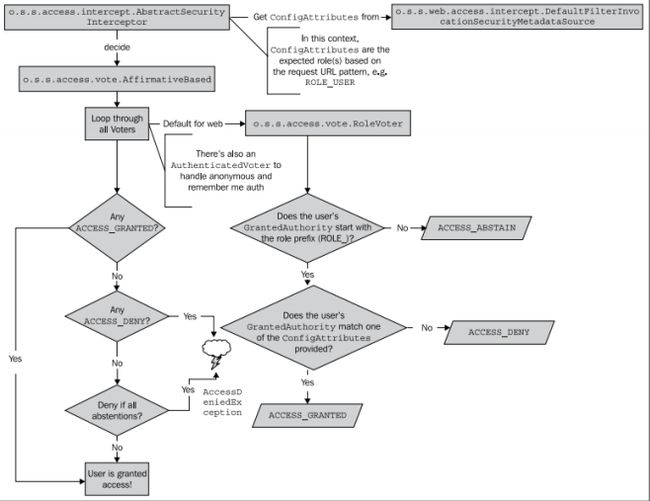
鉴权过滤器FilterSecurityInterceptor是11个默认过滤器的最后一个,也是流程很复杂的一个过滤器。它的鉴权不仅仅针对web领域,我们主要讨论对web的鉴权
FilterSecurityInterceptor:安全过滤器
SecurityMetadataSource:资源元数据
ConfigAttribute:访问该资源的配置信息
AccessDecisionManager:访问决策管理器,可以用
AuthenticationManager:认证管理器,通过getAuthorities()方法返回权限列表,这里是由ProviderManager实现的。
voter(投票器)是在授权过程中的一个重要角色,它的作用是评估以下的内容:
- 要访问受保护资源的请求所对应上下文(如URL请求的IP 地址);
- 用户的凭证信息(如果存在的话);
- 要试图访问的受保护资源;
- 系统的配置以及要访问资源本身的配置参数。
怎么配置的,我们看解析security命名空间时对过滤器的初始化方法createFilterSecurityInterceptor
void createFilterSecurityInterceptor(BeanReference authManager) {
//解析use-expressions
boolean useExpressions = FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser.isUseExpressions(httpElt);
//配置资源元数据对象
BeanDefinition securityMds = FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser.createSecurityMetadataSource(interceptUrls, httpElt, pc);
//访问决策器对象
RootBeanDefinition accessDecisionMgr;
//voter对象集合
ManagedList voters = new ManagedList(2);
if (useExpressions) {
voters.add(new RootBeanDefinition(WebExpressionVoter.class));
} else {
voters.add(new RootBeanDefinition(RoleVoter.class));
voters.add(new RootBeanDefinition(AuthenticatedVoter.class));
}
//访问决策对象默认是AffirmativeBased,即如果有任何一个投票器允许访问,请求将被立刻允许,而不管之前可能有的拒绝决定。
accessDecisionMgr = new RootBeanDefinition(AffirmativeBased.class);
accessDecisionMgr.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("decisionVoters", voters);
accessDecisionMgr.setSource(pc.extractSource(httpElt));
// Set up the access manager reference for http
// 获取配置文件中决策控制器bean的id
String accessManagerId = httpElt.getAttribute(ATT_ACCESS_MGR);
//如果配置文件没有指定访问控制器,定义默认的
if (!StringUtils.hasText(accessManagerId)) {
accessManagerId = pc.getReaderContext().generateBeanName(accessDecisionMgr);
pc.registerBeanComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(accessDecisionMgr, accessManagerId));
}
//设置过滤器对象
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(FilterSecurityInterceptor.class);
builder.addPropertyReference("accessDecisionManager", accessManagerId);
//设置authenticationManager认证对象
builder.addPropertyValue("authenticationManager", authManager);
//设置observeOncePerRequest属性,是否每个请求只鉴权一次
if ("false".equals(httpElt.getAttribute(ATT_ONCE_PER_REQUEST))) {
builder.addPropertyValue("observeOncePerRequest", Boolean.FALSE);
}
builder.addPropertyValue("securityMetadataSource", securityMds);
BeanDefinition fsiBean = builder.getBeanDefinition();
String fsiId = pc.getReaderContext().generateBeanName(fsiBean);
pc.registerBeanComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(fsiBean,fsiId));
// Create and register a DefaultWebInvocationPrivilegeEvaluator for use with taglibs etc.
BeanDefinition wipe = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultWebInvocationPrivilegeEvaluator.class);
wipe.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(new RuntimeBeanReference(fsiId));
pc.registerBeanComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(wipe, pc.getReaderContext().generateBeanName(wipe)));
this.fsi = new RuntimeBeanReference(fsiId);
} 下面再看默认的鉴权流程
FilterSecurityInterceptor继承了AbstractSecurityInterceptor,看他的doFilter方法
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}invoke方法
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
if ((fi.getRequest() != null) && (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
// 如果已经鉴权、且只进行一次鉴权
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
} else {
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
// 鉴权发生在这里
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
} finally {
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
}看看AbstractSecurityInterceptor的beforeInvocation流程
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Security invocation attempted for object "
+ object.getClass().getName()
+ " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: "
+ getSecureObjectClass());
}
// 获取此次访问的资源元数据,默认是从ExpressionBasedFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource,根据url和http method获取的
Collection attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object);
if (attributes == null) {
if (rejectPublicInvocations) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Secure object invocation " + object +
" was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "
+ "This indicates a configuration error because the "
+ "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Public object - authentication not attempted");
}
publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object));
return null; // no further work post-invocation
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Secure object: " + object + "; Attributes: " + attributes);
}
// authentication对象也不能为空
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
credentialsNotFound(messages.getMessage("AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound",
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"), object, attributes);
}
// 校验authentication对象,如果isAuthenticated是flase则再次校验,不通过会抛出AuthenticationException
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// Attempt authorization
try {
//访问决策管理器的decide方法
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));
// 如果鉴权失败抛出AccessDeniedException
throw accessDeniedException;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authorization successful");
}
publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));
// Attempt to run as a different user
// 将此资源元数据中以RUN_AS开头的角色赋予此用户
Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object, attributes);
if (runAs == null) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("RunAsManager did not change Authentication object");
}
// no further work post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(authenticated, false, attributes, object);
} else {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Switching to RunAs Authentication: " + runAs);
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);
// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(authenticated, true, attributes, object);
}
} 再看访问控制管理器的decide方法,默认的控制器是AffirmativeBased,只要有一个投票器通过就通过。
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection configAttributes)
throws AccessDeniedException {
// 被禁止数
int deny = 0;
for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {
int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result);
}
switch (result) {
// 只要有一个投票器通过,即返回
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED:
return;
// 不通过数+1
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED:
deny++;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (deny > 0) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage("AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied",
"Access is denied"));
}
// To get this far, every AccessDecisionVoter abstained
checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();
} 在鉴权不通过时都会抛出AccessDeniedException异常,整个鉴权的流程大概就是这样的。