一个sql查询多次会走一级缓存,而不开启事务时,每一查询都是不同的sqlsession即缓存为“失效”状态。
总结
看完上面的还有点懵逼?
没关系我们总结一下:
直接看代码讲解吧:
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
//1.根据sessionFacotry去threadlocal中获取sqlsessionholder
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
//2.若holder不为null则获取sqlsession,若未null则session为null
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Creating a new SqlSession");
}
//3.创建一个sqlsession
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
//4.将key为:sessionFacotry value为holder 放入threadlocal中对应步骤2,若这里set了,则步骤2就能获取到相应的holder
//4.1此处会去判断是否开启了事务,若开启了事务,则进行thraedlocal的set操作
//4.2若未开启事务,则打印日志
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
在发表一下结论:
当同一个线程开启事务时同一个sql查询多次会走一级缓存,而不开启事务时,每一查询都是不同的sqlsession即缓存为“失效”状态。