链表的创建、查找、增加、删除
//参考了胡凡、曾磊的《算法笔记》这本书 侵删致歉
/*线性表是一类很常用的数据结构 分为顺序表和链表
顺序表可以理解为数组 连续的地址
链表有若干个结点组成,且结点在内存中存储位置通常是不连续的。
两个结点之间一般通过一个指针来从一个结点指向另一个结点
因此,链表的结点一般有两部分构成:数据域【存储数据】和指针域【指向下一个结点的地址】
struct node
{
typename data;//typedef是指数据类型 比如以后可以写int data;
node *next;
};
有无头结点head分为带头结点【头结点下一个结点是“第一个结点”】和不带头结点
最后一个结点的next是NULL
////////////////////////////
给链表的结点分配空间:malloc和new
1:malloc函数 是头文件stdlib.h下申请的动态内存函数 其返回类型是申请的同变量类型的指针
typename *p=(typename*)malloc(sizeof(typename));
比如申请一个int型和一个人node型结构体变量:
int *p=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
node *p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
释放开辟出的空间free(p);
2:new预算符
typename *p=new typename;
比如申请一个int型和一个人node型结构体变量:
int *p=new int;
node *p=new node;
释放开辟出的空间delete(p);*/
//1:创建链表(有头结点)
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct node//定义结构体 数据域和地址域
{
int data;
node *next;
};
node *create(int Array[])
{
node *p,*pre,*head;//pre保存当前结点的前驱结点,head为头结点
head=new node;//创建头结点
head->next=NULL;
pre=head;//最后要把头结点返回 所以后面不能操作head
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
p=new node;//新建结点
p->data=Array[i];//赋给新建结点数据域 也可以scanf输入
p->next=NULL;
pre->next=p;
pre=p;
}
return head;//返回头结点
}
int main()
{
int Array[5]={5,3,6,1,2};
node* L=create(Array);//创建
L=L->next;//这里创建的是带头结点 返回的是head 所以next以下指向第一个结点
while(L!=NULL)//输出每个结点的数据域
{
printf("%d",L->data);
L=L->next;
}
return 0;
}
//2.查找某元素在链表中的个数
/*int search(node *head,int x)
{
int count=0;
node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data==x)
count++;
p=p->next;
}
return count;
}*/
//这个可以直接放在创建链表里 head就是创建返回的head,即L
//3.插入元素

/*void insert(node *head,int pos,int x)
{
node *p=head;
for(int i=0;i
node *m=new node;
m->data=x;
m->next=p->next;
p->next=m;
}*/
//放到创建链表程序一起
/*#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct node//定义结构体 数据域和地址域
{
int data;
node *next;
};
node *create(int Array[])
{
node *p,*pre,*head;//pre保存当前结点的前驱结点,head为头结点
head=new node;//创建头结点
head->next=NULL;
pre=head;//最后要把头结点返回 所以后面不能操作head
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
p=new node;//新建结点
p->data=Array[i];//赋给新建结点数据域 也可以scanf输入
p->next=NULL;
pre->next=p;
pre=p;
}
return head;
}
void insert(node *head,int pos,int x)
{
node *p=head;
for(int i=0;i
node *m=new node;
m->data=x;
m->next=p->next;
p->next=m;
}
int main()
{
int Array[5]={5,3,6,1,2};
node* m=create(Array);//创建
node *L=m->next;//这里创建的是带头结点 返回的是head 所以next以下指向第一个结点
printf("链表为:");
while(L!=NULL)//输出每个结点的数据域
{
printf("%d",L->data);
L=L->next;
}
insert(m,3,3);
printf("插入后链表为:");
m=m->next;
while(m!=NULL)//输出每个结点的数据域
{
printf("%d",m->data);
m=m->next;
}
return 0;
}
*/
//4.删除元素
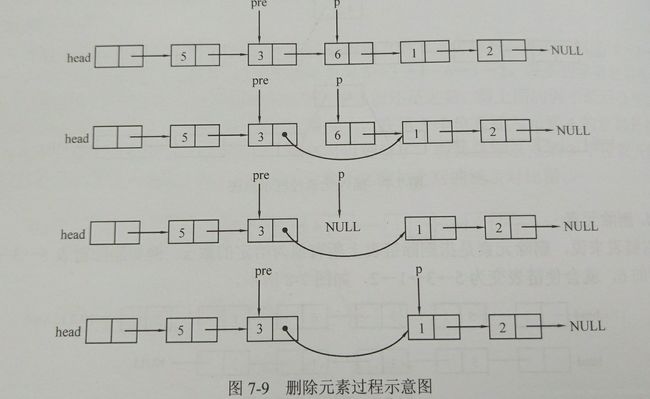
/*void del(node *head,int x)
{
node *p=head->next;
node *pre=head;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data==x)
{
pre->next=p->next;
delete(p);
p=pre->next;
}
else
{
pre=p;
p=p->next;
}
}
}*/
//放在创建链表一起
/*
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct node//定义结构体 数据域和地址域
{
int data;
node *next;
};
void del(node *head,int x)
{
node *p=head->next;
node *pre=head;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data==x)
{
pre->next=p->next;
delete(p);
p=pre->next;
}
else
{
pre=p;
p=p->next;
}
}
}
node *create(int Array[])
{
node *p,*pre,*head;//pre保存当前结点的前驱结点,head为头结点
head=new node;//创建头结点
head->next=NULL;
pre=head;//最后要把头结点返回 所以后面不能操作head
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
p=new node;//新建结点
p->data=Array[i];//赋给新建结点数据域 也可以scanf输入
p->next=NULL;
pre->next=p;
pre=p;
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
int Array[5]={5,3,6,1,2};
int n;
node* m=create(Array);//创建
node *L=m->next;//这里创建的是带头结点 返回的是head 所以next以下指向第一个结点
printf("链表为:");
while(L!=NULL)//输出每个结点的数据域
{
printf("%d",L->data);
L=L->next;
}
printf("\n\n请输入删除的元素:");
scanf("%d",&n);
del(m,n);
m=m->next;
printf("删除%d后为:",n);
while(m!=NULL)//输出每个结点的数据域
{
printf("%d",m->data);
m=m->next;
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}*/

