2019 ICPC Asia Nanjing Regional C. Digital Path
Zhe the bully, is condemned by all kinds of evil, like bullying those who are weaker. His teammates have been mistreated for a long time. Finally, they decided not to put up with their buddy any more and flee to Digital Village, with the bully in hot pursuit. Due to difficult terrain and a considerable amount of Digital Paths staggered, they can’t be easily arrested.
Getting familiar with the terrain as soon as possible is important for these innocents to escape the threat of bullying. All they need now is to count the number of Digital Paths in Digital Village.
To simplify the problem, Digital Village is abstracted into a grid with nn rows and mm columns filled by integers. A Digital Path is a continuous walk in the grid satisfying the following conditions:
- adjacent boxes in the walk share a common edge;
- the walk is maximal, which cannot be extended;
- the walk contains at least four boxes;
- going from one end to the other, the increment of values for any two adjacent boxes is exactly one.
Here we have some examples.

The path in Figure 1 is invalid because its length is less than 44.
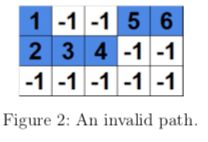
The path in Figure 2 is invalid because it is not continuous.
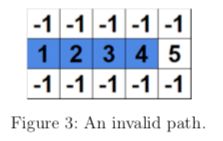
The path in Figure 3 is invalid because it can be extended further.
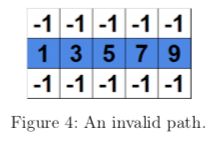
The path in Figure 4 is also invalid because values in the path are not strictly increased by one.
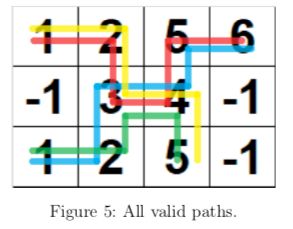
Digital Paths may partially overlap. In Figure 5, there are 4 Digital Paths marked by different colours.
Input
The first line contains two positive integers n and m (1≤n,m≤1000) describing the size of the grid.
Each of the next nn lines contains mm integers, the jj-th of which, denoted by ai,j (−107≤ai,j≤107), represents the value of the box in the ii-th row and the jj-th column.
Output
Output the number of Digital Paths modulo (10^9+7).
样例输入1
3 5
1 2 3 8 7
-1 -1 4 5 6
1 2 3 8 7
样例输出1
4
样例输入2
4 4
1 2 3 4
2 3 4 3
3 4 3 2
4 3 2 1
样例输出2
16
题意
n×m的矩阵,找寻最长路径的数目,路径长度>=4,并且路径中的数值严格增加1,得到结果 mod 1e9 + 7。
思路
有用拓扑+dpAC的
我这里用的是记忆化搜素+dp。
首先定义一下结构体:
struct node{
ll a,b,c,d;
bool flag;
}dp[maxn][maxn];
- flag:就是记录是否DFS过,记忆化。
- a:该点能否可以向外延伸一个点,可以的话就是 0,不可以是 1
- b:该点是否可以向外延伸两个点,假设该点是 now,与它相邻的点是 nxti,那么很明显 now.b = ∑ nxti.a。
- c:该点是否可以向外延伸三个点,假设该点是 now,与它相邻的点是 nxt1,那么很明显 now.c = ∑ nxti.b。
- d:该点是否可以向外延伸四个及以上的点,假设该点是 now,与它相邻的点是 nxt1,那么很明显 now.d = ∑ (nxti.c+nxt.d)。
然后三个判断函数:
bool judge(int x,int y) //判断是否出界
{
if(x<1||y<1||x>n||y>m)
return false;
return true;
}
bool vis1(int i,int j) //判断是否可以向外移一个点
{
if(i-1>=1&&p[i-1][j]-p[i][j]==1) return true;
if(i+1<=n&&p[i+1][j]-p[i][j]==1) return true;
if(j-1>=1&&p[i][j-1]-p[i][j]==1) return true;
if(j+1<=m&&p[i][j+1]-p[i][j]==1) return true;
return false;
}
//判断是否可以由四周向该点移动也就是判断该点是否是最大路径的起点
bool vis2(int i,int j)
{
if(i-1>=1&&p[i][j]-p[i-1][j]==1) return false;
if(i+1<=n&&p[i][j]-p[i+1][j]==1) return false;
if(j-1>=1&&p[i][j]-p[i][j-1]==1) return false;
if(j+1<=m&&p[i][j]-p[i][j+1]==1) return false;
return true;
}
我们先更新结构体里的 a,两层 for + vis1
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
if(vis1(i,j)) dp[i][j].a = 0;
else dp[i][j].a = 1;
}
}
然后记忆化搜索全部矩阵
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
DFS(i,j);
}
}
node DFS(int i,int j)
{
if(dp[i][j].flag) return dp[i][j];
dp[i][j].flag = true;
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int nx = i + mx[k];
int ny = j + my[k];
if(judge(nx,ny)&&p[nx][ny]-p[i][j]==1){
node nxt = DFS(nx,ny);
dp[i][j].b += nxt.a;
dp[i][j].b %= mod;
dp[i][j].c += nxt.b;
dp[i][j].c %= mod;
dp[i][j].d += (nxt.c+nxt.d);
dp[i][j].d %= mod;
}
}
return dp[i][j];
}
然后就,遍历矩阵,+d了,这里要注意,为了避免重复,我们应该只加路径起点的d,也就是要用 vis2 函数判断一下。
ll ans = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
if(vis2(i,j)){
ans = (ans+dp[i][j].d) % mod;
}
}
}
AC代码:
#include