JDBC(一)--JDBC核心API/JDBC工具类/Statement/PreparedStatement/CallableStatement
JDBC入门
1.之前操作MySQL数据库:使用MySQL客户端工具连接MySQL服务器,发送sql语句到MySQL服务器,执行。
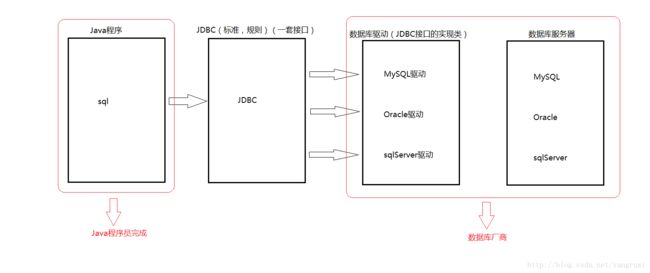
2.JDBC:使用Java程序发送sql语句到数据库服务器端执行。JDBC是Oracle-Sun公司设计的一套专门用于Java程序操作数据库的接口。
java.sql:常用接口
javax.sql:扩展或者新特性的一些接口
Java连接数据库图解:

语句执行者可以理解为船,connection连接可以理解为河流,船带着sql语句穿过河流到达数据库。
3.使用JDBC发送sql的条件:
连接MySQL数据库:
(1)MySQL数据库主机地址;
(2)端口号;
(3)数据库用户名;
(4)数据库密码;
(5)连接的数据库。
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/XSGL";
//jdbc协议:mysql协议://主机地址:端口号/需要连接的数据库名称4.Java程序连接数据库需要引用mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar包:
(1)选择mysql驱动包里面的mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar文件并复制:

(2)将mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar拷在项目下的webroot/web-inf/lib目录:

(3)选中mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar文件右键–>Build Path–>Add to Bulid Path,显示如下图即代表成功:
JDBC核心API
1.Driver接口:每个驱动程序类必须实现的接口。
DriverManager 会试着加载尽可能多的它可以找到的驱动程序,然后,对于任何给定连接请求,它会让每个驱动程序依次试着连接到目标 URL。
(1)注册驱动:
在加载某一 Driver 类时,它应该创建自己的实例并向 DriverManager 注册该实例。我们发现mysql驱动程序的Driver实现类已经帮我们在静态代码块中注册好了驱动,我们在此时只需要将Driver实现类加载到我们的内存中,static代码块就会自动执行,我们的驱动也就自动注册了。
Class.forName("foo.bah.Driver")(2)通过类 DriverManager创建一个到给定 URL 的数据库连接:
static Connection getConnection(String url)
static Connection getConnection(String url, Properties info)
static Connection getConnection(String url, String user, String password)
需求:利用Driver接口获取Java程序连接数据库的连接对象。
package com.jdbc.a_driver;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Driver;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DriverDemo {
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/XSGL"";
//jdbc协议:mysql协议://主机地址:端口号/需要连接的数据库名称
private static String user = "root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
conn();
}
private static void conn() throws Exception {
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//获取Java连接数据库的对象
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//打印这个连接对象
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
2.Connection接口:与具体的数据库的连接(会话)。
(1)创建一个静态sql语句对象:
Statement createStatement() (2)创建预编译的sql语句对象:
PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) (3)创建存储过程的sql语句对象:
CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) 3.Statement接口:用于执行静态sql语句。
(create/alter/drop) DDL语句
(insert/update/delete)DML语句
(select)DQL查询语句
(1)执行更新操作的sql语句:
int executeUpdate(String sql) (2)执行查询操作的sql语句:
ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) 4.PreparedStatement接口:用于执行预编译的 SQL 语句(是Statement的子接口)。
(1)执行更新操作的sql语句:
int executeUpdate() (2)执行查询操作的sql语句:
ResultSet executeQuery() 5.CallableStatement接口:用于执行 SQL 存储过程的接口(是PreparedStatement的子接口)。
执行存储过程的sql语句:
ResultSet executeQuery() 6.ResultSet接口:结果集对象。 存储所有数据库查询的结果,用该对象进行数据遍历。
(1)ResultSet对象具有指向其当前数据行的光标。最初,光标被置于第一行之前。
next()方法把光标移动到下一行。如果下一行有数据,返回true,如果没有下一行数 据,返回false。
boolean next() (2)ResultSet接口提供用于从当前行获取列值得方法(getBoolean,getLong等)。可以使用列的索引编号或列的名称获取值。
getXXX(列索引|列字段名称)一般情况下,使用索引较为高效。但是建议以后使用的时候,最好使用列名称,这样会提高程序的维护性。
(3)用作获取方法的输入的列名称不区分大小写。
- 注意:
- 如果光标在第一行之前,使用rs.getXX()获取列值,报错:Before start of result set
- 如果光标在最后一行之后,使用rs.getXX()获取列值,报错:After end of result set
如何从结果集中取出我们想要的数据:
(1)根据每一列的列号和每一列的数据类型调用相应的getXxx(int columnIndex)获取该字段的数据:
int getInt(int columnIndex) throws SQLException
String getString(int columnIndex) throws SQLException(2)根据每一列的字段名称和每一列的数据类型调用getXxx(String columnLabel)获取该字段的数据:
int getInt(String columnLabel) throws SQLException
String getString(String columnLabel) throws SQLExceptionStatement对象执行sql操作
1.执行DDL操作:
public class Demo1 {
//数据库的连接的URL
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/XSGL"";
//数据库用户名
private static String user = "root";
//数据库密码
private static String password = "root";
public static void main(String[] args){
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
//1.驱动驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.从驱动程序管理类获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//3.通过Connection对象获取Statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4.准备sql语句
String sql = "CREATE TABLE student(id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,NAME VARCHAR(20),gender VARCHAR(2))";
//5.执行sql语句,返回结果
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响了"+count+"行");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally{
//6.关闭资源(先关闭statement,再关闭connection)
if(stmt!=null)
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if(conn!=null)
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
2.执行DML操作:
public class Demo2 {
//数据库的连接的URL
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/XSGL"";
//数据库用户名
private static String user = "root";
//数据库密码
private static String password = "root";
/**
* 执行插入操作
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//创建Statment对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//准备sql
String sql = "INSERT INTO student(NAME,gender) VALUES('张三','男')";
//执行sql,返回结果
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响了"+count+"行");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally{
//关闭资源
if(stmt!=null)
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if(conn!=null)
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
/**
* 执行更新操作
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
//声明外部变量
String name = "陈六";
int id=2;
try {
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//创建Statment对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//准备sql
String sql = "UPDATE student SET NAME='"+name+"' WHERE id="+id+""; //变量和String拼接sql
//执行sql,返回结果
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响了"+count+"行");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally{
//关闭资源
if(stmt!=null)
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if(conn!=null)
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
/**
* 执行删除操作
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
//声明外部变量
int id=2;
try {
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//创建Statment对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//准备sql
String sql = "DELETE FROM student WHERE id="+id+""; //变量和String拼接sql
//执行sql,返回结果
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响了"+count+"行");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally{
//关闭资源
if(stmt!=null)
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if(conn!=null)
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
3.执行DQL查询操作:
public class Demo3 {
//数据库的连接的URL
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/XSGL"";
//数据库用户名
private static String user = "root";
//数据库密码
private static String password = "root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//创建Statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//准备sql
String sql = "SELECT * FROM student";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//移动光标到下一行
//rs.next();
/**
* 注意:
* 1)如果光标在第一行之前,使用rs.getXX()获取列值,报错:Before start of result set
* 2)如果光标在最后一行之后,使用rs.getXX()获取列值,报错:After end of result set
*/
//获取列值
/*if(rs.next()){
//使用列索引
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString(2);
String gender = rs.getString(3);
//使用列名称
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String gender = rs.getString("gender");
System.out.println(id+"\t"+name+"\t"+gender+"\t");
}*/
//迭代结果集
while(rs.next()){
//使用列索引
/*
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString(2);
String gender = rs.getString(3);
*/
//使用列名称
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String gender = rs.getString("gender");
System.out.println(id+"\t"+name+"\t"+gender+"\t");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally{
if(rs!=null)
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e1);
}
//关闭资源
if(stmt!=null)
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if(conn!=null)
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
4.JDBC工具类的抽取:
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/XSGL";
private static String user = "root";
private static String password = "root";
private static String className = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static{
//注册驱动,注册一次就可以了
//注册驱动
try {
Class.forName(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取连接
public static Connection getConnection(){
try {
//获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//返回conn
return conn;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
//释放资源
public static void close(ResultSet rs,Statement stmt,Connection conn){
//先判空后释放
if (rs!=null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
if (stmt!=null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
if (conn!=null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
}PreparedStatement对象执行SQL操作
public class Demo1 {
/**
* 插入操作
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
try{
//获取连接
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "INSERT INTO student(NAME,gender) VALUES(?,?)"; //预编译sql:使用?号代替参数值。一个?号代表一个参数值
//创建PreparedStatement对象,执行预编译的sql语句
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数
/**
* 参数一: 参数位置。从1开始
* 参数二: 参数实际值
* 注意: 所有参数必须要赋值
*/
stmt.setString(1, "rose");
stmt.setString(2, "女");
//发送参数,执行sql语句
int count = stmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
//关闭资源
JdbcUtil.close(conn, stmt, null);
}
}
/**
* 修改操作
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
//声明变量
String name = "jacky";
int id = 8;
try{
//获取连接
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "UPDATE student SET NAME=? WHERE id=?"; //预编译sql:使用?号代替参数值。一个?号代表一个参数值
//创建PreparedStatement对象,执行预编译的sql语句
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数
stmt.setString(1,name);
stmt.setInt(2, id);
//发送参数,执行sql语句
int count = stmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
//关闭资源
JdbcUtil.close(conn, stmt, null);
}
}
/**
* 删除操作
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
//声明变量
int id = 8;
try{
//获取连接
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "DELETE FROM student WHERE id=?"; //预编译sql:使用?号代替参数值。一个?号代表一个参数值
//创建PreparedStatement对象,执行预编译的sql语句
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数
//任何类型都可以使用setObject进行赋值
stmt.setObject(1, id);
//发送参数,执行sql语句
int count = stmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
//关闭资源
JdbcUtil.close(conn, stmt, null);
}
}
/**
* 查询操作
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
//声明变量
String name = "张%";
try{
//获取连接
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM student WHERE NAME LIKE ?";
//创建PreparedStatement,预编译sql语句
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数
stmt.setObject(1, name);
//发送参数,执行sql,返回结果集
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery();
//遍历结果集
while(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String nameStr = rs.getString("name");
String gender = rs.getString("gender");
System.out.println(id+"\t"+nameStr+"\t"+gender+"\t");
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
//关闭资源
JdbcUtil.close(conn, stmt, null);
}
}
}
Statement和PreparedStatement的区别
1.语法结构不同
(1)Statment执行静态sql语句,且sql可以拼接;
(2)PreparedStatement可以先执行预编译的sql语句,在预编译sql语句中使用,?进行参数占位,后面再进行参数赋值。
2.原理不同
(1)Statement不能进行sql缓存;
(2)而PreparedStatement可以进行sql缓存,执行效率会比Statement快。
3.安全性不同
(1)Statement存在sql注入的风险;
(2)而PreparedStatement可以有效防止用户注入。
创建一张user表(sql注入):
CREATE TABLE USER(
userName VARCHAR(20),
PASSWORD VARCHAR(20)
);给表中添加数据:
INSERT INTO USER VALUES('james','123456');
INSERT INTO USER VALUES('weide','123456');查询表:
SELECT * FROM USER;如果用户可以登陆成功的话,一定是满足下面的sql语句的:
SELECT * FROM USER WHERE userName='james' AND PASSWORD='123456';查询全部表给予肯定条件:
SELECT * FROM USER WHERE 1=1; -- 恒成立查询全张表给予否定条件:
SELECT * FROM USER WHERE 1<>1;-- 恒不成立查询表(sql注入):
将上面的查询语句拿下来做一个更改:
SELECT * FROM USER WHERE userName='james' OR 1=1 -- ' AND PASSWORD='123456';CallableStatement对象执行存储过程
1.执行带输入参数的存储过程:
public void test1(){
Connection conn = null;
CallableStatement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
//获取连接
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
//创建CallableStatement对象
String sql = "CALL pro_findById(?)";//预编译sql、可以带?号
//执行预编译的sql
stmt = conn.prepareCall(sql);
//设置参数
stmt.setInt(1, 4);
//发送参数,执行sql,返回结果
rs = stmt.executeQuery();// 注意: 执行存储过程必须使用exeuteQuery。
//遍历结果
while(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String gender = rs.getString("gender");
System.out.println(id+"\t"+name+"\t"+gender+"\t");
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
//关闭资源
JdbcUtil.close(conn, stmt, rs);
}
}
2.执行带有输出参数的存储过程:
public void test2(){
Connection conn = null;
CallableStatement stmt = null;
try{
//获取连接
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "CALL pro_findById2(?,?)"; // 第一个参数时输入参数,第二个参数是输出参数
//创建CallableStatement对象
stmt = conn.prepareCall(sql);
//设置输入参数
stmt.setObject(1, 4);
//注册一个输出参数
/**
* 参数一: 参数位置
* 参数二: 表示存储过程中的OUT参数的数据库类型
*/
stmt.registerOutParameter(2, java.sql.Types.VARCHAR);
//发送参数,执行存储过程
stmt.executeQuery();
/**
* 如何获取存储过程的返回值:OUT参数值。使用getXXX方法
*/
String name = stmt.getString(2);//和预编译语句中的参数位置保持一致。
System.out.println("结果:"+name);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
//关闭资源
JdbcUtil.close(conn, stmt, null);
}
}
优化JDBC 工具类
private static String url = null;
private static String user = null;
private static String password = null;
private static String className = null;
static{
//注册驱动,注册一次就可以了
//注册驱动
try {
//给成员变量赋值,将文件中的键值对加载到properties集合中
Properties prop = new Properties();
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("db.properties");
prop.load(in);
url = prop.getProperty("url");
user = prop.getProperty("user");
password = prop.getProperty("password");
className = prop.getProperty("className");
System.out.println(url);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(password);
System.out.println(className);
Class.forName(className);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取连接
public static Connection getConnection(){
try {
//获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//返回conn
return conn;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
//释放资源
public static void close(ResultSet rs,Statement stmt,Connection conn){
//先判空后释放
if (rs!=null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
if (stmt!=null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
if (conn!=null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
}