CSS之字体属性与文本属性
本文主要介绍TreeSet集合的基本使用方法
TreeSet之自然排序
自然排序(元素具备比较性):让元素所属的类实现自然排序接口 Comparable
先看一个简单的例子,TreeSet集合,存入整数,进行排序
import java.util.TreeSet;
/*
* TreeSet:能够对元素按照某种规则进行排序。
* 排序有两种方式
* A:自然排序
* B:比较器排序
*
* TreeSet集合的特点:排序和唯一
*
* 通过观察TreeSet的add()方法,我们知道最终要看TreeMap的put()方法。
*/
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
// 自然顺序进行排序
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet();
// 创建元素并添加
// 20,18,23,22,17,24,19,18,24
ts.add(20);
ts.add(18);
ts.add(23);
ts.add(22);
ts.add(17);
ts.add(24);
ts.add(19);
ts.add(18);
ts.add(24);
// 遍历
for (Integer i : ts) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
- 此处能够对整数进行排序,是因为Integer类实现了Comparable接口.
- Comparable接口强行对实现它的每个类的对象进行整体排序。这种排序被称为类的自然排序,类的 compareTo 方法被称为它的自然比较方法。
再来看一个例子,在TreeSet中,存入学生对象的数据,并根据学生的年龄从小到大进行排序
- 创建一个学生类,实现自然排序Comparable接口,传入的泛型为Student
/*
* 如果一个类的元素要想能够进行自然排序,就必须实现自然排序接口
*/
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student s) {
// return 0;
// return 1;
// return -1;
// 这里返回什么,其实应该根据我的排序规则来做
// 按照年龄排序,主要条件
int num = this.age - s.age;
// 次要条件
// 年龄相同的时候,还得去看姓名是否也相同
// 如果年龄和姓名都相同,才是同一个元素
int num2 = num == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(s.name) : num;
return num2;
}
}- 编写测试类
import java.util.TreeSet;
/*
* TreeSet存储自定义对象并保证排序和唯一。
*
* A:你没有告诉我们怎么排序
* 自然排序,按照年龄从小到大排序
* B:元素什么情况算唯一你也没告诉我
* 成员变量值都相同即为同一个元素
*/
public class TreeSetDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet();
// 创建元素
Student s1 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s2 = new Student("zhangguorong", 29);
Student s3 = new Student("wanglihong", 23);
Student s4 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s5 = new Student("liushishi", 22);
Student s6 = new Student("wuqilong", 40);
Student s7 = new Student("fengqingy", 22);
// 添加元素
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6);
ts.add(s7);
// 遍历
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge());
}
}
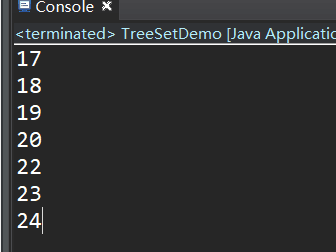
} 运行结果:

* 可以看到,成功将学生的信息按照年龄从小到大输出了,并把重复的学生信息去除了
再更改需求添加学生数据,并根据学生的姓名长度,从小到大排序
- 创建一个学生类,实现自然排序Comparable接口,传入的泛型为Student,重写compareTo方法
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student s) {
// 主要条件 姓名的长度
int num = this.name.length() - s.name.length();
// 姓名的长度相同,不代表姓名的内容相同
int num2 = num == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(s.name) : num;
// 姓名的长度和内容相同,不代表年龄相同,所以还得继续判断年龄
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? this.age - s.age : num2;
return num3;
}
}- 编写测试类
/*
* 需求:请按照姓名的长度排序
*/
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet();
// 创建元素
Student s1 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s2 = new Student("zhangguorong", 29);
Student s3 = new Student("wanglihong", 23);
Student s4 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s5 = new Student("liushishi", 22);
Student s6 = new Student("wuqilong", 40);
Student s7 = new Student("fengqingy", 22);
Student s8 = new Student("linqingxia", 29);
// 添加元素
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6);
ts.add(s7);
ts.add(s8);
// 遍历
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge());
}
}
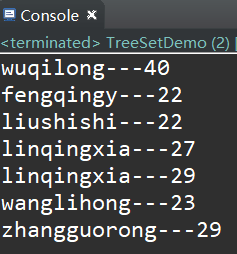
} 运行结果:

* 可以看到,成功按照姓名的长度排序,由长到短输出了.
TreeSet之比较器排序
比较器排序(集合具备比较性):让集合的构造方法接收一个比较器接口的子类对象 Comparator
还是上一步的要求:添加学生数据,并根据学生的姓名长度,从小到大排序.改为比较器排序做.
- 创建学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
- 创建一个比较器接口的子类对象
import java.util.Comparator;
public class MyComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
// int num = this.name.length() - s.name.length();
// this -- s1
// s -- s2
// 姓名长度
int num = s1.getName().length() - s2.getName().length();
// 姓名内容
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : num;
// 年龄
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? s1.getAge() - s2.getAge() : num2;
return num3;
}
}- 编写测试类
import java.util.TreeSet;
/*
* 需求:请按照姓名的长度排序
*
* TreeSet集合保证元素排序和唯一性的原理
* 唯一性:是根据比较的返回是否是0来决定。
* 排序:
* A:自然排序(元素具备比较性)
* 让元素所属的类实现自然排序接口 Comparable
* B:比较器排序(集合具备比较性)
* 让集合的构造方法接收一个比较器接口的子类对象 Comparator
*/
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合对象
//TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(); //自然排序
// public TreeSet(Comparator comparator) //比较器排序
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(new MyComparator());
// 创建元素
Student s1 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s2 = new Student("zhangguorong", 29);
Student s3 = new Student("wanglihong", 23);
Student s4 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s5 = new Student("liushishi", 22);
Student s6 = new Student("wuqilong", 40);
Student s7 = new Student("fengqingy", 22);
Student s8 = new Student("linqingxia", 29);
// 添加元素
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6);
ts.add(s7);
ts.add(s8);
// 遍历
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge());
}
}
}
上题中,匿名内部类的写法:如果一个方法的参数是接口,那么真正要的是接口的实现类的对象,而匿名内部类就可以实现这个东西
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 如果一个方法的参数是接口,那么真正要的是接口的实现类的对象
// 而匿名内部类就可以实现这个东西
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
// 姓名长度
int num = s1.getName().length() - s2.getName().length();
// 姓名内容
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName())
: num;
// 年龄
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? s1.getAge() - s2.getAge() : num2;
return num3;
}
});
// 创建元素
Student s1 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s2 = new Student("zhangguorong", 29);
Student s3 = new Student("wanglihong", 23);
Student s4 = new Student("linqingxia", 27);
Student s5 = new Student("liushishi", 22);
Student s6 = new Student("wuqilong", 40);
Student s7 = new Student("fengqingy", 22);
Student s8 = new Student("linqingxia", 29);
// 添加元素
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6);
ts.add(s7);
ts.add(s8);
// 遍历
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge());
}
}
} TreeSet应用题
键盘录入5个学生信息(姓名,语文成绩,数学成绩,英语成绩),按照总分从高到低输出到控制台
分析:
A:定义学生类
B:创建一个TreeSet集合
C:总分从高到底如何实现呢?
D:键盘录入5个学生信息
E:遍历TreeSet集合
* 创建学生类
public class Student {
// 姓名
private String name;
// 语文成绩
private int chinese;
// 数学成绩
private int math;
// 英语成绩
private int english;
public Student(String name, int chinese, int math, int english) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.chinese = chinese;
this.math = math;
this.english = english;
}
public Student() {
super();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getChinese() {
return chinese;
}
public void setChinese(int chinese) {
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public int getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(int math) {
this.math = math;
}
public int getEnglish() {
return english;
}
public void setEnglish(int english) {
this.english = english;
}
public int getSum() {
return this.chinese + this.math + this.english;
}
}- 编写测试类,采用匿名内部类,实现Comparator的写法
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个TreeSet集合
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
// 总分从高到低
int num = s2.getSum() - s1.getSum();
// 总分相同的不一定语文相同
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese() : num;
// 总分相同的不一定数序相同
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? s1.getMath() - s2.getMath() : num2;
// 总分相同的不一定英语相同
int num4 = num3 == 0 ? s1.getEnglish() - s2.getEnglish() : num3;
// 姓名还不一定相同呢
int num5 = num4 == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName())
: num4;
return num5;
}
});
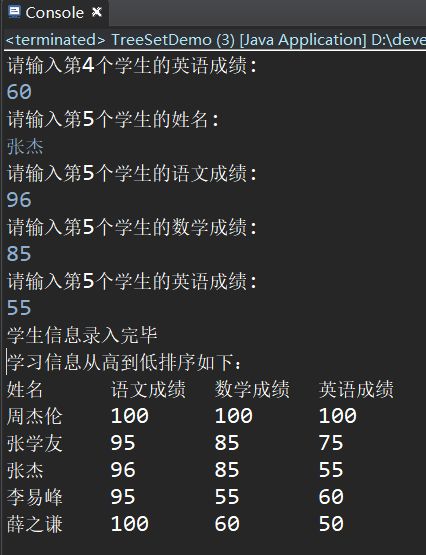
System.out.println("学生信息录入开始");
// 键盘录入5个学生信息
for (int x = 1; x <= 5; x++) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第" + x + "个学生的姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第" + x + "个学生的语文成绩:");
String chineseString = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第" + x + "个学生的数学成绩:");
String mathString = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第" + x + "个学生的英语成绩:");
String englishString = sc.nextLine();
// 把数据封装到学生对象中
Student s = new Student();
s.setName(name);
s.setChinese(Integer.parseInt(chineseString));
s.setMath(Integer.parseInt(mathString));
s.setEnglish(Integer.parseInt(englishString));
// 把学生对象添加到集合
ts.add(s);
}
System.out.println("学生信息录入完毕");
System.out.println("学习信息从高到低排序如下:");
System.out.println("姓名\t语文成绩\t数学成绩\t英语成绩");
// 遍历集合
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "\t" + s.getChinese() + "\t"
+ s.getMath() + "\t" + s.getEnglish());
}
}
}