把LabelImg标注的YOLO格式标签转化为VOC格式标签
把LabelImg标注的YOLO格式标签转化为VOC格式标签
文章目录:
- 1 用LabelImgvoc和yolo标注标签格式说明
- 1.1 LabelImg标注的VOC数据格式
- 1.2 LabelImg标注的YOLO数据格式
- 2 voc转换为yolo格式计算
- 3 yolo转换为voc格式计算
- 4 yolo格式标签转化为voc格式标签代码
1 用LabelImgvoc和yolo标注标签格式说明
关于LabelImg工具的使用,参考
1.1 LabelImg标注的VOC数据格式
VOC数据格式,会直接把每张图片标注的标签信息保存到一个xml文件中
例如:我们上面标注的JPEGImage/000001.jpg图片,标注的标签信息会保存到Annotation/000001.xml文件中,000001.xml中的信息如下:
<annotation>
<folder>JPEGImage</folder>
<filename>000000.jpg</filename>
<path>D:\ZF\2_ZF_data\3_stamp_data\标注公章数据\JPEGImage\000000.jpg</path>
<source>
<database>Unknown</database>
</source>
<size>
<width>500</width>
<height>402</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>circle_red</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>168</xmin>
<ymin>2</ymin>
<xmax>355</xmax>
<ymax>186</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>circle_red</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>2</xmin>
<ymin>154</ymin>
<xmax>208</xmax>
<ymax>367</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>circle_red</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>305</xmin>
<ymin>174</ymin>
<xmax>493</xmax>
<ymax>364</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
xml中的关键信息说明:
- 图片的名字
- 每个目标的标定框坐标:即
左上角的坐标和右下角的坐标xminyminxmaxymax
1.2 LabelImg标注的YOLO数据格式
YOLO数据格式,会直接把每张图片标注的标签信息保存到一个txt文件中
例如:我们上面标注的JPEGImage/000001.jpg图片,标注的标签信息会保存到Annotation/000001.txt文件中(同时会生成一个classes.txt文件,也保存到Annotation/classes.txt),000001.txt中的信息如下:
0 0.521000 0.235075 0.362000 0.450249
0 0.213000 0.645522 0.418000 0.519900
0 0.794000 0.665423 0.376000 0.470149
txt中信息说明:
- 每一行代表标注的一个目标
- 第一个数代表标注目标的标签,第一目标circle_red,对应数字就是0
- 后面的四个数代表标注框的中心坐标和标注框的相对宽和高(进行了归一化,如何归一化可以参考我的这篇博客中的介绍)
同时会生成一个Annotation/classes.txt实际类别文件classes.txt,里面的内容如下:
circle_red
circle_gray
rectangle_red
rectangle_gray
fingeprint_red
fingeprint_gray
other
2 voc转换为yolo格式计算
标注好的VOC格式的标签xml文件,存储的主要信息为:
- 图片的名字
- 图片的
高height、宽width、通道depth - 标定框的坐标位置:
xmin、ymin、xmax、ymax
例如下图代表的是一样图片:
- 红框代表的是原图大小:height=8,width=8
- 蓝框代表的是标注物体的框:左上角坐标为 (xmin, ymin)=(2,2),右下角的坐标为 (xmax, ymax)=(6,6)
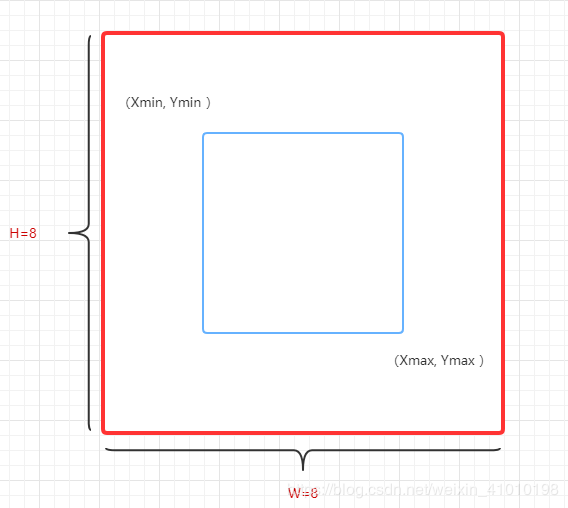
而voc_label.py目的就是把标注为VOC格式数据转化为标注为yolo格式数据: VOC格式标签:图片的实际宽和高,标注框的左上角和右下角坐标YOLO格式标签:标注框的中心坐标(归一化的),标注框的宽和高(归一化的)
VOC格式标签转换为YOLO格式标签计算公式:
框中心的实际坐标(x, y):(一般可能还会在后面减去1)
x _ c e n t e r = x m a x + x m i n 2 = 6 + 2 2 = 4 x\_center=\frac{xmax+xmin}{2}=\frac{6+2}{2}=4 x_center=2xmax+xmin=26+2=4
y _ c e n t e r = y m a x + y m i n 2 = 6 + 2 2 = 4 y\_center=\frac{ymax+ymin}{2}=\frac{6+2}{2}=4 y_center=2ymax+ymin=26+2=4
框归一化后的中心坐标(x, y):
x = x _ c e n t e r w i d t h = 4 8 = 0.5 x=\frac{x\_center}{width}=\frac{4}{8}=0.5 x=widthx_center=84=0.5
y = y _ c e n t e r h e i g h t = 4 8 = 0.5 y=\frac{y\_center}{height}=\frac{4}{8}=0.5 y=heighty_center=84=0.5
框的高和框(归一化的):
w = x m a x − x m i n w i d t h = 6 − 2 8 = 0.5 w=\frac{xmax-xmin}{width}=\frac{6-2}{8}=0.5 w=widthxmax−xmin=86−2=0.5
h = y m a x − y m i n h e i g h t = 6 − 2 8 = 0.5 h=\frac{ymax-ymin}{height}=\frac{6-2}{8}=0.5 h=heightymax−ymin=86−2=0.5
3 yolo转换为voc格式计算
voc中保存的坐标信息为:xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax,所以只要根据上面的公式,推导出这四个值即可,推导如下:
推导:xmin, xmax
{ x m a x + x m i n = 2 x _ c e n t e r x m a x − x m i n = w ∗ w i d t h \begin{cases} xmax+xmin=2x\_center\\ xmax-xmin=w*width \end{cases} {xmax+xmin=2x_centerxmax−xmin=w∗width
{ 2 x m a x = 2 x _ c e n t e r + w ∗ w i d t h = > x m a x = x _ c e n t e r + 1 2 ∗ w ∗ w i d t h 2 x m i n = 2 x _ c e n t e r − w ∗ w i d t h = > x m i n = x _ c e n t e r − 1 2 ∗ w ∗ w i d t h \begin{cases} 2xmax=2x\_center+w*width=>xmax=x\_center+\frac{1}{2}*w*width\\ 2xmin=2x\_center-w*width=>xmin=x\_center-\frac{1}{2}*w*width \end{cases} {2xmax=2x_center+w∗width=>xmax=x_center+21∗w∗width2xmin=2x_center−w∗width=>xmin=x_center−21∗w∗width
推导:ymin, ymax
{ y m a x + y m i n = 2 y _ c e n t e r y m a x − y m i n = y ∗ h e i g h t \begin{cases} ymax+ymin=2y\_center\\ ymax-ymin=y*height \end{cases} {ymax+ymin=2y_centerymax−ymin=y∗height
{ 2 y m a x = 2 y _ c e n t e r + h ∗ h e i g h t = > y m a x = y _ c e n t e r + 1 2 ∗ h ∗ h e i g h t 2 y m i n = 2 y _ c e n t e r − h ∗ h e i g h t = > y m i n = y _ c e n t e r − 1 2 ∗ h ∗ h e i g h t \begin{cases} 2ymax=2y\_center+h*height=>ymax=y\_center+\frac{1}{2}*h*height\\ 2ymin=2y\_center-h*height=>ymin=y\_center-\frac{1}{2}*h*height \end{cases} {2ymax=2y_center+h∗height=>ymax=y_center+21∗h∗height2ymin=2y_center−h∗height=>ymin=y_center−21∗h∗height
4 yolo格式标签转化为voc格式标签代码
- 代码是把txt标签转化为voc标签
- 代码支持一个标签文件中有多个目标
__Author__ = "Shliang"
__Email__ = "[email protected]"
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from xml.dom.minidom import Document
import cv2
'''
import xml
xml.dom.minidom.Document().writexml()
def writexml(self,
writer: Any,
indent: str = "",
addindent: str = "",
newl: str = "",
encoding: Any = None) -> None
'''
class YOLO2VOCConvert:
def __init__(self, txts_path, xmls_path, imgs_path):
self.txts_path = txts_path # 标注的yolo格式标签文件路径
self.xmls_path = xmls_path # 转化为voc格式标签之后保存路径
self.imgs_path = imgs_path # 读取读片的路径个图片名字,存储到xml标签文件中
self.classes = ["shirt", "non_shirt", "western_style_clothes", "coat", "down_filled_coat",
"cotton", "sweater", "silk_scarf", "tie", "bow_tie"]
# 从所有的txt文件中提取出所有的类别, yolo格式的标签格式类别为数字 0,1,...
# writer为True时,把提取的类别保存到'./Annotations/classes.txt'文件中
def search_all_classes(self, writer=False):
# 读取每一个txt标签文件,取出每个目标的标注信息
all_names = set()
txts = os.listdir(self.txts_path)
# 使用列表生成式过滤出只有后缀名为txt的标签文件
txts = [txt for txt in txts if txt.split('.')[-1] == 'txt']
print(len(txts), txts)
# 11 ['0002030.txt', '0002031.txt', ... '0002039.txt', '0002040.txt']
for txt in txts:
txt_file = os.path.join(self.txts_path, txt)
with open(txt_file, 'r') as f:
objects = f.readlines()
for object in objects:
object = object.strip().split(' ')
print(object) # ['2', '0.506667', '0.553333', '0.490667', '0.658667']
all_names.add(int(object[0]))
# print(objects) # ['2 0.506667 0.553333 0.490667 0.658667\n', '0 0.496000 0.285333 0.133333 0.096000\n', '8 0.501333 0.412000 0.074667 0.237333\n']
print("所有的类别标签:", all_names, "共标注数据集:%d张" % len(txts))
# 把从xmls标签文件中提取的类别写入到'./Annotations/classes.txt'文件中
# if writer:
# with open('./Annotations/classes.txt', 'w') as f:
# for label in all_names:
# f.write(label + '\n')
return list(all_names)
def yolo2voc(self):
# 创建一个保存xml标签文件的文件夹
if not os.path.exists(self.xmls_path):
os.mkdir(self.xmls_path)
# # 读取每张图片,获取图片的尺寸信息(shape)
# imgs = os.listdir(self.imgs_path)
# for img_name in imgs:
# img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.imgs_path, img_name))
# height, width, depth = img.shape
# # print(height, width, depth) # h 就是多少行(对应图片的高度), w就是多少列(对应图片的宽度)
#
# # 读取每一个txt标签文件,取出每个目标的标注信息
# all_names = set()
# txts = os.listdir(self.txts_path)
# # 使用列表生成式过滤出只有后缀名为txt的标签文件
# txts = [txt for txt in txts if txt.split('.')[-1] == 'txt']
# print(len(txts), txts)
# # 11 ['0002030.txt', '0002031.txt', ... '0002039.txt', '0002040.txt']
# for txt_name in txts:
# txt_file = os.path.join(self.txts_path, txt_name)
# with open(txt_file, 'r') as f:
# objects = f.readlines()
# for object in objects:
# object = object.strip().split(' ')
# print(object) # ['2', '0.506667', '0.553333', '0.490667', '0.658667']
# 把上面的两个循环改写成为一个循环:
imgs = os.listdir(self.imgs_path)
txts = os.listdir(self.txts_path)
txts = [txt for txt in txts if not txt.split('.')[0] == "classes"] # 过滤掉classes.txt文件
print(txts)
# 注意,这里保持图片的数量和标签txt文件数量相等,且要保证名字是一一对应的 (后面改进,通过判断txt文件名是否在imgs中即可)
if len(imgs) == len(txts): # 注意:./Annotation_txt 不要把classes.txt文件放进去
map_imgs_txts = [(img, txt) for img, txt in zip(imgs, txts)]
txts = [txt for txt in txts if txt.split('.')[-1] == 'txt']
print(len(txts), txts)
for img_name, txt_name in map_imgs_txts:
# 读取图片的尺度信息
print("读取图片:", img_name)
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.imgs_path, img_name))
height_img, width_img, depth_img = img.shape
print(height_img, width_img, depth_img) # h 就是多少行(对应图片的高度), w就是多少列(对应图片的宽度)
# 获取标注文件txt中的标注信息
all_objects = []
txt_file = os.path.join(self.txts_path, txt_name)
with open(txt_file, 'r') as f:
objects = f.readlines()
for object in objects:
object = object.strip().split(' ')
all_objects.append(object)
print(object) # ['2', '0.506667', '0.553333', '0.490667', '0.658667']
# 创建xml标签文件中的标签
xmlBuilder = Document()
# 创建annotation标签,也是根标签
annotation = xmlBuilder.createElement("annotation")
# 给标签annotation添加一个子标签
xmlBuilder.appendChild(annotation)
# 创建子标签folder
folder = xmlBuilder.createElement("folder")
# 给子标签folder中存入内容,folder标签中的内容是存放图片的文件夹,例如:JPEGImages
folderContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(self.imgs_path.split('/')[-1]) # 标签内存
folder.appendChild(folderContent) # 把内容存入标签
annotation.appendChild(folder) # 把存好内容的folder标签放到 annotation根标签下
# 创建子标签filename
filename = xmlBuilder.createElement("filename")
# 给子标签filename中存入内容,filename标签中的内容是图片的名字,例如:000250.jpg
filenameContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(txt_name.split('.')[0] + '.jpg') # 标签内容
filename.appendChild(filenameContent)
annotation.appendChild(filename)
# 把图片的shape存入xml标签中
size = xmlBuilder.createElement("size")
# 给size标签创建子标签width
width = xmlBuilder.createElement("width") # size子标签width
widthContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(width_img))
width.appendChild(widthContent)
size.appendChild(width) # 把width添加为size的子标签
# 给size标签创建子标签height
height = xmlBuilder.createElement("height") # size子标签height
heightContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(height_img)) # xml标签中存入的内容都是字符串
height.appendChild(heightContent)
size.appendChild(height) # 把width添加为size的子标签
# 给size标签创建子标签depth
depth = xmlBuilder.createElement("depth") # size子标签width
depthContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(depth_img))
depth.appendChild(depthContent)
size.appendChild(depth) # 把width添加为size的子标签
annotation.appendChild(size) # 把size添加为annotation的子标签
# 每一个object中存储的都是['2', '0.506667', '0.553333', '0.490667', '0.658667']一个标注目标
for object_info in all_objects:
# 开始创建标注目标的label信息的标签
object = xmlBuilder.createElement("object") # 创建object标签
# 创建label类别标签
# 创建name标签
imgName = xmlBuilder.createElement("name") # 创建name标签
imgNameContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(self.classes[int(object_info[0])])
imgName.appendChild(imgNameContent)
object.appendChild(imgName) # 把name添加为object的子标签
# 创建pose标签
pose = xmlBuilder.createElement("pose")
poseContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("Unspecified")
pose.appendChild(poseContent)
object.appendChild(pose) # 把pose添加为object的标签
# 创建truncated标签
truncated = xmlBuilder.createElement("truncated")
truncatedContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
truncated.appendChild(truncatedContent)
object.appendChild(truncated)
# 创建difficult标签
difficult = xmlBuilder.createElement("difficult")
difficultContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
difficult.appendChild(difficultContent)
object.appendChild(difficult)
# 先转换一下坐标
# (objx_center, objy_center, obj_width, obj_height)->(xmin,ymin, xmax,ymax)
x_center = float(object_info[1])*width_img + 1
y_center = float(object_info[2])*height_img + 1
xminVal = int(x_center - 0.5*float(object_info[3])*width_img) # object_info列表中的元素都是字符串类型
yminVal = int(y_center - 0.5*float(object_info[4])*height_img)
xmaxVal = int(x_center + 0.5*float(object_info[3])*width_img)
ymaxVal = int(y_center + 0.5*float(object_info[4])*height_img)
# 创建bndbox标签(三级标签)
bndbox = xmlBuilder.createElement("bndbox")
# 在bndbox标签下再创建四个子标签(xmin,ymin, xmax,ymax) 即标注物体的坐标和宽高信息
# 在voc格式中,标注信息:左上角坐标(xmin, ymin) (xmax, ymax)右下角坐标
# 1、创建xmin标签
xmin = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmin") # 创建xmin标签(四级标签)
xminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(xminVal))
xmin.appendChild(xminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmin)
# 2、创建ymin标签
ymin = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymin") # 创建ymin标签(四级标签)
yminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(yminVal))
ymin.appendChild(yminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymin)
# 3、创建xmax标签
xmax = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmax") # 创建xmax标签(四级标签)
xmaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(xmaxVal))
xmax.appendChild(xmaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmax)
# 4、创建ymax标签
ymax = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymax") # 创建ymax标签(四级标签)
ymaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(ymaxVal))
ymax.appendChild(ymaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymax)
object.appendChild(bndbox)
annotation.appendChild(object) # 把object添加为annotation的子标签
f = open(os.path.join(self.xmls_path, txt_name.split('.')[0]+'.xml'), 'w')
xmlBuilder.writexml(f, indent='\t', newl='\n', addindent='\t', encoding='utf-8')
f.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
txts_path1 = './Annotations_txt'
xmls_path1 = './Annotations_xml'
imgs_path1 = './JPEGImages'
yolo2voc_obj1 = YOLO2VOCConvert(txts_path1, xmls_path1, imgs_path1)
labels = yolo2voc.search_all_classes()
print('labels: ', labels)
yolo2voc_obj1.yolo2voc()
![]()
![]()
♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠ ⊕ ♠