注意:本文记录作者在学习和使用vuejs开发中的点点滴滴,从vuejs1.0开始直到现在的vuejs2.0以后的版本。期中部分1.0的内容已经过时,仅作各位朋友参考,建议重点关注2.0相关的内容,会随着我对vuejs有了更多的体会后不断维护更新,也欢迎朋友们批评指正共同学习提高。
所有的vuejs组件都是被扩展的vue实例;
var MyComponent = Vue.extend({
//扩展选项对象
})
var myComponentInstance = new MyComponent();
每个Vue实例都会代理这个实例的data属性对象里的所有属性:
var data = { a: 1 }
var vm = new Vue({
data: data
})
vm.a === data.a // -> true
// 设置属性也会影响到原始数据
vm.a = 2
data.a // -> 2
// ... 反之亦然
data.a = 3
vm.a // -> 3
所有Vue实例本身暴露的属性和方法,都以$为头来区别,对应Vue.set global API
例如:vm.$data,vm.$elvm.$watch,这个有利于和data属性对象的数据来区分;
所有directive都以v-xxx形式存在:
if="greeting">Hello!
//根据greeting表达式的值真假来插入或者删除p元素;
//href是argument,表示将a元素的href属性和url表达式绑定起来
其对应的简写形式为:
//这个是一种缩写的形式
//click是参数,表示on click时,执行doSomething这个表达式(函数)
//href为argument,literal为修饰符,表示后面"/a/b/c"为字面值而不是表达式!!
<button :disabled="someDynamicCondition">Buttonbutton> // 绑定到一个布尔值,如果真则disabled属性就加在button上
directive object context暴露出来供update/bind函数使用的属性:
el: the element the directive is bound to.
vm: the context ViewModel that owns this directive.
expression: the expression of the binding, excluding arguments and filters.
arg: the argument, if present.
name: the name of the directive, without the prefix.
modifiers: an object containing modifiers, if any.
descriptor: an object that contains the parsing result of the entire directive.
params: an object containing param attributes.
比如下面的directive例子中:
// 注意需要watch directive的parameter才能实现xdata变化就能触发directive内部的变化
Vue.directive('example', {
params: ['parax'],
paramWatchers: {
parax: function (val, oldVal) {
console.log('parax changed!')
}
}
})
绑定css class和style:
这是class绑定的演示
data: { styleObject: { color: 'red', fontSize: '13px' } }
data: {
classObject: {
'class-a': true,
'class-b': false
}
}
v-if directive:条件渲染:
注意v-if会直接在DOM中插入删除对应的元素
<h1 v-if="ok">Yesh1>
<h1 v-else>Noh1>
<template v-if="ok">
<h1>Titleh1>
<p>Paragraph 1p>
<p>Paragraph 2p>
template>
v-show条件显示
不会删除元素,只会使用display:none css的方式
<h1 v-show="ok">Hello!h1>
v-for列表数据渲染(注意在v-for子块内可以访问父组件作用域内的属性,还有一个$index)
<ul id="example-2">
<li v-for="(index, item) of items">
{{index}} {{ parentMessage }} - {{ $index }} - {{ item.message }}
li>
ul>
var example2 = new Vue({
el: '#example-2',
data: {
parentMessage: 'Parent',
items: [
{ message: 'Foo' },
{ message: 'Bar' }
]
}
})
//结果:
0 Parent - 0 -Foo
1 Parent - 1 -Foo
//v-for也可以应用在template标签上,这样做的好处是:不用额外的无意义的tag,template tag不会被渲染出来
<ul>
<template v-for="item in items">
<li>{{ item.msg }}li>
<li class="divider">li>
template>
ul>
vuejs可以被应用在数组的push,pop,shift,unshift,splice,sort,reverse方法改变数组的场景,但是如果你使用下面的语法1. vm.items[0]={}; 2.vm.items.length=0改变数组vuejs则无法感知这个变化,vuejs推荐的解决方案是:1.使用$set方法: example1.items.$set(0,{});
2.使用空数组来替换items即可 example1.items = [];
vuejs也提供了直接删除一个数组一个元素的简单方法 this.items.$remove(item)
v-for应用在对象上面(而不是数组)
<ul id="repeat-object" class="demo">
<li v-for="value in object">
{{ $key }} : {{ value }}
li>
ul>
new Vue({
el: '#repeat-object',
data: {
object: {
FirstName: 'John',
LastName: 'Doe',
Age: 30
}
}
})
//输出一下结果
<ul id="repeat-object" class="demo">
<li>
FirstName : John
li><li>
LastName : Doe
li><li>
Age : 30
li>
ul>
v-on内联语句访问event参数:如果是一个函数作为v-on绑定的表达式的话,该函数自动带有(event参数),这个和普通的js事件处理函数是一样的。
<button v-on:click="say('hello!', $event)">Submitbutton>
// ...
methods: {
say: function (msg, event) {
// 现在我们可以访问原生事件对象
event.preventDefault()
}
}
事件修饰符:
v-on:click.stop/v-on:submit.prevent/v-on:click.stop/v-on:click.capture/v-on:click.self="dothat"
v-model表单控件绑定:
http://vuejs.org.cn/guide/forms.html
过渡动画
http://vuejs.org.cn/guide/transitions.html
组件:
需要确保在初始化root instance之前注册了组件!
// 定义
var MyComponent = Vue.extend({
template: 'A custom component!
'
})
// 注册
Vue.component('my-component', MyComponent)
// 创建根实例
new Vue({
el: '#example'
})
//结果:
注意:组件的模板会替换自定义元素my-component标签,也就是说my-component只是作为一个挂载点而已,当然,这可以通过replace选项来改变这个缺省行为
组件的局部注册:
有时我们可能希望一个组件只能在其他组件内使用,那么可以用实例选项components来注册:
var Child = Vue.extend({
template: 'A custom component!
'
})
var Parent = Vue.extend({
template: '...',
components: {
// 只能用在父组件模板内
'my-component': Child
}
})
组件注册语法糖
上面全局和局方方式注册组件总是使用Vue.extend来定义组件,随后传入Vue.component()或者components选项,有时显得很啰嗦,vuejs提供了一种简化方式来声明定义组件(参数传入还是分两种情况:全局和局部)
// 在一个步骤中扩展与注册
Vue.component('my-component', {
template: 'A custom component!
'
})
// 局部注册也可以这么做
var Parent = Vue.extend({
components: {
'my-component': {
template: 'A custom component!
'
}
}
})
组件选项数据隔离问题(data和el选项)
传入Vue构造器的多数选项(new Vue({el,data,components,prop...}))都可以用在Vue.extend()中,但是data和el是两个特例,不能直接简单地把一个对象作为data选项传给Vue.extend(),原因如下:
var data = { a: 1 }
var MyComponent = Vue.extend({
data: data
})
如果直接传入data对象给data选项,那么所有的MyComponent组件的实例都将共享同一个data对象!!因此我们正确的做法是利用javascript的闭包的概念,使用一个函数来返回对应的数据:
var MyComponent = Vue.extend({
data: function () {
return { a: 1 }
}
})
关于组件重用的一篇参考文章
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/3maEjiF
watch
watch: {
// whenever question changes, this function will run
question: function (newQuestion) {
this.answer = 'Waiting for you to stop typing...'
this.getAnswer()
},
deepwachedArrayOrObject: {
handler: function(nv,ov){
// watch handler function body
},
deep: true // 指示深度侦测
}
需要注意的是在vuejs2.0中初次mount的组件并不会调用这个watch,而只有数据变化后才会调用,不像1.0中初次mount时也会调用
注意: 对于object对象或者array对象最好使用deep: true的参数,否则可能不会对对象key值变更做出反应
Computed属性
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
message: 'Hello'
},
computed: {
// 计算属性的 getter
reversedMessage: function () {
// `this` 指向 vm 实例
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
})
模板解析问题:
vue的模板是DOM模板,使用的是浏览器原生的解析器,DOM模板必须是有效的HTML片段。我们必须注意有一些HTML元素对于什么元素能够放在他里面是有限制的,比如:
a不能包含其他的交互元素(比如按钮,链接)
ul/ol只能包含li
select只能包含option和optgroup,
table只能包含thead,tbody,tfoot,tr,caption,col,colgroup,
tr只能包含th,td
我们如果违反这些规则,比如把
这种方式来组织的话,浏览器会把my-component提到元素的外面,导致渲染不正确。
这时,如果我们又必须使用这样的结构,总么办?
我们使用is属性吧!!!
<table>
<tr is="my-component">tr>
table>
组件component实例作用域
组件实例的scope作用域是孤立的,这意味着不能并且也不应该在子组件的模板内直接引用父组件的数据,但是我们可以使用props属性来吧数据传给子组件:
prop是组件数据的一个字段,期望从父组件传下来。子组件需要显式地用props选项声明props:
Vue.component('child', {
// 声明 props
props: ['msg'],
// prop 可以用在模板内
// 可以用 `this.msg` 设置
template: '{{ msg }}'
})
//传入一个普通的字符串给child组件的msg属性
camelCase和kebab-case的转换
由于HTML属性是不区分大小写的,因此我们组件的prop使用camelCase来定义时,需要转为短横线隔开(这个和angular类似:
Vue.component('child', {
// camelCase in JavaScript
props: ['myMessage'],
template: '{{ myMessage }}'
})
Vue.component('child', {
// camelCase in JavaScript
props: ['myMessage'],
template: '{{ myMessage }}'
})
绑定自定义组件的属性
类似于绑定一个普通的属性到一个表达式,我们也可以使用v-bind来绑定自定义组件的props到父组件的数据,这样每当父组件的数据发生变化时,也会传导这个数据给子组件:
<div>
<input v-model="parentMsg">
<br>
<child v-bind:my-message="parentMsg">child>
div>
//简化版本:
<child :my-message="parentMsg">child>
传递值给prop
初学者往往犯错的是直接传递数值给prop,但是实际上是传递了一个字符串,我们必须使用:前缀,这样告诉vue,我们后面的是一个表达式,而不是字面量:
<comp some-prop="1">comp>
<comp :some-prop="1">comp>
prop从父亲到儿子双向绑定(在vuejs2.0中反向回传是严正反对的!但v2.2之后又满血复活了,久违啦)
默认情况下prop是单向绑定:当父组件属性变化时,传递给子组件,但是反过来不会。你可以使用.sync或者.once绑定修饰符来显式地强制双向绑定或者单次绑定:
<child :msg="parentMsg">child>
<child :msg.sync="parentMsg">child>
<child :msg.once="parentMsg">child>
需要注意的是:如果prop本身是一个对象或者数组的话,由于javascript对象是引用方式,无论是什么绑定方式都会是双向绑定!!
父子组件通信:
子组件可硬用this.$parent访问父组件,this.$root访问祖根实例,每个父组件都有一个数组this.$children来包含所有子元素。
但是在vuejs2.0中,任何试图在组件内修改通过props传入的父组件数据都被认为是anti-pattern的,报以下错误:
Avoid mutating a prop directly since the value will be overwritten whenever the parent component re-renders
我们必须重新思考如何架构我们的应用:
1. 不要在组件内试图修改props传进来的父组件数据,数据只应该由该数据的源头组件来负责app内的CRUD;
2. 数据永久性功能(就是和后台数据库交互保存)最好是由需要处理数据的子组件来和数据库交互,但是通过$emit一个事件通知该数据的源头组件来更新web app的数据;(在子组件tag引用处以@resource-deleted来引用父组件的事件函数) 这种模式带来的问题是数据来源和数据消费者有事件交互的强烈耦合。
还有一种小方案是将数据永久性功能以及web app内部的数据一致两个功能合为一处,即:子组件需要修改源数据时,$emit消息给父亲,由owner来同时完成数据永久性保存和内部app数据一致
3.对于大型web app可以使用vuex来实现解耦:父子之间通过vuex store state tree来保持联系,任何时候需要获取数据则getter,如果需要修改数据则setter,数据修改后的reactive则由vuejs处理,这种方式最大限度地实现了解耦
4. 但是有时也需要一些平衡:难道每一片小数据都得通过$emit事件给数据源头来做修改吗?由于如果传入的数据是Object类型或者array类型的,则本身由于是reference传参的,也就是说子组件prop传入供子组件读/写的object/array和“源头object/array”实际上是一个对象,因此只要我们不直接简单粗暴以
this.objFromParent = newObjectCreatedByChild //这样会导致vuejs报错 Avoid mutating a prop directly ...
但是如果我们这样操作,则是可以的,并且数据完全是同步的!
this.objFromParent.propertyChangedByChild = newObjectCreatedByChild.propertyChangedByChild //这样数据就很轻松保持了一致性,而不用$emit消息到数据源来维护数据了!!!
5.第4点和vuex的机制比较类似。你可以在需要共享给儿子组件的数据(起源于hosted by本组件)存放在一个localStore对象的属性中,将localStore对象作为属性值传给儿子组件,比如:pstore="localStore",在儿子组件中,则可以直接操作pstore.parentData = somedatahandledbyson ,曲线救国,绕过了vuejs2.0不允许对属性赋值操作的限制。
6. 如果是需要共享给后代子孙的数据,则可以引入一种thisrootstore机制,所有这类数据作为thisrootstore的属性对象存在,后代以this.rootstore.xxx来引用它。
5和6的好处是剔除大部分不需要$emit事件来sync数据的冗余代码,更加易于实现组件功能的抽象和重用
7. 也可以考虑利用slot机制的特性: slot本身所在html js scope属于父组件,这样就可以以下面的形式来解决这个数据同步问题:
<son v-for="son in sons">
<div @click="removeThisSon(son)"> some operation affected parent datadiv>
son>
心法:对整个属性对象替换(赋值),新增,或者删除操作必须由数据源来操作,但是对传入的属性对象的某些property修正,则可以在子组件内部直接操作,数据就同步反映到父组件中
心法:数据优先,你首先抽象驱动你的app的state,所有代码就围绕着这些个state的变迁,而让vuejs本身来执行构建和更新DOM的工作。
The whole idea is "data first". you define what the state of your application should look like, and let Vue build and update the DOM accordingly
自定义事件
Vue实例的事件系统独立于DOM事件系统,做法有不同:
使用$on()监听事件;
使用$emit()在这个组件上面触发事件;
使用$dispatch()来派发事件,事件沿着父链冒泡;
$broadcast()广播事件,从父亲向下到所有后代;
子组件索引v-ref
<div id="parent">
<user-profile v-ref:profile>user-profile>
div>
var parent = new Vue({ el: '#parent' })
// 访问子组件
var child = parent.$refs.profile
transclusion: slot分发内容
学过angular,你可能知道有一个非常晦涩难懂的概念:transclusion,在vuejs中也有类似的说法slot
我们先搞清楚编译作用域吧,看看下面的代码:
这个代码中的msg到底是绑定到父组件的数据,还是绑定到子组件的数据呢??正确答案是父组件。关于组件的作用域有以下心法,牢牢记住:
父组件模板的内容在父组件的作用域内编译;子组件模板的内容在子组件作用域内编译。
一个常见的错误是试图在父组件的模板内将一个directive绑定到子组件的属性和方法:
<child v-show="someChildProperty">child>
注意:分发内容是在父组件的作用域内编译
v-for和组件共用:
v-for可以像普通元素上一样在compent tag上面使用:
<my-component
v-for="item in items"
:item="item"
:index="$index">
my-component>
上例中每个my-component实例将会传入item数据/index索引以便使用
async components:
有时候,我们的组件在render之前,可能需要一些数据准备的工作:比如从后端ajax过来数据,并且feed到组件中去,这时就需要使用async组件的概念了。
http://jsbin.com/maqagocise/edit?html,js,output
上面的代码例子可以参考:
Vue.component('async-example', function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
resolve({
template: 'I am async!
'
});
}, 1000);
});
new Vue({
el: '#body'
});
<async-example>async-example>
动态插入和删除一个vue组件
你虽然可以通过以下代码实现动态插入和删除vue组件的需求,但是这种方式的问题是:在vue devtool中并未看到数据链的关系,我们还是建议使用v-if来实现这种应用场景。
methods:{
attachNewPermission: function(){
var vm = this;
var html = ' ';
var vmtemp = Vue.extend({
template: html,
replace: false,
el: function(){
return vm.$el.getElementsByClassName('asyncloadednode')[0];
}
});
new vmtemp();
}
通过prop向子组件传入父组件的函数作为callback,并且访问子组件的数据
http://012.vuejs.org/guide/components.html#Passing_Callbacks_as_Props
prop传入父组件数据例子
1
2 <update-text-inplace :url='"/admin/roles/"+role.id' fieldname="name">
3 <div class="role-name">@{{ role.name }}div>
4 update-text-inplace>
VUEJS 2.0新feature及变化
https://github.com/vuejs/vue/issues/2873
vue component定义及引用命名约定
// PascalCase
import TextBox from './components/text-box';
import DropdownMenu from './components/dropdown-menu';
export default {
components: {
// use in templates as and
TextBox,
DropdownMenu
}
}
// in a component definition
components: {
// register using camelCase
myComponent: { /*... */ }
}
何为fragment instance
http://vuejs.org/guide/components.html#Fragment-Instance
ES6 moudle export/import
// flash-message.js
function alertMessage(message) {
alert(message);
}
function logMessage(message) {
console.log(message);
}
export {alertMessage, logMessage};
//app.js
import {alertMessage, logMessage} from './flash-message';
alertMessage("Hello");
logMessage("Hello");
//flash-message.js
export default function(message){
alert(message);
}
//app.js
import flashMessage from './flast-message';
flashMessage("Hello");
http://www.cnblogs.com/Answer1215/p/5131548.html
注意root Vue instance不能多次初始化,否则可能会出现组件找不到的情况
javascript模块化开发模式:
每个文件都组织为一个模块;
文件的开头通过import(es6)/require(cmd,amd)方式声明需要从外部导入的依赖;
每个文件需要输出的比如component defination object, function,object等通过export定义;
第三方组件通过npm install --save-dev或者bower install --save下载安装,通过require('jquery')(这种方式是通过npm安装的,可以不用传入路径)或者require('path/to/jquery/jquery')(这种是非npm安装模式从本地文件require)来引入
所有第三方组件(如果本身不支持CMD,AMD,ES6模块化加载的话)或者自己写的过程式js文件需要做简单的改造,改造成ES6/CMD/AMD模块格式,以支持模块化开发模式
关于vuejs大小写,camcase等
在使用vueify时,需要import一个组件的配置对象,这时建议全部使用首字母大写的命名方式,下例:
import MyComponent from './my-component'
export default {
components: {
MyComponent // es2015 shorhand
}
}
//然后在template中使用-代替非首单词大写字母:
以js模块化方式写一个export一个singleton object:
var Spinner = require('spin.js');
// export singleton:这是由于require会cache一个object
module.exports = exports = new Spinner;
在需要引用该singleton object的地方:
var spin = require('./supportlibs/spinner');
var spin2 = require('./supportlibs/spinner');
spin===spin2 //返回true!
hot reloading
我们在使用browsersync这个工具做前端开发时,可以只对页面的css进行注入,这个概念在vueify的组件开发中也是可以的
参考: http://vuex.vuejs.org/zh-cn/hot-reload.html
在browserify工具链下有以下plugin实现类似的功能: https://github.com/AgentME/browserify-hmr/

如何在Html inspection pannel中清楚查看一段html属于哪个组件?
在组件式开发模式下,我们的页面就是一堆component组件按照逻辑关系堆砌出来的,很多时候我们发现找到对应的html片段属于哪个组件的模版定义的不是一件容易的事情,如何处理这种棘手的问题使得开发更容易和有趣?
我总结下来一个简单有效的方法是:在组件的root node下增加一行html注释: , 这样在html inspection界面就一眼看出是什么组件了,对应你想修改的话,打开那个组件.vue文件修改即可。
vuejs组件vueify开发模式下的依赖问题
我们使用vueify开发模式来开发vuejs组件,将所有的代码:html+javascript+css都放在component.vue文件中,这对于前端开发可以说是一种革命,大大地便利了组件的迭代式开发,大大增加了代码的可重用性,但是同时也带来一些“问题”,其中一个问题就是:当我们更改一个component.vue后,必须重新编译所有引用过这个vue文件的bundle.js文件才能自动使用最新的component逻辑,这在以往纯粹
强烈建议参考 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004368132 该文章对各种模块化的写法解释的很清楚
动态load html并且编译
如果你有一个组件,它会动态加载一部分html代码,而这个代码中包含一些vuejs代码,你需要使用$compile功能:
_self.vm.$compile(_self.vm.$el); //这个是不行的,因为dom已经是编译过的
//下面的代码是获取需要recompile的html node,并且$compile,这样就形成了活动的代码了!
_.each($('[recompile]'), function(el){
_self.vm.$compile(el);
});
以上方法未经过验证,也没有完全搞清楚,但是替代方案我是亲手测试过的: 1. 通过async component;2.通过v-if async组件的方式动态向后端获取数据和模版,在resolve方法中将对应数据和模版及数据来绑定;通过v-if的方式可以将html partial作为一个变量方式绑定在模版中,当该partial数据ready时,v-if自然会启动编译过程
Dynamic components with prop data传入
如果你需要在同一个mount point显示不同的component,这时Dynamic components就很合适了。
<div id="app">
by dynamic Component:
<component
v-for="item in items"
:is="item.component" //这里根据item.component来决定渲染哪类组件
:opts="item.options"> //同时通过opts传入要渲染组件的props
component>
div>
Vue.component('node', {
template: "node: {{ opts }}
",
props: ['opts']
});
Vue.component('node2', {
template: "node2: {{ opts }}
",
props: ['opts']
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data() {
return {
items: [{
component: "node", //node节点类型
options: 'node节点数据'
}, {
component: "node2", //node2节点类型
options: 'node2节点数据'
}]
};
}
methods: {
addItem() {
this.items.push(this.newItem);
this.newItem = {
component: "",
options: ""
}
}
}
});
https://jsfiddle.net/matiascx/qn29r3vt/
https://jsbin.com/nikimigaju/edit?html,output
webpack构建环境相关内容
什么是webpack:
webpack是和browserify/gulp/grunt等相似的构建工具(Webpack is a module bundler. It takes a bunch of files, treating each as a module, figuring out the dependencies between them, and bundle them into static assets that are ready for deployment.),webpack比较完美地解决了前端模块化开发的工具链支持。特别是webpack的loader插件机制使得可以任意加载第三方开发的插件来扩展其支持的功能。接下来要说的vue-loader就是其中的一个典型案例;
什么是loader:
Webpack 由于本身只能处理 JavaScript 模块(commonJS,AMD,ES6),如果要处理其他类型的文件,就需要使用 loader 进行转换。
Loader 可以理解为是模块和资源的转换器,它本身是一个函数,接受源文件作为参数,返回转换的结果。这样,我们就可以通过 require 来加载任何类型的模块或文件,比如 CoffeeScript、 JSX、 LESS 或图片。
先来看看 loader 有哪些特性?
- Loader 可以通过管道方式链式调用,每个 loader 可以把资源转换成任意格式并传递给下一个 loader ,但是最后一个 loader 必须返回 JavaScript。
- Loader 可以同步或异步执行。
- Loader 运行在 node.js 环境中,所以可以做任何可能的事情。
- Loader 可以接受参数,以此来传递配置项给 loader。
- Loader 可以通过文件扩展名(或正则表达式)绑定给不同类型的文件。
- Loader 可以通过
npm 发布和安装。
- 除了通过
package.json 的 main 指定,通常的模块也可以导出一个 loader 来使用。
- Loader 可以访问配置。
- 插件可以让 loader 拥有更多特性。
- Loader 可以分发出附加的任意文件。
Loader 本身也是运行在 node.js 环境中的 JavaScript 模块,它通常会返回一个函数。大多数情况下,我们通过 npm 来管理 loader,但是你也可以在项目中自己写 loader 模块。
按照惯例,而非必须,loader 一般以 xxx-loader 的方式命名,xxx 代表了这个 loader 要做的转换功能,比如 json-loader。
在引用 loader 的时候可以使用全名 json-loader,或者使用短名 json。这个命名规则和搜索优先级顺序在 webpack 的 resolveLoader.moduleTemplates api 中定义。
什么是vue-loader(browerify下对应vueify工具):
vue-loader是even you为了支持web组件在一个.vue文件中组织js,css,html的梦幻开发模式,独创性地定义了一种文件类型component.vue, 这个vue文件中用script,style, template来分别代表js,css,html,这种文件格式是浏览器不认识的哦,webpack构建工具也是不认识的哦,要能使用必须先编译打包成webpakc bundle,而在webpack生态系统中,vue-loader就是干这个用的。一旦webpack遇到.vue文件就会调用这个vue-loader分别将js,css,html抽取出来,并且调用对应的代码transpiler工具:比如css可能用less,也可能用sass;js可能用coffee,也可能用jsx;html可能用yaml等都需要转换。这个工作就是vue-loader来完成的。
简单一句话,vue-loader就是将一个.vue文件转换为一个js模块的
chrome下vue dev-tool无法显示问题
Vue.config.devtools = true; //在new Vue()之前执行
//Vue.config.debug = true;
//window.__VUE_DEVTOOLS_GLOBAL_HOOK__.Vue = Vue;
directive的webpack引用
// diretive定义
module.exports = {
update: function(newValue, oldValue) {
console.log(newValue)
console.log(oldValue)
},
bind: function() {
},
unbind: function() {
}
}
// component定义应用directive
module.exports = {
template: require('./template.html'),
directives: {
currency: require('./directives/currency.js')
}
}
//在template中
$1.00
VueX
http://skyronic.com/2016/01/03/vuex-basics-tutorial/
vuex对于构建大型应用是非常重要的,主要解决数据状态维护和传递的问题(比如不相干的多个组件需要更新数据,同时需要通知多个不相干的组件来应对这些数据的更新来更新视图):整个应用只有一个地方负责对状态数据的更新,任何一个地方都可以引用这个数据,需要更新则发消息给vuex来完成更新操作,其他任何引用了这个状态的地方都会reactive更新(computed属性)
主要的思路是保持single source of truth,比如有两个vue instance vmA和vmB,都依赖于一个状态,这时如何保持状态的同步就会是一个问题
var sourceOfTruth = {}
var vmA = new Vue({
data: sourceOfTruth
})
var vmB = new Vue({
data: sourceOfTruth
})
动态创建并且mount组件到dom中
import ExecPlayer from './components/pages/exercise/exec-player.vue'; //这里exec-player只是export了一个component option object
var execplayercomp = Vue.extend(ExecPlayer); //这里通过传入定义好的component option object作为Vue.extend的参数,以写程序的方式获得了component的构造函数
var execplayer = new execplayercomp({
// 'el': '#execplayer', //调用new xxx的方式来创建组件,如果给了el配置项,则无需再调用$mount
// 需要注意的是这种方式创建的组件在devtool中并不会显示为rootvm的子组件,但是实际上他们是有父子关系的!!!
// 如果在html代码中直接以 调用的方式来composite组件的话,则在devtool中能够正确显示父子关系~!
created(){
this.exercises = rootvm.exercises;
}
}).$mount(document.getElementById('execplayer'));
vm.$set vs Vue.set vs Object.assign
1. For Vue instances, you can use the $set(path, value) instance method:
vm.$set('b', 2)
// `vm.b` and `data.b` are now reactive
2. For plain data objects, you can use the global Vue.set(object, key, value) method
Vue.set(data, 'c', 3)
// `vm.c` and `data.c` are now reactive
3. 如果想使用.assign来一次性给一个object添加多个属性和value,需要注意:
// instead of `Object.assign(this.someObject, { a: 1, b: 2 })`
this.someObject = Object.assign({}, this.someObject, { a: 1, b: 2 })
vm.$nextTick() vs Vue.nextTick(callback)
到底nextTick是干什么的:
看一个牛人的回答: it's a way to execute a callback function after the data is set.
To add an example to that, lets say you have a jQuery plugin that creates a pie chart. The data on those charts are fetched and set by vuejs. You can't initialize the charts until after the data is set / until the "next tick". Here's a quick example...
https://jsfiddle.net/kr9b4o8f/
If you try to initialize the charts without nextTick(), it won't work because the data has not been changed yet.
{{msg}}
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
msg: '123'
}
})
vm.msg = 'new message' // change data
vm.$el.textContent === 'new message' // false
Vue.nextTick(function () {
vm.$el.textContent === 'new message' // true
})
// 对于component下面的调用方法
Vue.component('example', {
template: '{{msg}}',
data: function () {
return {
msg: 'not updated'
}
},
methods: {
updateMessage: function () {
this.msg = 'updated'
console.log(this.$el.textContent) // => 'not updated'
this.$nextTick(function () {
console.log(this.$el.textContent) // => 'updated'
})
}
}
})
通过extends选项继承基础组件,使用js代码创建新组件,作为独立.vue文件方式构建新组建的替代方案,无须多个.vue文件
var CompA = { ... }
// extend CompA without having to call Vue.extend on either
var CompB = {
extends: CompA,
...
}
心法:在同一类组件需要在同一个mount point加载时,这种场景下最好的方案就是使用dynamic component。而使用动态组件又有两种方案:
1. 直接生成多个.vue组件,比如component-typeA.vue,component-typeB.vue,这种方式比较适合组件代码差异巨大的场景,具体应用时在使用该dynamic组件的父组件template中直接import这些.vue文件,并且components option中引用这些组件的定义
import CompTypeA from 'comp-type-a.vue'
import CompTypeB from 'comp-type-b.vue'
export default {
...
components: [ CompTypeA, CompTypeB ]
}
// html:
2. 只生成一个generic的.vue组件,随后其他组件extends这个generic组件,在引用该dynamic组件的父组件的script中直接使用js代码方式"声明"新的组件,并在父组件的template中使用:
import Comp from 'generic-comp.vue'
var CompTypeA = {
extends: Comp,
templates: 'A',
methods: ..A..
}
var CompTypeB = {
extends: Comp,
templates: 'B',
methods: ..B..
}
export default {
...
components: [ CompTypeA, CompTypeB ]
}
// html:
vuejs中重用代码的几种方案
1. 创建自包含的组件,可以任意重用
2. 创建抽象组件,比如node,实体组件extends这个抽象组件,再添加自己的options,形成新的concret组件
3. mixins: 部分代码可以被任意无关的类,组件共用,这部分最适合使用mixin
// mixin引用方法
import VuexStateGetterMixin from './mixin.js'
export default {
mixins: [ VuexStateGetterMixin ],
}
4. 只负责对DOM操作的功能,则可以抽象为directive来重用
javascript中用到的各个版本术语 ES5,ES6,ES2016,ECMAScript
- ECMAScript:一个由 ECMA International 进行标准化,TC39 委员会进行监督的语言。通常用于指代标准本身。
- JavaScript:ECMAScript 标准的各种实现的最常用称呼。这个术语并不局限于某个特定版本的 ECMAScript 规范,并且可能被用于任何不同程度的任意版本的 ECMAScript 的实现。
- ECMAScript 5 (ES5):ECMAScript 的第五版修订,于 2009 年完成标准化。这个规范在所有现代浏览器中都相当完全的实现了。
- ECMAScript 6 (ES6) / ECMAScript 2015 (ES2015):ECMAScript 的第六版修订,于 2015 年完成标准化。这个标准被部分实现于大部分现代浏览器。可以查阅这张兼容性表来查看不同浏览器和工具的实现情况。
- ECMAScript 2016:预计的第七版 ECMAScript 修订,计划于明年夏季发布。这份规范具体将包含哪些特性还没有最终确定
- ECMAScript Proposals:被考虑加入未来版本 ECMAScript 标准的特性与语法提案,他们需要经历五个阶段:Strawman(稻草人),Proposal(提议),Draft(草案),Candidate(候选)以及 Finished (完成)。
ES6中的=> arrow function
// ES5
var total = values.reduce(function (a, b) {
return a + b;
}, 0);
// ES6
var total = values.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0);
// ES5
$("#confetti-btn").click(function (event) {
playTrumpet();
fireConfettiCannon();
});
// ES6
$("#confetti-btn").click(event => {
playTrumpet();
fireConfettiCannon();
});
arrow函数在vuejs event bus handler中的应用
vuejs2.0开始提倡使用event bus这个机制来实现代码解耦和任何模块之间的数据通信,非常强大,但是使用中可能会遇到这样的困惑:在event handler中的this指针怎么才能够引用到event handler所在的vue instance呢?这时ES6的=>arrow函数就起到了作用,因为它不会改变this指针:
this.pcomBus.$on('toggle-checked-all-for-role', e => {
// 这里this指针就指向的是定义这个pcomBus.$on调用的那个vue instance了!
}
ES6 destruturing解构
参考 http://www.zcfy.cc/article/498
const obj = { first: 'Jane', last: 'Doe' };
const {first: f, last: l} = obj;
// f = 'Jane'; l = 'Doe'
// {prop} 是 {prop: prop} 的缩写
const {first, last} = obj;
// first = 'Jane'; last = 'Doe'
强烈建议参考 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004365693 讲解ES6基础语法
https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Functions/Arrow_functions
npm安装vue, vuex等next分支上的最新版本:
npm install vue@next --save
npm install vuex@next --save
vue2.0版本文件以及开发环境工具不匹配带来的问题
$ npm run dev
Vue packages version mismatch:
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
This may cause things to work incorrectly. Make sure to use the same version for both.
If you are using vue-loader or vueify, re-installing them should bump vue-template-compiler to the latest.
解决办法npm install vue-loader@next --save-dev
如何安装或者更新vue相关组件?
vue,vuex,vue-router,vue-loader是我们需要安装的组件,如果你已经使用了以前的版本,可以先npm uninstall, 然后再npm install他们即可
npm install vue-template-compiler
vuex mapActions导入methods和local methods混用的语法
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods:{
doJob: function(){
this.changeme(content)
},
...mapActions([
'changeme'
])
}
}
vuejs1.0 v-for track-by vs vuejs2.0 :key="item.id"
在vue v-for渲染一个列表时,如果不用被操作的item数据id作为key的话,那么vuejs会默认使用数组index作为key,而这时如果数据列表发生变化,比如一个item被删除,则可能会发生数据不同步的怪异错误,强烈建议永远在v-for处理列表数据时,加上:key="item.id"!!!
v-for="skill in pskills" :key="skill.id"
什么是抽象组件以(transition组件为例)?
抽象组件具有以下特点:
1. 它是以引入功能而不是构建视图为目的而存在的
2. 它不会在DOM中有任何节点
3. 它也不会在inspect component hierarchy中显示出来
抽象组件和无template的组件有什么区别??
非常典型的例子是vuejs2.0中引入的transition组件:
<transition>
<div v-if="ok">toggled contentdiv>
transition>
transition组件支持以下props:
1. name: 用于自动产生transition class name,比如如果name=fade,则对应的transition class将有.fade-enter,.fade-enter-active,.fade-leave,.fade-leave-active
2. appear: 是否在初次渲染时引用transition,默认为false;
3. css: 是否引用css transition class。默认为true,如果是false的话,则仅触发javascript hooks
4. type: 指定需要等待何种event来决定transition的结束。比如: "transition",或者"animation"
5. mode: 控制leaving/entering transition的timing sequence,可能的选项是:in-out或者out-in
6.enterClass,leaveClss,enterActiveClass,leaveActiveClass,appearClass,appearActiveClass分别用于设置对应的css class为客制内容.
比如:
<transition name="fade" mode="out-in" appear>
<component :is="view">component>
transition>
支持的事件:
before-enter,enter,after-enter,before-leave,leave,after-leave,before-appear,appear,after-appear
例子:
<transition @after-enter="transitionComplete">
<div v-show="ok">toggled contentdiv>
transition>
组件
如果需要对多个元素执行transition效果,则需要使用transition-group组件。和transition组件所不同的是该组件须插入dom
live demo
Vue.component('fade', {
functional: true,
render (createElement, { children }) {
const data = {
props: {
name: 'fade'
},
on: {
beforeEnter () { /* ... */ }, // <-- Note hooks use camelCase in JavaScript (same as 1.x)
afterEnter () { /* ... */ }
}
}
return createElement('transition', data, children)
}
})
<fade>
<div v-if="ok">toggled contentdiv>
fade>
参考 http://vuejs.org/guide/render-function#Functional-Components
vuejs compile和mount过程
当vuejs app启动时,首先入口程序根据#el来找到本应用对应的html片段,该片段作为root的template,开始启动编译链接过程。每找到一个componennt,就开始walk through该组件的template,继续compile,直到编译完成。在vuejs2.0中由于没有了compiled钩子,我们可以理解created事件就是按照上面的timing来完成的。如果对应有v-for,则开始启动loop过程,就像普通的js代码一样,先把第一次Loop的数据传给对应组件开始编译,直到所有的loop都完成了,这时compile过程可以认为是完全完成了。mount过程则和compile完全相反,由compile形成的dom node map反序逐级mount。也就是说先子组件后父组件直到root组件被mounted.
比如,如果我们有下面的html结构,以及外围loop两次,a组件template内需要loop三次,则会按照下面的timing图来执行:
<div class="root" v-for="(item,index) of outerloop2times">
<a>a>
<b>b>
div>
<script type="x/template" id="a-template">
<div class="a-root">
<a-sub v-for="(item,index) of innerloop3times"></a-sub>
</div>
script>
<script type="x/template" id="b-template">
<div class="b-root">
</div>
script>
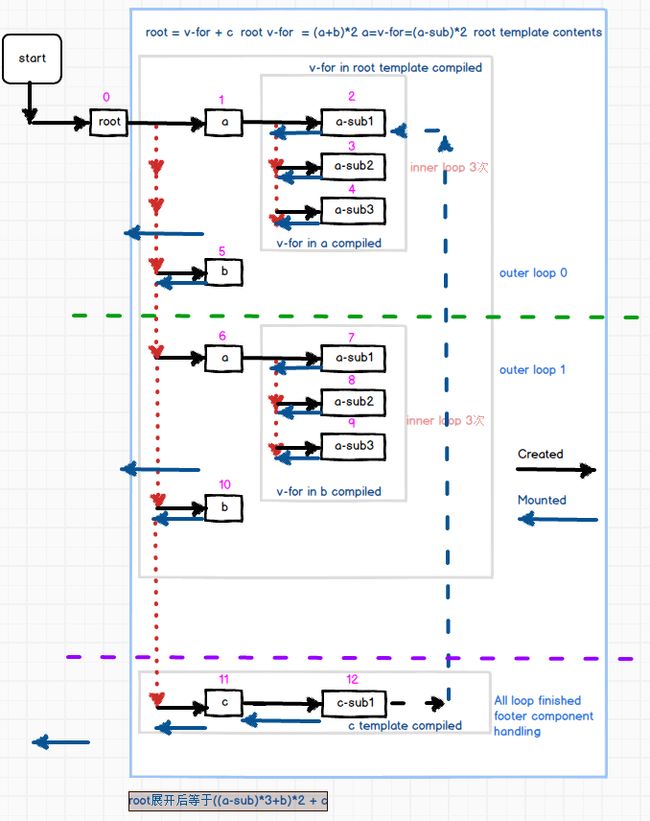
所有watcher代码都mounted之后才可能被触发。
关于vue组件的styling探讨
1. vuejs组件需要有一个container class来负责该vue组件的position, layout,display,float等style设置;
2. vue-root, vue-root-{skin}作为root元素的class
3. {skin}可以考虑通过global vuex state驱动传入,方便换肤
新增属性reactive注意事项:
新增单个属性,可以使用:
Vue.set(vm.someobj,'newprop',propvalue)
新增多个属性对象,可以使用:
this.someObject = Object.assign({}, this.someObject, { a: 1, b: 2 })
对于对象的操作整体替换,修改等强烈建议使用Vue.set因为这样能够确保vuejs能够感知到这个变化
基于jqueryui select2组件在vuejs2.0(不支持prop.sync)下如何实现v-model模式的功能?
我们知道vuejs2.0一个重大的变化是不再支持prop.sync功能,也就是说从外部传入的数据是不能通过vue组件内部逻辑直接来实现更新的。而我们在封装jquery-ui的select2组件形成我们自己的select2组件时,又必须要实现v-model的功能,肿么办?还有就是如果销毁vuejs select2组件,而其底层的jqueryuiselect2控件并不会自动销毁,肿么办?
我们看看官方的封装代码,解读一下:
Vue.component('select2', {
props: ['options', 'value'],
template: '#select2-template',
mounted: function () {
var vm = this
$(this.$el)
.val(this.value)
// init select2
.select2({ data: this.options })
// emit event on change.
.on('change', function () {
vm.$emit('input', this.value) //这个非常重要,通过emit一个input事件来更新v-model数据
})
},
watch: {
value: function (value) {
// update value
$(this.$el).select2('val', value)
},
options: function (options) {
// update options
$(this.$el).select2({ data: options })
}
},
destroyed: function () {
// 这里也很重要,在vue组件销毁时,jquery ui自己生成的dom并不会销毁,我们要通过jquery ui select2的api来实现销毁
$(this.$el).off().select2('destroy')
}
})
html
<select2 v-model="selectedValue"
<input v-bind:value="message" @input="message = $event.target.value">
<my-component v-model="message">my-component>
<my-component v-bind:value="message" @input="setMessage"> my-component>
参考官方v-model文档:
https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#Using-v-model-on-Components
custom input实现v-model的例子:
<custom-input
v-bind:value="searchText"
v-on:input-customized="searchText = $event"
>custom-input>
在这个custom-input例子中,内部的input组件必须:1.绑定value attribute到value prop;2.在内部input元素上,监听input元素原生的input事件,并且转化并emit customized input事件,并带上new value。注意:实际上customized event并非须用input作为事件名称
Vue.component('custom-input', {
props: ['value'],
template: `
<input
v-bind:value="value"
v-on:input="$emit('input-customized', $event.target.value)"
>
`
})
这样v-model就可以像下面来使用了:
<custom-input v-model="searchText">custom-input>
v-model定制使用特定的prop而非默认的value及input事件
默认情况下v-model会使用valude作为prop,而input作为监听的event。有的时候,可能并不是很合适,比如checkbox/radio都会使用value prop作为特殊目的,这时,我们可能希望使用一个新的prop,比如checked用作prop,change作为变更的event来监听。
Vue.component('my-checkbox', {
model: {
prop: 'checked',
event: 'change'
},
props: {
// this allows using the `value` prop for a different purpose
value: String,
// use `checked` as the prop which take the place of `value`
checked: {
type: Number,
default: 0
}
},
// ...
})
<my-checkbox v-model="foo" value="some value">my-checkbox>
以上两段代码就等价于:
<my-checkbox
:checked="foo"
@change="val => { foo = val }"
value="some value">
my-checkbox>
vuejs2.0动态渲染模版
https://cinwell.com/post/vue-2-dynamic-template/
通过router-view给对应组件传递参数
<router-view class="view" :users="users">router-view>
程序控制实现router路由变换
// literal string path
router.push('home')
// object
router.push({ path: 'home' })
// named route
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId: 123 }})
// with query, resulting in /register?plan=private
router.push({ path: 'register', query: { plan: 'private' }})
https://router.vuejs.org/en/essentials/navigation.html
vuejs嵌套路由
有时我们希望在routed 组件中进一步使用路由,这时就要用到嵌套路由的概念了:
<div id="app">
<p>
<router-link to="/user/foo">/user/foorouter-link>
<router-link to="/user/foo/profile/greatinfo">/user/foo/profilerouter-link>
<router-link to="/user/foo/posts">/user/foo/postsrouter-link>
p>
<router-view>router-view>
div>
- javascript ->
const User = {
template: `
<div class="user">
<h2>User {{ $route.params.id }}h2>
<router-view>router-view>
div>
`
}
const UserHome = { template: '<div>Homediv>' }
const UserProfile = { template: `<div>Profile for {{$route.params.id}} with info {{$route.params.info}}div>` }
const UserPosts = { template: '<div>Postsdiv>' }
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/user/:id', component: User,
children: [
// UserHome will be rendered inside User's <router-view>
// when /user/:id is matched
{ path: '', component: UserHome },
// UserProfile will be rendered inside User's <router-view>
// when /user/:id/profile is matched
{ path: 'profile/:info', component: UserProfile },
// UserPosts will be rendered inside User's <router-view>
// when /user/:id/posts is matched
{ path: 'posts', component: UserPosts }
]
}
]
})
const app = new Vue({ router }).$mount('#app')
router-link不使用a标签
在vue app中,有时候不希望使用默认的a标签来渲染router-link,原因可能有:预渲染时,html中不会生成无意义的a标签.这时,我们就可以使用tag属性。同时,这时你也希望有一个类似a标签的样式存在,这时,就应该使用class来指定一个样式.
比如:
<li class="link"><span class="hwtitle">口算能力训练 span>
li>
响应route参数的变化
当route参数发生变化时,由于路由到相同的route,对应组件并不会自动再次创建,那么我们如何响应这个参数的变化呢?
两种方案:
1. 在组件中watch route参数
2.定义beforeRouteUpdate
watch: {
'$route' (to, from) {
// 对路由变化作出响应...
}
},
beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) {
// react to route changes...
// don't forget to call next()
}
route路由命名视图
有时我们需要为响应路由需要定义多个视部分图,比如希望有sidebar,maincontent两个视图渲染在root路由中:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
components: {
default: Foo,
a: Bar,
b: Baz
}
}
]
})
使用ES6的特性创建动态key值的对象
看下面的代码:
export default{
data: function () {
return {
["thisrootstore_"+this.$options.name]: {
bus: new Vue()
}
}
}
}
上面这段代码可以作为mixin来被每一个组件重用,动态创建包含本组件名称的本地全局数据变量 thisrootstore_xxname,其中的bus就可以用于本组件和其子孙组件事件通信
并且可以被vuejs安全地merge,也就是说你可以再手工创建其他需要共享的数据在这个对象中
如何给webpack构建出来的bundle瘦身?
用过webpack你一定会发现往往就几行代码加到entry里面最终做出来的bundle却好几百k,对于带宽资源非常昂贵的主机来说是一个噩梦,一方面加载龟速,另一方面如果是手机访问更是噩梦。如何给他瘦身?首先找到哪些是我们需要的,哪些是不应该出现的,对解决问题就做对了一半:
source-map-explorer 这个工具可以对build出来的sourcemap做分析,给出依赖关系,你可以慢慢研究
webpack-bundle-analyzer : 这个也很棒,他可以可视化地列出你的bundle最终是由哪些个js代码构成的,都是哪些臃肿的代码导致了你最终的bundle过于庞大了
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/BjIrEj6
如何在production build中自动将console.log清除掉?
strip-loader可以完成这个工作
如何获取vuejs powered plain data?
有时候我们可能需要一个未经vuejs define propery(get/set)处理过的原始js数据,一个workaround方案:
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify($vm.action.roles))

如何侦听custom component的native事件,比如click? (使用.native修饰符)
<my-component v-on:click.native="doTheThing">my-component>
如何绑定html元素属性要么为一个值,要么就没有?
<a :href="shouldhavehref ? 'http://xx.com/yy' : null">
上面的代码中判断shouldhavehref data值,如果该值为真则在a元素上存在href="http://xx.com/yy",如果该值为假,则返回null,从而a元素上就不存在href属性!
心法:只要expression的值为null,就会被清除掉!
v-if和v-for共存
如果v-if和v-for在同一个element上出现,则和angular类似,也有一个directive优先级的问题。在vuejs中,v-for的优先级要高于v-if,也就是说先做v-for的loop,随后对每一个loop再应用v-if判断,比如下面的代码:对loop后的每一个todo,只有在todo没有完成的情况下,我们才render这个todo!!
for="todo in todos" v-if="!todo.isComplete">
{{ todo }}
何时使用inline-template
通常,组件用于重用,但是有些时候,我们可能只需要在一个页面增加一些交互性,这时我们可能使用Inline-template的组件就比较合适了,原因是其布置非常方便
// 将这段代码放在你的html页面中
You have complete {{ count }} lessons
// 这段代码放在html页面引用的js文件中
Vue.component('complete-progress',{
data: function(){
return {
count: 50
}
}
})
import Hello from '@/components/Hello'中的@是何意思?
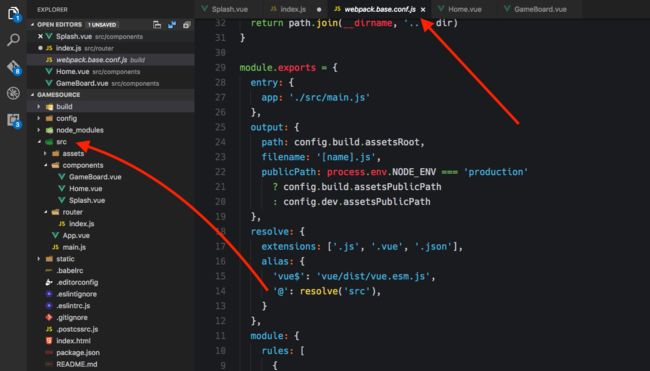
在vue-cli创建的代码中,使用了webpack的resolve.alias来实现将@直接替换为src目录的路径,这样就方便代码目录管理,不用都使用./ ../等特殊相对路径了。
再比如,上面的vue$实际上也设计成import vue from 'vue'就替换为import vue from 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js'了。
windows git bash下webpack build时的大小写问题
WARNING in (webpack)/buildin/module.js
There are multiple modules with names that only differ in casing.
This can lead to unexpected behavior when compiling on a filesystem with other case-semantic.
Use equal casing. Compare these module identifiers:
* D:\devenv\js\vueapp\node_modules\webpack\buildin\module.js
Used by 4 module(s), i. e.
D:\devenv\js\vueapp\node_modules\.4.6.0@lodash.findindex\index.js * d:\devenv\js\vueapp\node_modules\webpack\buildin\module.js Used by 2 module(s), i. e. d:\devenv\js\vueapp\node_modules\lodash.orderby\index.js
可能的解决方案:使用windows power shell,它不存在这个盘符大小写问题;或者在git bash下 cd D/devenv/js/xxxx 再做build
再见了vue-resource,推荐使用axios
由于vuejs2.0以上特别推出了SSR(server side rendering),这个是要在服务端使用node.js做服务端渲染的,因此存在着在浏览器端和服务器nodejs端同时使用http请求的需求,而axios正好满足这个需求,因此evan就写了一篇文章推荐使用axios,不再official推荐vue-resource plugin。
If you’d like to access this.$http like in vue-resource, you can just set Vue.prototype.$http = axios
https://github.com/axios/axios
借用axios拦截器实现web app的授权token问题
https://www.jianshu.com/p/ff8541e0976a
需求描述:
每个请求都需要携带 token ,所以我们可以使用 axios request 拦截器,在这里,我们给每个请求都加 token,这样就可以节省每个请求再一次次的复制粘贴代码。
token 失效问题,当我们token 失效,我们服务端会返回一个特定的错误表示,比如 token invalid,但是我们不能在每个请求之后去做刷新 token 的操作呀,所以这里我们就用 axios response 拦截器,我们统一处理所有请求成功之后响应过来的数据,然后对特殊数据进行处理,其他的正常分发
Vue.use(Vuex)
Vue.use(VueAxios, axios)
Vue.use(qs)
注:qs,使用axios,必须得安装 qs,所有的Post 请求,我们都需要 qs,对参数进行序列化。
在 request 拦截器实现
axios.interceptors.request.use(
config => {
config.baseURL = '/api/'
config.withCredentials = true // 允许携带token ,这个是解决跨域产生的相关问题
config.timeout = 6000
let token = sessionStorage.getItem('access_token')
let csrf = store.getters.csrf
if (token) {
config.headers = {
'access-token': token,
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
}
}
if (config.url === 'refresh') {
config.headers = {
'refresh-token': sessionStorage.getItem('refresh_token'),
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
}
}
return config
},
error => {
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
//在 response 拦截器实现
axios.interceptors.response.use(
response => {
// 定时刷新access-token
if (!response.data.value && response.data.data.message === 'token invalid') {
// 刷新token
store.dispatch('refresh').then(response => {
sessionStorage.setItem('access_token', response.data)
}).catch(error => {
throw new Error('token刷新' + error)
})
}
return response
},
error => {
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
如何解决v-if/v-show还未完全编译时其{{message}}内容会闪现的问题?
使用v-cloak这个directive来解决:
<div v-cloak>
{{ message }}
div>
配合以下css
[v-cloak] {
display: none;
}
如何安全地使用jquery plugin在vue app中?
https://dzone.com/articles/how-to-safely-use-a-jquery-plugin-with-vuejs
要点是设计一个vue wrapper组件,讲jquery相关操作封装为一个组件,并使用v-once使得update不会操作jquery已经更改过的dom



